每次的学习都应该记录下来~!~!
文章代码来自:(Android19,java1.7)
这几天看Android的Handle、Loop、Message。以前自己总是在用但没有仔细的去看过源码,查看源代码的时候发现ThreadLocal这个类的使用。这时发现好熟悉EvenBus里面好像也用到了这个类,于是在网上翻看了好多关于ThreadLocal的文章。
ThreadLocal的作用是提供线程内的局部变量,这种变量在线程的生命周期内起作用,减少同一个线程内多个函数或者组件之间一些公共变量的传递的复杂度。
//ThreadLocal提供get和set方法可以获取当前线程中的ThreadLocal<Object>的值
public T get();
public void set(T value);ThreadLocal不是解决多线程安全并发访问资源的在学习的过程中自己发现了以前很少使用的一个叫做AtomicInteger,他好像可以提供所线程并发访问统一资源的问题,因为它能保证资源的原子性。
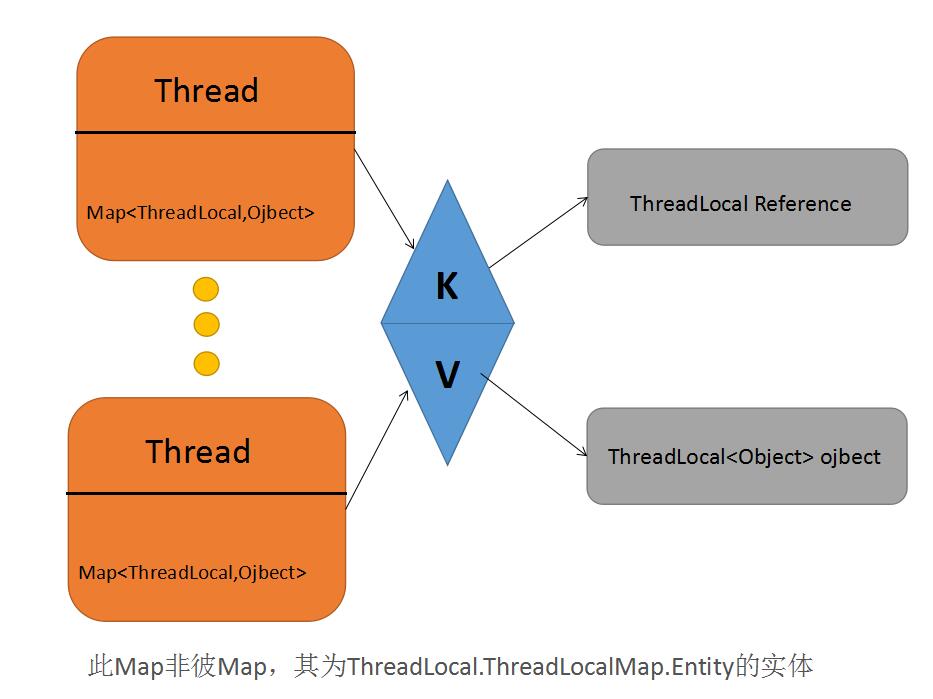
上图很形象的解释的ThreadLocal的运用,Thread中有一个ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap成员变量,用它来存储当前Thread中的ThreadLocal<Object>对象,以ThreadLocal为K,以Object为V进行一对一的存储。
一个使用ThreadLocal的Demo:
public class ThreadLocalTest {
static ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<String>() {
//设定threadLocal在线程中的初始值
@Override
protected String initialValue() {
return "Init";
}
};
static class MyThread implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + threadLocal.get());
threadLocal.set(Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + threadLocal.get());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(new MyThread()).start();
new Thread(new MyThread()).start();
new Thread(new MyThread()).start();
}
}输出结果:
Thread-1Init
Thread-2Init
Thread-0Init
Thread-2Thread-2
Thread-1Thread-1
Thread-0Thread-0JDK中:
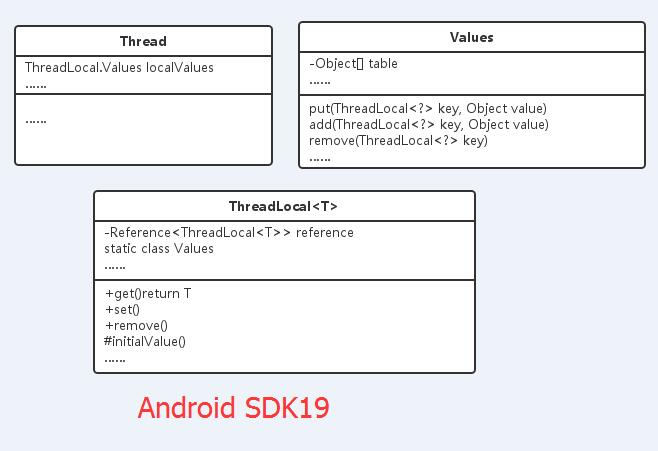
SDK中:
JDK和SDK的ThreadLocal其实在构想上是一样的,只不过具体代码实现是有些不同。
JDK使用的是ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap,它的静态内部类是Entry,ThreadLocalMap内部有一个数组Entry[] table,ThreadLocal对象实例有一个threadLocalhashCode变量
private static final int HASH_INCREMENT = 0x61c88647;
private final int threadLocalHashCode = nextHashCode();
private static int nextHashCode() {
return nextHashCode.getAndAdd(HASH_INCREMENT);
}
private static AtomicInteger nextHashCode = new AtomicInteger();和一个nexhasCode静态变量。一个JVM中每产生一个ThreadLocal对象该对象的threadLocalHashCode的值增加0x61c88647。为什么会增加0x61c88647因为:
//ThreadLocalMap:
private void set(ThreadLocal key, Object value) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
//这样生成的index才不会重复
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
……
}然后再获取ThreadLocal<Object>值得时候根据当前的实例的trheadLocalHashCode作为ThreadLocalMap的index找到对应的Object。
SDK:中用ThreadLocal.Values代替了,JDK中的ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap和ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap.Entry。
private final int hash = hashCounter.getAndAdd(0x61c88647 * 2);
private static AtomicInteger hashCounter = new AtomicInteger(0);
private final Reference<ThreadLocal<T>> reference
= new WeakReference<ThreadLocal<T>>(this);从上面代码可以看出来android每个虚拟机中产生一个ThreadLocal对象hash的值增加0x61c88647*2,其原因是ThreadLocal.Values没有采用Map的形式做查找。而是采用table[index]=threadLocal.reference,table[index+1]=object。
//ThreadLocal:
public T get() {
// Optimized for the fast path.
Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread();
Values values = values(currentThread);
if (values != null) {
Object[] table = values.table;
int index = hash & values.mask;
if (this.reference == table[index]) {
return (T) table[index + 1];
}
} else {
values = initializeValues(currentThread);
}
return (T) values.getAfterMiss(this);
}
//ThreadLodal.Vaules:
private void initializeTable(int capacity) {
this.table = new Object[capacity * 2];
this.mask = table.length - 1;
this.clean = 0;
this.maximumLoad = capacity * 2 / 3; // 2/3
}
Object getAfterMiss(ThreadLocal<?> key) {
Object[] table = this.table;
//产生table.length之类的不重复的非奇数
int index = key.hash & mask;
……
table[index] = key.reference;
table[index + 1] = value;
……
}
























 384
384

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








