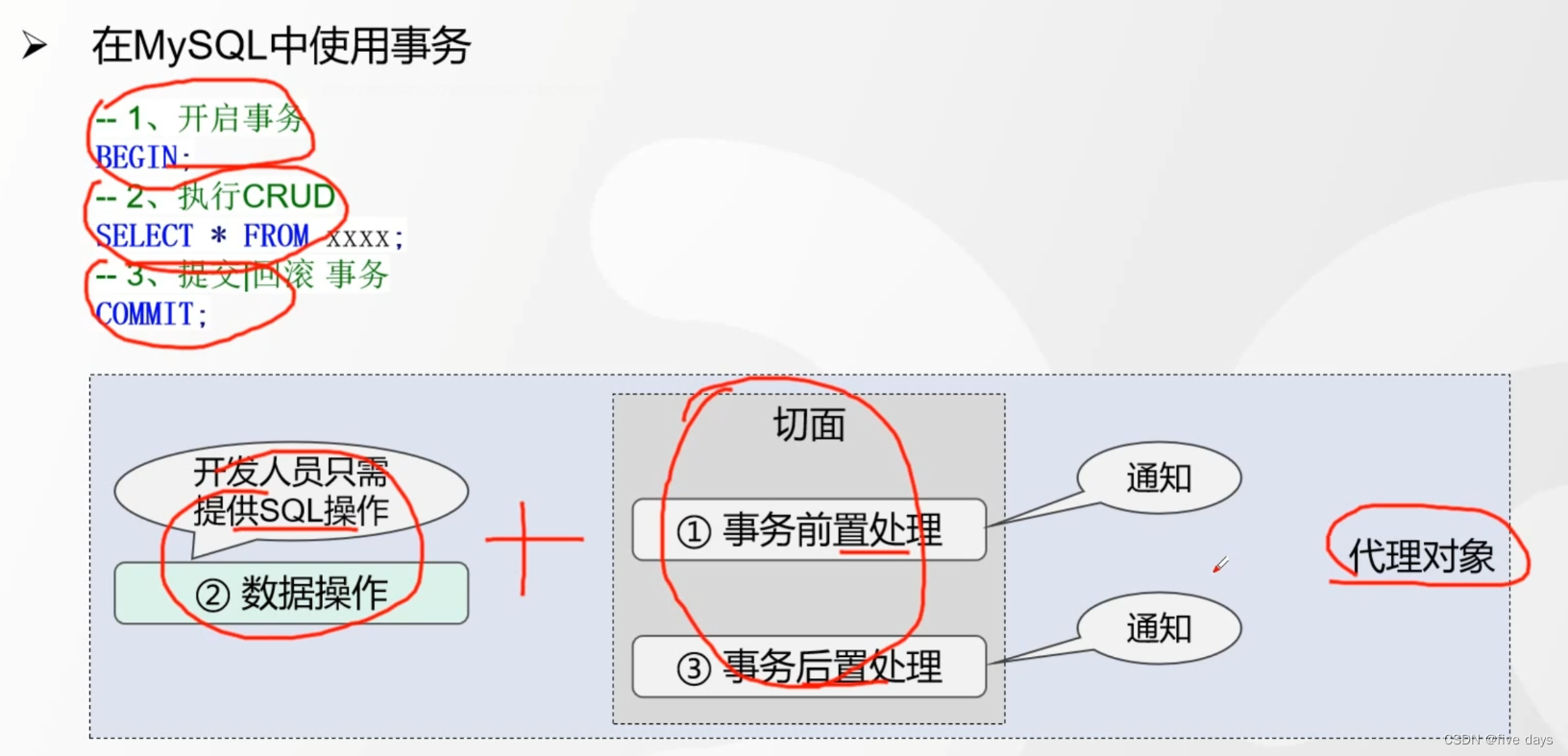
1. 什么是事务
- 多个操作在逻辑上构成一组操作,要么执行,要么都不执行
- 事务运用场景
- 转账业务
- 订单与库存业务
- Spring有事务吗? NO
- Spring事务本质: 对数据库事务的包装
- 在MySql中使用事务 第一步 第三步可以交给Spring去做
事务需要满足ACID特性(可参考博客Mysql之事务-CSDN博客)
2. Spring中的事务管理
2.1 基于XML文件的形式
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.1.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.gupaoedu.*" />
<context:property-placeholder location="db.properties"/>
<!-- 配置数据源 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource" id="dataSource">
<property name="url" value="${jdbc_url}"/>
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc_driver}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc_username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc_password}"/>
</bean>
<!-- 配置JdbcTemplate -->
<bean class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate" >
<constructor-arg name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="txManager">
<!-- the transactional semantics... -->
<tx:attributes>
<!-- all methods starting with 'get' are read-only -->
<tx:method name="bus*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<!-- other methods use the default transaction settings (see below) -->
<tx:method name="*"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="tx" expression="execution(* com.zsc.service..*.*(..))"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="tx"/>
</aop:config>
</beans>2.2 基于注解的方式
放开对注解的支持
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.1.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.gupaoedu.*" />
<context:property-placeholder location="db.properties"/>
