策略模式
动机:在软件构建过程中,某些对象使用的算法可能多种多样,经常改变,如果将这些算法都编码到对象中,将会使对象变得异常复杂,而且有时候支持不使用的算法也是一个性能负担
为了在运行时根据需要透明地更改对象的算法,将算法与对象本身解耦,避免上述问题,提出了策略模式。
例:商城收银软件
public class sheji {
public String list=" ";
public Double totalPrice=0.00;
public void buttonOK()
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("输入单价:");
String price =sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("输入数量:");
String num =sc.nextLine();
Double xiaoji=Double.parseDouble(price)*Integer.parseInt(num);
list+="单价:"+price+",数量:"+num+",小计:"+xiaoji+"\n";
totalPrice+=xiaoji;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
sheji cash=new sheji();
boolean flag=true;
while(flag)
{
cash.buttonOK();
if(cash.totalPrice>10)
{
flag=false;
}
}
System.out.println("=============");
System.out.println("清单:\n"+cash.list);
System.out.println("总价:"+cash.totalPrice);
}
}
如果商城搞活动所有商品打八折:加一个输入折扣
String num =sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("输入折扣:");
String zhekou =sc.nextLine();
Double xiaoji=Double.parseDouble(price)*Integer.parseInt(num)*Double.parseDouble(zhekou)/10;
list+="单价:"+price+",数量:"+num+",折扣:"+",小计:"+xiaoji+"\n";
totalPrice+=xiaoji;
活动加大,需要满300返100的促销
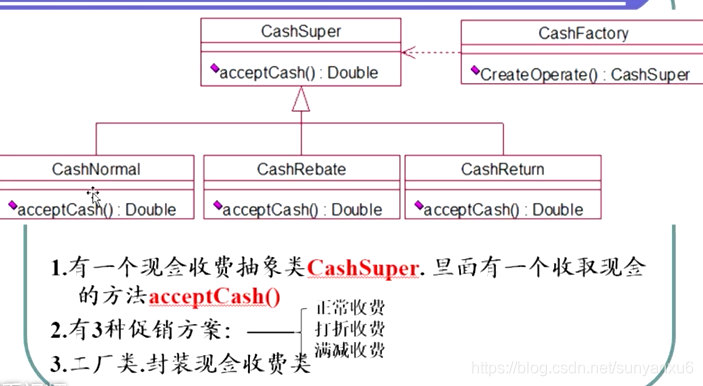
abstract class CashSuper//抽象方法:收取现金,参数为原价,返回为当前价
{
public abstract double acceptCash(double money);
}
class CashNormal extends CashSuper//正常收费类
{
public double acceptCash(double money)
{
return money;
}
}
//打折收费类。继承CashSuper
class CashRebate extends CashSuper {
private double discount = 0.00;
//初始化时,必需要输入折扣率
public CashRebate(double discount) {
this.discount = discount / 10;
}
public double acceptCash(double money) {
return this.discount * money;
}
public double getDiscount() {
return discount;
}
public void setDiscount(double discount) {
this.discount = discount;
}
}
//返利收费继承CashSuper
class CashReturn extends CashSuper
{
private double baseCash;//基础金额
private double returnCash;//返现金额
//初始化时必须要输入返利条件和返回值,比如满300返100,则baseCash为300,returnCash为100
public CashReturn(double baseCash,double returnCash)
{
this.baseCash=baseCash;
this.returnCash=returnCash;
}
public double acceptCash(double money)
{
double result=money;
if(money>=baseCash)//若大于返利条件,则需要减去返利值
{
result=money-Math.floor(money/baseCash)*returnCash;
return result;
}
return result;
}
public double getBaseCash()
{
return baseCash;
}
public void setBaseCash(double baseCash)
{
this.baseCash=baseCash;
}
public double getReturnCash()
{
return returnCash;
}
public void setReturnCash(double returnCash)
{
this.returnCash=returnCash;
}
}
class CashAcceptFactory//现金收取工厂类
{
//根据条件生成相应的对象
public static CashSuper createCashAccept(String type,double discount,double basePrice,double returnPrice)
{
CashSuper cs=null;
if("1".equals(type))
{
cs=new CashNormal();
}else if ("2".equals(type)) {
cs = new CashRebate(discount);
}
else if("3".equals(type))
{
cs=new CashReturn(basePrice,returnPrice);
}
return cs;
}
}
public class sheji {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String list=" ";
boolean flag=true;
Double totalPrice=0.00;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
while(flag)
{
System.out.println("输入单价:");
String price =sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("输入数量:");
String num =sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("输入折扣类型(1.无 2.打折 3.满减):");
String type =sc.nextLine();
double discount=0.0d;
double basePrice=0;
double returnPrice=0;
if("2".equals(type))
{
System.out.println("输入折扣:");
discount=Double.parseDouble(sc.nextLine());
}
if("3".equals(type))
{
System.out.println("返现基础金额:");
basePrice=Double.parseDouble(sc.nextLine());
System.out.println("返现金额:");
returnPrice=Double.parseDouble(sc.nextLine());
}
Double xianjin=Double.parseDouble(price)*Integer.parseInt(num);
CashSuper cs=CashAcceptFactory.createCashAccept(type,discount,basePrice,returnPrice);
