以下讲解例子来自《windows网络编程》随书代码第五章blocking。都是大神的代码,拿出来讲解学习下,能收获不少东西。
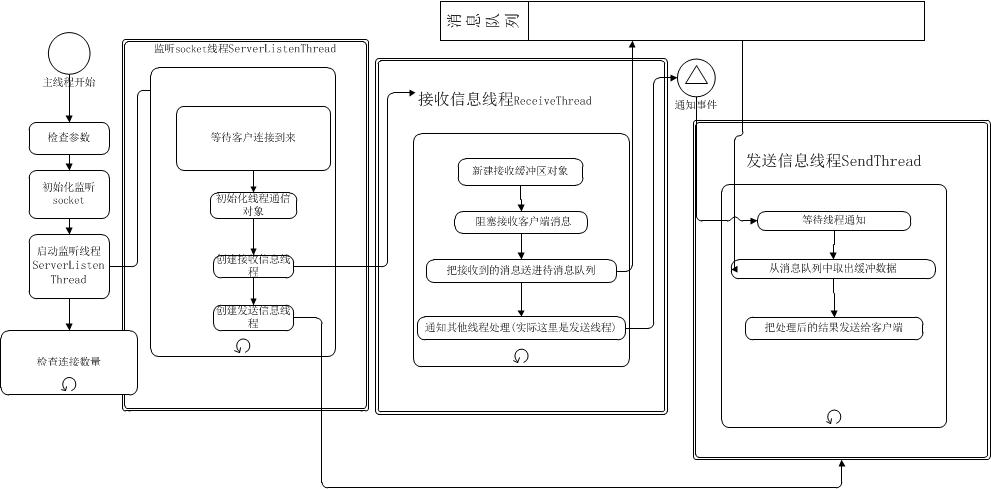
为方便理解,我根据server端代码流程,画了上面这个流程图。
原代码里面有针对TCP及UDP的处理,原理都是差不多的,我们这里只针对TCP协议使用IPV4地址来作讲解。
整个流程需要用到四个线程,分别是:
1. 主线程,负责检查输入的参数并以参数初始化监听socket,然后启动监听线程,接下来就是一个每5秒检查一次连接状态的无限轮询。
2. 监听线程,通过使用阻塞的accept函数等待连接的到来;一旦有连接到来,完成连接建立,新建并初始化接收和发送线程之前通信需要的对象,然后启动接收和发送这两个线程;再回到accept等待下一个连接。
3. 接收消息线程,通过使用阻塞的recv函数等待客户端数据的到来;一旦有数据到来,把数据封装后送进消息队列,然后通过监听线程初始化过的通信对象通知处理线程(这里就是发送消息线程)。
根据不同的业务需求,可以在接收到数据以后做不同的处理,比如验证数据的正确性,确认处理,发送回结果等。下面帖上原代码:
//
// Sample: Blocking IPv4/IPv6 Server
//
// Files:
// bserver.cpp - this file
// resolve.cpp - routines for resovling addresses, etc.
// resolve.h - header file for resolve.c
//
// Description:
// This sample illustrates simple blocking IO for TCP and UDP for
// both IPv4 and IPv6. This sample uses the getaddrinfo/getnameinfo
// APIs which allows this application to be IP agnostic. That is the
// desired address family (AF_INET or AF_INET6) can be determined
// simply from the string address passed via the -l command.
//
// For TCP, a listening thread is spawned for each available address family.
// Each thread blocks on an accept call. Once accept completes, two threads
// are created for each client: a sending thread and a receiving thread.
// The sending thread sends the requested amount of data while the receive
// thread read data until the socket is closed. Each client thread exits
// once its task is completed. The receiving thread will close the socket
// after it has received all the echoed data.
//
// For UDP, a main thread is spawned for each available address family.
// Then a receive thread is spawned from there. The main thread then sends
// the requested data and waits on the receive thread's handle.
//
// For example:
// If this sample is called with the following command lines:
// bserver.exe -l fe80::2efe:1234 -e 5150
// bserver.exe -l ::
// Then the server creates an IPv6 socket as an IPv6 address was
// provided.
