2. DATASETS & DATALOADERS
PyTorch提供了两个数据基元:torch.utils.data.DataLoader和torch.uutils.data.data集,允许使用预加载的数据集以及自己的数据。数据集存储样本及其相应的标签,DataLoader在数据集周围包装了一个可迭代项,以便于访问样本。
PyTorch域库提供了许多预加载的数据集(如FashionMNIST),这些数据集是torch.utils.data.Dataset的子类,并实现特定于特定数据的函数。它们可以用于原型和基准测试您的模型。数据集信息如下:图像数据集、文本数据集和音频数据集
2.1 载入数据集
接下来将展示如何通过TorchVision载入Fashion-MNIST数据集。Fashion MNIST是Zalando文章图像的数据集,由60000个训练示例和10000个测试示例组成。每个示例都是一个28x28灰度图像,与10个类中的一个标签相关联。Fashion-MNIST数据集包含了10个类别的图像,分别是:t-shirt(T恤),trouser(牛仔裤),pullover(套衫),dress(裙子),coat(外套),sandal(凉鞋),shirt(衬衫),sneaker(运动鞋),bag(包),ankle boot(短靴)。
我们使用下列参数载入Fashion-MNIST数据集:
-
root是训练\测试数据的存储路径 -
train指定训练或测试数据集 -
download=True表示若root中没有数据,则从互联网下载 -
transform和target_transform指定功能和标签转换
import torch
from torch.utils.data import Dataset
from torchvision import datasets
from torchvision.transforms import ToTensor
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
training_data = datasets.FashionMNIST(
root="data",
train=True,
download=True,
transform=ToTensor()
)
test_data = datasets.FashionMNIST(
root="data",
train=False,
download=True,
transform=ToTensor()
)
2.2 数据集的迭代和可视化
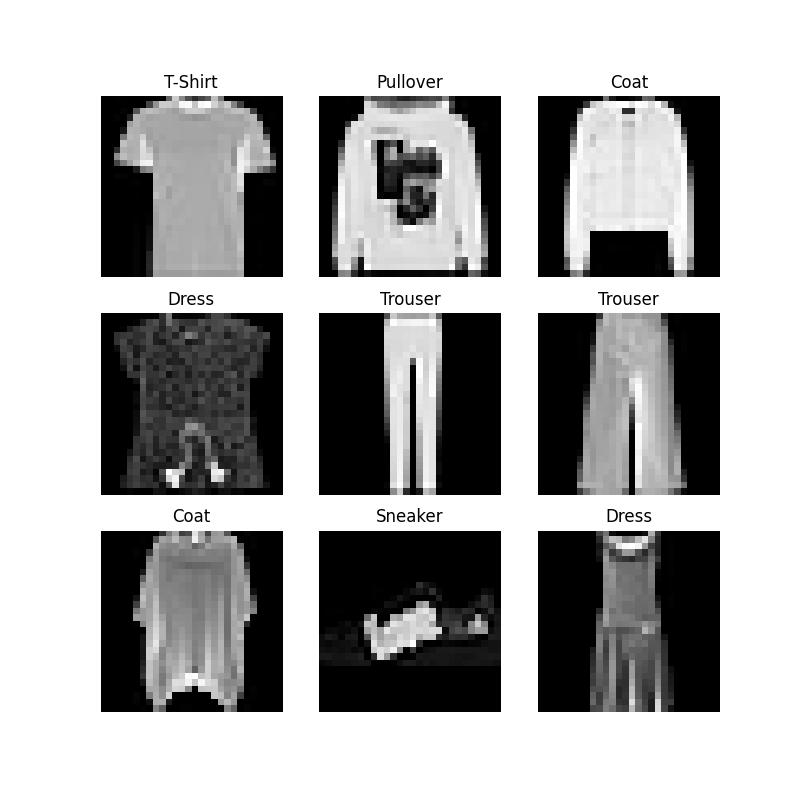
我们可以像列表一样手动索引数据集:training_data[index]。我们使用matplotlib来可视化训练数据中的一些样本。
labels_map = {
0: "T-Shirt",
1: "Trouser",
2: "Pullover",
3: "Dress",
4: "Coat",
5: "Sandal",
6: "Shirt",
7: "Sneaker",
8: "Bag",
9: "Ankle Boot",
}
figure = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
cols, rows = 3, 3
for i in range(1, cols * rows + 1):
sample_idx = torch.randint(len(training_data), size=(1,)).item()
img, label = training_data[sample_idx]
figure.add_subplot(rows, cols, i)
plt.title(labels_map[label])
plt.axis("off")
plt.imshow(img.squeeze(), cmap="gray")
plt.savefig("figure.jpg")
plt.show()
2.3 为文件创建自定义数据集
自定义数据集类必须实现三个函数:__init__、__len__和__getitem__。FashionMNIST图像存储在变量img_dir中,它们的标签分别存储在CSV文件annotations_file中。
在接下来的部分中,我们将分解这些函数中的每一个函数。
import os
import pandas as pd
from torchvision.io import read_image
class CustomImageDataset(Dataset):