double xiaoji=cs.acceptCash(xianjin);
list+="单价:"+price+",数量:"+num+",折扣:"+discount+",小计:"+xiaoji+"\n";
totalPrice+=xiaoji;
if(totalPrice>10) {
flag = false;
}
}
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println("总价:"+totalPrice);
}
}
如果增加促销手段,满100积分10点,以后积分到一定时候可以领取奖品
A:增加一个积分类,构造方法有两个参数,条件和返点,让它继承CashSuper,工厂也增加同样的分支条件。
//现金收取控制类 因为每次维护或拓展收费方式都要去改动工厂是因为工厂与具体收费方式类耦合所以要改造现金收取工厂
class CashContext
{
private CashSuper cs;//声明一个现金收费父类对象
public CashContext(CashSuper csuper)
{
//构造方法,传入具体的收费策略对象(正常,打折或返利)
this.cs=csuper;
}
public double GetResult(double money)
{
//根据不同收费策略,获得合计结果
return cs.acceptCash(money);
}
}
- 在策略模式下,若增加收费方式,则
- 不需要修改:
- 现金收费抽象类
- 不变的具体策略类
- CashContent类
- 需要更改/增加
- 新的具体的策略类
- 客户端
策略模式让算法的变化不会影响到使用算法的用户。
用意是针对一组算法,将每一组算法封装到具有共同接口的独立的类中,从而使得他们可以相互替换。
策略模式基本代码
//抽象算法类
abstract class Strategy
{
//算法方法
public abstract void AlgorithmInterface();
}
//具体算法A
class ConcreteStrategyA extends Strategy
{
//算法A实现方法
public void AlgorithmInterface()
{
System.out.println("算法A实现");
}
}
//具体算法B
class ConcreteStrategyB extends Strategy
{
//算法B实现方法
public void AlgorithmInterface()
{
System.out.println("算法B实现");
}
}
//具体算法C
class ConcreteStrategyC extends Strategy
{
//算法C实现方法
public void AlgorithmInterface()
{
System.out.println("算法C实现");
}
}
//上下文
class Context
{
Strategy strategy;
public Context(Strategy strategy)
{
this.strategy = strategy;
}
//上下文接口
public void ContextInterface()
{
strategy.AlgorithmInterface();
}
}
}
public class sheji {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Context context;
context=new Context(new ConcreteStrategyA());
context.ContextInterface();
context=new Context(new ConcreteStrategyB());
context.ContextInterface();
context=new Context(new ConcreteStrategyC());
context.ContextInterface();
}
}
简单工厂和策略模式对比:
工厂有进货也有出货,然后使用出货
策略有进货没出货,然后使用得货着
策略模式功能
- 把具体算法从具体业务处理中独立
策略模式与if-else语句 - 多个语句出现考虑使用策略模式
使用策略模式的情况:
一个系统中有多个类,他们之间的区别仅在于他们的行为,希望动态的让一个对象在许多行为中选择一种行为时;
当一个系统需要动态地在几种算法中选择一种时。
优点:
策略模式之间可以自由切换
避免使用多重条件选择语句,充分体现面向对象设计思想
拓展性良好
缺点:
客户端需要知道所有的策略类,意味着所有策略类都需要对外暴露
策略类增多
本质:分离算法,选择实现
针对缺点改进
改变CashContext类,把分支判断放到环境角色中,与简单工厂结合
class CashContext
{
private CashSuper cs=null;//声明一个现金收费父类对象
public CashContext()//注意构造函数的参数不再是一个具体策略对象
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("输入折扣类型(1.无 2.打折 3.满减):");
String type =sc.nextLine();
double discount=0.0d;
double basePrice=0;
double returnPrice=0;
if("1".equals(type))
{
cs=new CashNormal();
}
else if("2".equals(type))
{
System.out.println("输入折扣:");
discount=Double.parseDouble(sc.nextLine());
cs=new CashRebate(discount);
}
if("3".equals(type))
{
System.out.println("返现基础金额:");
basePrice=Double.parseDouble(sc.nextLine());
System.out.println("返现金额:");
returnPrice=Double.parseDouble(sc.nextLine());
cs=new CashReturn(basePrice,returnPrice);
}
}
public double GetResult(double money)
{
//根据不同收费策略,获得合计结果
return cs.acceptCash(money);
}
}
public class sheji {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String list=" ";
boolean flag=true;
Double totalPrice=0.00;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
while(flag)
{
System.out.println("输入单价:");
String price =sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("输入数量:");
String num =sc.nextLine();
Double xianjin=Double.parseDouble(price)*Integer.parseInt(num);
CashContext cc=new CashContext();
double xiaoji=cc.GetResult(xianjin);
list+="单价:"+price+",数量:"+num+",小计:"+xiaoji+"\n";
totalPrice+=xiaoji;
if(totalPrice>10) {
flag = false;
}
}
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println("总价:"+totalPrice);
}
}
简单工厂模式需要让客户端认识两个类:收费父类CashSuper和CashAcceptFactory
与简单工厂结合的策略模式只需要让客户认识环境类CashContext





















 8万+
8万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