//
// On the other hand, with the following command line:
// bserver.exe -l 7.7.7.1 -e 5150
// bserver.exe -l 0.0.0.0
// Then the server creates an IPv4 socket.
//
// Compile:
// cl -o bserver.exe bserver.cpp resolve.cpp ws2_32.lib
//
// Usage:
// bserver.exe [options]
// -a 4|6 Address family, 4 = IPv4, 6 = IPv6 [default = IPv4]
// -b size Size of send/recv buffer in bytes
// -e port Port number
// -l addr Local address to bind to [default INADDR_ANY for IPv4 or INADDR6_AN
// -p proto Which protocol to use [default = TCP]
// tcp Use TCP protocol
// udp Use UDP protocol
//
#include <winsock2.h>
#include <ws2tcpip.h>
#include <windows.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "resolve.h"
#pragma comment(lib,"ws2_32.lib")
#define DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE 4096 // default buffer size
#define MAX_LISTEN_SOCKETS 8 // maximum listening sockets
int gAddressFamily = AF_UNSPEC, // default to unspecified
gSocketType = SOCK_STREAM, // default to TCP socket type
gProtocol = IPPROTO_TCP, // default to TCP protocol
gBufferSize = DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE;
char *gBindAddr = NULL, // local interface to bind to
*gBindPort = "5150"; // local port to bind to
struct _BUFFER_OBJ;
//
// Allocated for each client connection
//
typedef struct _CONNECTION_OBJ
{
SOCKET s; // Client socket
HANDLE hRecvSema; // Semaphore incremented for each receive
struct _BUFFER_OBJ *PendingSendHead, // List of pending buffers to send
*PendingSendTail; // End of the list
CRITICAL_SECTION SendRecvQueueCritSec; // Protect access to this structure
} CONNECTION_OBJ;
//
// Allocated for each receiver posted
// Each receive thread allocates one of these for a receive operation.
// After data is read, this object is queued for the send thread to
// echo back to the client (sender).
//
typedef struct _BUFFER_OBJ
{
char *buf; // Data buffer for data
int buflen; // Length of buffer or number of bytes contained in buffer
SOCKADDR_STORAGE addr; // Address data was received from (UDP)
int addrlen; // Length of address
struct _BUFFER_OBJ *next;
} BUFFER_OBJ;
//
// Statistics counters
//
volatile LONG gBytesRead=0,
gBytesSent=0,
gStartTime=0,
gBytesReadLast=0,
gBytesSentLast=0,
gStartTimeLast=0,
gConnectedClients=0;
//
// Function: usage
//
// Description:
// Prints usage information and exits the process.
//
void usage(char *progname)
{
fprintf(stderr, "usage: %s [-a 4|6] [-e port] [-l local-addr] [-p udp|tcp]\n",
progname);
fprintf(stderr, " -a 4|6 Address family, 4 = IPv4, 6 = IPv6 [default = IPv4]\n"
" -b size Buffer size for send/recv [default = %d]\n"
" -e port Port number [default = %s]\n"
" -l addr Local address to bind to [default INADDR_ANY for IPv4 or INADDR6_ANY for IPv6]\n"
" -p tcp|udp Which protocol to use [default = TCP]\n",
gBufferSize,
gBindPort
);
ExitProcess(-1);
}
//
// Function: GetConnectionObj
//
// Description:
// This routine allocates a CONNECTION_OBJ structure and initializes its
// members. For sake of simplicity, this routine allocates a object from
// the process heap. For better performance, you should modify this to
// maintain a lookaside list of structures already allocated and freed
// and only allocate from the heap when necessary.
//
CONNECTION_OBJ *GetConnectionObj(SOCKET s)
{
CONNECTION_OBJ *newobj=NULL;
// Allocate the object
newobj = (CONNECTION_OBJ *)HeapAlloc(GetProcessHeap(), HEAP_ZERO_MEMORY, sizeof(CONNECTION_OBJ));
if (newobj == NULL)
{
printf("GetConnectionObj: HeapAlloc failed: %d\n", WSAGetLastError());
ExitProcess(-1);
}
newobj->s = s;
// Create the semaphore for signaling the send thread
newobj->hRecvSema = CreateSemaphore(NULL, 0, 0x0FFFFFFF, NULL);
if (newobj->hRecvSema == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "GetConnectionObj: CreateSemaphore failed: %d\n", GetLastError());
ExitProcess(-1);
}
InitializeCriticalSection(&newobj->SendRecvQueueCritSec);
return newobj;
}
//
// Function: FreeConnectionObj
//
// Description:
// This routine frees a CONNECTIN_OBJ. It first frees the critical section.