# __init__函数在实例化数据集对象时运行一次。初始化包含图像、注释文件和这两个转换的目录。
# labels.csv文件如下所示:
# tshirt1.jpg, 0
# tshirt2.jpg, 0
# ......
# ankleboot999.jpg, 9
def __init__(self, annotations_file, img_dir, transform=None, target_transform=None):
self.img_labels = pd.read_csv(annotations_file)
self.img_dir = img_dir
self.transform = transform
self.target_transform = target_transform
# __len__函数返回数据集的样本数
def __len__(self):
return len(self.img_labels)
# __getitem__函数从给定索引idx的数据集中加载并返回一个样本。根据索引,它识别图像在磁盘上的位置,使用read_image将其转换为张量,从self.img_labels中的csv数据中检索相应的标签,调用它们上的转换函数(如果适用),并在元组中返回张量图像和相应的标签。
def __getitem__(self, idx):
img_path = os.path.join(self.img_dir, self.img_labels.iloc[idx, 0])
image = read_image(img_path)
label = self.img_labels.iloc[idx, 1]
if self.transform:
image = self.transform(image)
if self.target_transform:
label = self.target_transform(label)
return image, label
2.4 为使用DataLoaders进行培训准备数据
数据集检索数据集的特征,并一次标记一个样本。在训练模型时,我们通常希望在“迷你批次”中传递样本,在每个时期重新排列数据以减少模型过拟合,并使用Python的多处理来加快数据检索。
DataLoader是一个可迭代的程序,它用一个简单的API为我们抽象了这种复杂性。
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
train_dataloader = DataLoader(training_data, batch_size=64, shuffle=True)
test_dataloader = DataLoader(test_data, batch_size=64, shuffle=True)
2.5 遍历DataLoader
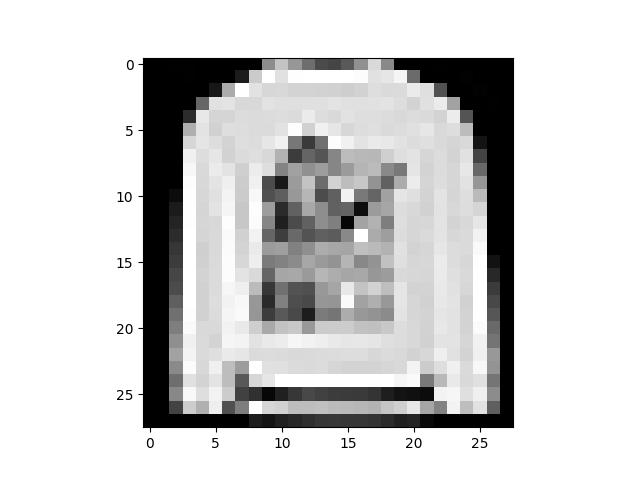
我们已经将该数据集加载到DataLoader中,并可以根据需要对数据集进行迭代。下面的每个迭代都返回一批train_features和train_labels(分别包含batch_size=64个特征和标签)。因为我们指定了shuffle=True,所以在迭代所有批次之后,数据将被打乱。
# 展示图像和标签
train_features, train_labels = next(iter(train_dataloader))
print(f"Feature batch shape: {train_features.size()}")
print(f"Labels batch shape: {train_labels.size()}")
img = train_features[0].squeeze()
label = train_labels[0]
plt.imshow(img, cmap="gray")
plt.show()
print(f"Label: {label}")
Feature batch shape: torch.Size([64, 1, 28, 28])
Labels batch shape: torch.Size([64])
Label: 2
参考资料
- https://pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/basics/data_tutorial.html
- https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45666566/article/details/107812603





















 348
348











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