<!-- 配置数据源 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource" id="dataSource">
<property name="url" value="${jdbc_url}"/>
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc_driver}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc_username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc_password}"/>
</bean>
<!-- 配置JdbcTemplate -->
<bean class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate" >
<constructor-arg name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!-- 开启事务的注解支持-->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="txManager"/>
</beans>在需要使用注解的方法获取类的头部加对应的注解@Transactional
@Transactional
public void business() throws Exception{
User user = new User("lisi",24);
addUser(user);
user.setId(13);
user.setUserName("bbbb");
updateUser(user);
}3. 事务的传播行为
举例说明
ServiceA
ServiceA {
void methodA() {
ServiceB.methodB();
}
}ServiceB
ServiceB {
void methodB() {
}
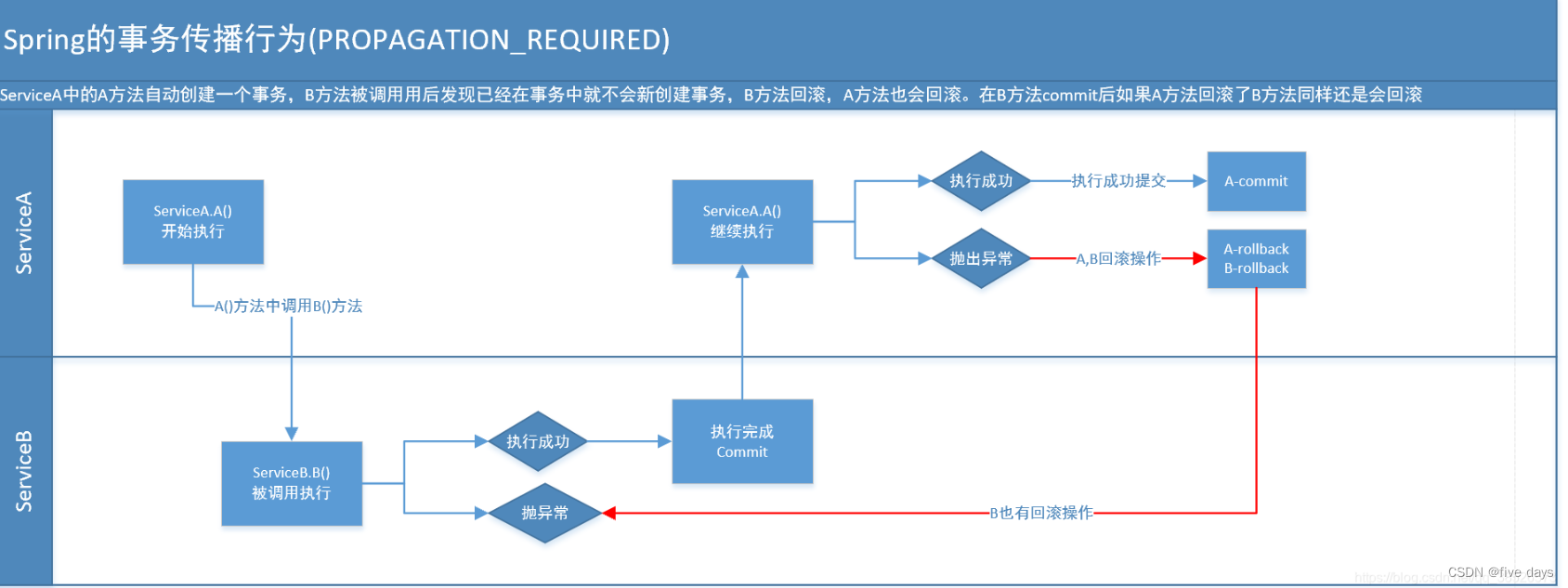
}3.1 PROPAGATION_REQUIRED
假如当前正要运行的事务不在另外一个事务里,那么就起一个新的事务 比方说,ServiceB.methodB的事务级别定义PROPAGATION_REQUIRED, 那么因为执行ServiceA.methodA的时候,ServiceA.methodA已经起了事务。这时调用ServiceB.methodB,ServiceB.methodB看到自己已经执行在ServiceA.methodA的事务内部。就不再起新的事务。而假如ServiceA.methodA执行的时候发现自己没有在事务中,他就会为自己分配一个事务。这样,在ServiceA.methodA或者在ServiceB.methodB内的不论什么地方出现异常。事务都会被回滚。即使ServiceB.methodB的事务已经被提交,可是ServiceA.methodA在接下来fail要回滚,ServiceB.methodB也要回滚
3.2 PROPAGATION_SPPORTS
假设当前在事务中。即以事务的形式执行。假设当前不在一个事务中,那么就以非事务的形式执行
3.3 PROPAGATION_MANDATORY
必须在一个事务中执行。也就是说,他仅仅能被一个父事务调用。否则,他就要抛出异常
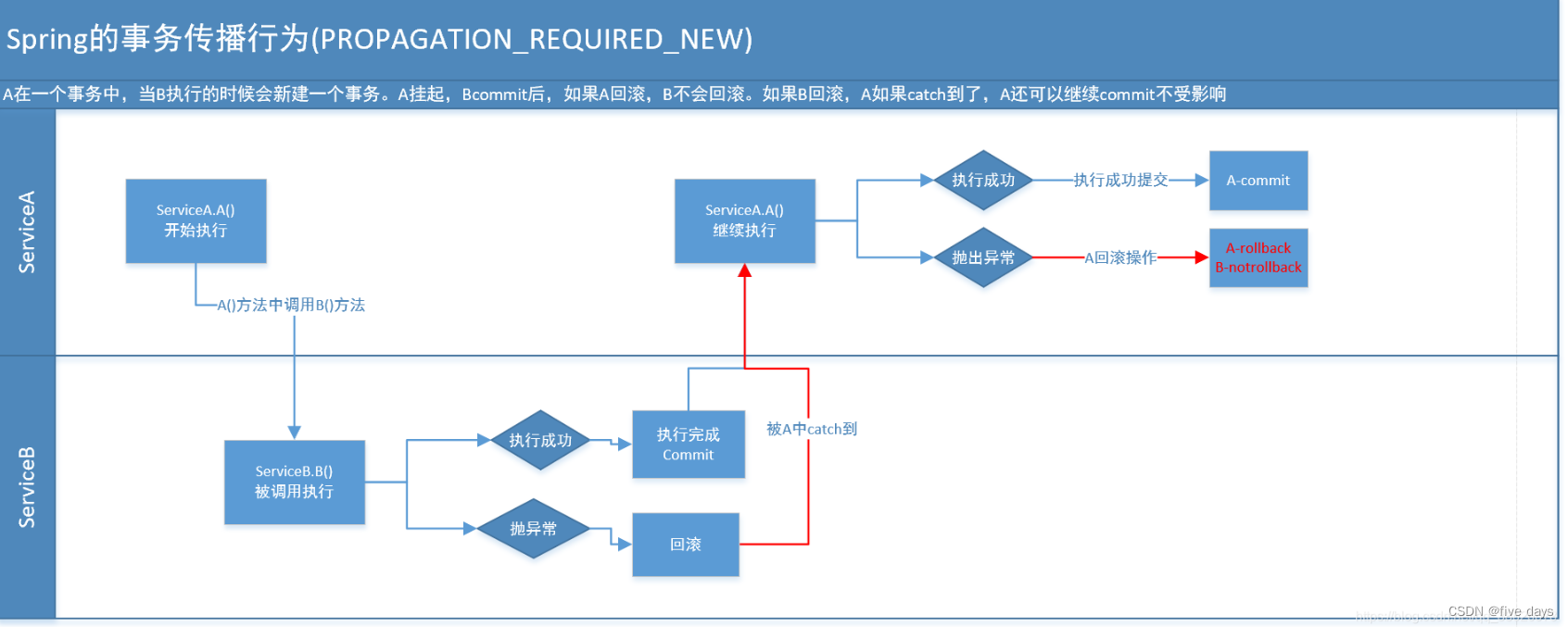