// See the comment for GetConnectionObj about using lookaside lists.
//
void FreeConnectionObj(CONNECTION_OBJ *obj)
{
DeleteCriticalSection(&obj->SendRecvQueueCritSec);
HeapFree(GetProcessHeap(), 0, obj);
}
//
// Function: GetBufferObj
//
// Description:
// Allocate a BUFFER_OBJ. Each receive posted by a receive thread allocates
// one of these. After the recv is successful, the BUFFER_OBJ is queued for
// sending by the send thread. Again, lookaside lists may be used to increase
// performance.
//
BUFFER_OBJ *GetBufferObj(int buflen)
{
BUFFER_OBJ *newobj=NULL;
// Allocate the object
newobj = (BUFFER_OBJ *)HeapAlloc(GetProcessHeap(), HEAP_ZERO_MEMORY, sizeof(BUFFER_OBJ));
if (newobj == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "GetBufferObj: HeapAlloc failed: %d\n", GetLastError());
ExitProcess(-1);
}
// Allocate the buffer
newobj->buf = (char *)HeapAlloc(GetProcessHeap(), HEAP_ZERO_MEMORY, sizeof(BYTE) *buflen);
if (newobj->buf == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "GetBufferObj: HeapAlloc failed: %d\n", GetLastError());
ExitProcess(-1);
}
newobj->buflen = buflen;
newobj->addrlen = sizeof(newobj->addr);
return newobj;
}
//
// Function: FreeBufferObj
//
// Description:
// Free the buffer object.
//
void FreeBufferObj(BUFFER_OBJ *obj)
{
HeapFree(GetProcessHeap(), 0, obj->buf);
HeapFree(GetProcessHeap(), 0, obj);
}
//
// Function: EnqueueBufferObj
//
// Description:
// Queue up a receive buffer for this connection. After enqueueing the receiver
// will release the counting semaphore which will release the sender to
// dequeue a buffer and send it.
//
void EnqueueBufferObj(CONNECTION_OBJ *conn, BUFFER_OBJ *obj)
{
EnterCriticalSection(&conn->SendRecvQueueCritSec);
if (conn->PendingSendHead == NULL)
{
// Queue is empty
conn->PendingSendHead = conn->PendingSendTail = obj;
}
else
{
// Put new object at the end
conn->PendingSendTail->next = obj;
conn->PendingSendTail = obj;
}
LeaveCriticalSection(&conn->SendRecvQueueCritSec);
}
//
// Function: DequeueBufferObj
//
// Description:
// Remove a BUFFER_OBJ from the given connection's queue for sending.
//
BUFFER_OBJ *DequeueBufferObj(CONNECTION_OBJ *conn)
{
BUFFER_OBJ *ret=NULL;
EnterCriticalSection(&conn->SendRecvQueueCritSec);
if (conn->PendingSendTail != NULL)
{
// Queue is non empty
ret = conn->PendingSendHead;
conn->PendingSendHead = conn->PendingSendHead->next;
if (conn->PendingSendTail == ret)
{
// Item is the only item in the queue
conn->PendingSendTail = NULL;
}
}
LeaveCriticalSection(&conn->SendRecvQueueCritSec);
return ret;
}
//
// Function: ValidateArgs
//
// Description:
// Parses the command line arguments and sets up some global
// variables.