3.4 PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW
这个就比较绕口了。 比方我们设计ServiceA.methodA的事务级别为PROPAGATION_REQUIRED,ServiceB.methodB的事务级别为PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW。那么当运行到ServiceB.methodB的时候,ServiceA.methodA所在的事务就会挂起。ServiceB.methodB会起一个新的事务。等待ServiceB.methodB的事务完毕以后,他才继续运行。
他与PROPAGATION_REQUIRED 的事务差别在于事务的回滚程度了。由于ServiceB.methodB是新起一个事务,那么就是存在两个不同的事务。假设ServiceB.methodB已经提交,那么ServiceA.methodA失败回滚。ServiceB.methodB是不会回滚的。假设ServiceB.methodB失败回滚,假设他抛出的异常被ServiceA.methodA捕获,ServiceA.methodA事务仍然可能提交。
3.5 PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED
当前不支持事务。比方ServiceA.methodA的事务级别是PROPAGATION_REQUIRED 。而ServiceB.methodB的事务级别是PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED ,那么当执行到ServiceB.methodB时。ServiceA.methodA的事务挂起。而他以非事务的状态执行完,再继续ServiceA.methodA的事务。
3.6 PROPAGATION_NEVER
不能在事务中执行。 如果ServiceA.methodA的事务级别是PROPAGATION_REQUIRED。 而ServiceB.methodB的事务级别是PROPAGATION_NEVER ,那么ServiceB.methodB就要抛出异常了。
3.7 PROPAGATION_NESTED
如果当前存在事务,则在嵌套事务内执行。如果当前没有事务,则执行与PROPAGATION_REQUIRED类似的操作。
xml的方式配置
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="txManager">
<tx:attributes>
<!--设置所有匹配的方法,然后设置传播级别和事务隔离-->
<tx:method name="save*" propagation="REQUIRED" />
<tx:method name="add*" propagation="REQUIRED" />
<tx:method name="create*" propagation="REQUIRED" />
<tx:method name="insert*" propagation="REQUIRED" />
<tx:method name="update*" propagation="REQUIRED" />
<tx:method name="merge*" propagation="REQUIRED" />
<tx:method name="del*" propagation="REQUIRED" />
<tx:method name="remove*" propagation="REQUIRED" />
<tx:method name="put*" propagation="REQUIRED" />
<tx:method name="get*" propagation="SUPPORTS" read-only="true" />
<tx:method name="count*" propagation="SUPPORTS" read-only="true" />
<tx:method name="find*" propagation="SUPPORTS" read-only="true" />
<tx:method name="list*" propagation="SUPPORTS" read-only="true" />
<tx:method name="*" propagation="SUPPORTS" read-only="true" />
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice> 注解的方式配置
<!--开启注解的方式-->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactioManager" />@Transactional(propagation=Propagation.REQUIRED) 如果有事务, 那么加入事务, 没有的话新建一个(默认情况下) 、
@Transactional(propagation=Propagation.NOT_SUPPORTED) 容器不为这个方法开启事务 @Transactional(propagation=Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW) 不管是否存在事务,都创建一个新的事务,原来的挂起,新的执行完毕,继续执行老的事务 @Transactional(propagation=Propagation.MANDATORY) 必须在一个已有的事务中执行,否则抛出异常
@Transactional(propagation=Propagation.NEVER) 必须在一个没有的事务中执行,否则抛出异常(与Propagation.MANDATORY相反) @Transactional(propagation=Propagation.SUPPORTS) 如果其他bean调用这个方法,在其他bean中声明事务,那就用事务.如果其他bean没有声明事务,那就不用事务.
4. Spring支持的隔离级别
不设置隔离级别可能发生的下列问题(脏读、不可重复读、幻读)可参考博客Mysql之事务-CSDN博客
Spring设置事务隔离级别
配置文件的方式
<tx:advice id="advice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="fun*" propagation="REQUIRED" isolation="DEFAULT"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>注解的方式
@Transactional(isolation=Isolation.DEFAULT)
public void fun(){
dao.add();
dao.udpate();
}注意: Spring建议的是使用DEFAULT,就是数据库本身的隔离级别,配置好数据库本身的隔离级别,无论在哪个框架中读写数据都不用操心了,而且万一Spring没有把这几种隔离级别实现的很完善,出了问题就麻烦了。






















 421
421











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