//
void ValidateArgs(int argc, char **argv)
{
int i;
for(i=1; i < argc ;i++)
{
if (((argv[i][0] != '/') && (argv[i][0] != '-')) || (strlen(argv[i]) < 2))
usage(argv[0]);
else
{
switch (tolower(argv[i][1]))
{
case 'a': // address family - IPv4 or IPv6
if (i+1 >= argc)
usage(argv[0]);
if (argv[i+1][0] == '4')
gAddressFamily = AF_INET;
else if (argv[i+1][0] == '6')
gAddressFamily = AF_INET6;
else
usage(argv[0]);
i++;
break;
case 'b': // buffer size for send/recv
if (i+1 >= argc)
usage(argv[0]);
gBufferSize = atol(argv[++i]);
break;
case 'e': // endpoint - port number
if (i+1 >= argc)
usage(argv[0]);
gBindPort = argv[++i];
break;
case 'l': // local address for binding
if (i+1 >= argc)
usage(argv[0]);
gBindAddr = argv[++i];
break;
case 'p': // protocol - TCP or UDP
if (i+1 >= argc)
usage(argv[0]);
if (_strnicmp(argv[i+1], "tcp", 3) == 0)
{
gProtocol = IPPROTO_TCP;
gSocketType = SOCK_STREAM;
}
else if (_strnicmp(argv[i+1], "udp", 3) == 0)
{
gProtocol = IPPROTO_UDP;
gSocketType = SOCK_DGRAM;
}
else
usage(argv[0]);
i++;
break;
default:
usage(argv[0]);
break;
}
}
}
}
//
// Function: ReceiveThead
//
// Description:
// One of these threads is started for each client connection.
// This thread sits in a loop, receiving data. For each receive, the
// buffer is queued for sending by the SenderThread for this connection.
//
DWORD WINAPI ReceiveThread(LPVOID lpParam)
{
CONNECTION_OBJ *ConnObj=NULL;
BUFFER_OBJ *BuffObj=NULL;
int rc;
// Retrieve the connection object for this connection
ConnObj = (CONNECTION_OBJ *)lpParam;
if (gProtocol == IPPROTO_UDP)
{
// For UDP all we do is receive packets on the port
while (1)
{
// Allocate the buffer for datagram send/recv
BuffObj = GetBufferObj(gBufferSize);
rc = recvfrom(
ConnObj->s,
BuffObj->buf,
BuffObj->buflen,
0,
(SOCKADDR *)&BuffObj->addr,
&BuffObj->addrlen);
BuffObj->buflen = rc;
if (rc > 0)
{
// Increment the statistics
InterlockedExchangeAdd(&gBytesRead, rc);
InterlockedExchangeAdd(&gBytesReadLast, rc);
}
// Queue the receive buffer for sending and signal the send thread
EnqueueBufferObj(ConnObj, BuffObj);
ReleaseSemaphore(ConnObj->hRecvSema, 1, NULL);
if (rc == 0)
{
break;
}
}
}
else if (gProtocol == IPPROTO_TCP)
{
// loop until the connection is closed or is aborted/terminated
while (1)
{
// Allocate the buffer for stream send/recv
BuffObj = GetBufferObj(gBufferSize);
rc = recv(
ConnObj->s,
BuffObj->buf,
BuffObj->buflen,
0);
BuffObj->buflen = rc;
printf("ReceiveThread receive data: %s\n",BuffObj->buf);
// Queue the receive buffer for sending and signal the send thread
EnqueueBufferObj(ConnObj, BuffObj);
ReleaseSemaphore(ConnObj->hRecvSema, 1, NULL);
if (rc == 0 || rc == SOCKET_ERROR)
{
break;
}
else if (rc != SOCKET_ERROR)
{
// Increment the statistics
InterlockedExchangeAdd(&gBytesRead, rc);
InterlockedExchangeAdd(&gBytesReadLast, rc);
}
}
}
ExitThread(0);
return 0;
}
//
// Function: SendThread
//
// Description:
// This is the send thread started for each client connection.
// This thread waits for the semaphore to be signaled indicating that
// the receive thread has queued a buffer for sending.
//
DWORD WINAPI SendThread(LPVOID lpParam)
{
CONNECTION_OBJ *ConnObj=NULL;
BUFFER_OBJ *BuffObj=NULL;
int rc,
nleft,
idx;
// Retrieve the connection object
ConnObj = (CONNECTION_OBJ *)lpParam;
while (1)
{
// Wait for the receive thread to signal us
rc = WaitForSingleObject(ConnObj->hRecvSema, INFINITE);
if (rc == WAIT_FAILED || rc == WAIT_TIMEOUT)
{
fprintf(stderr, "WaitForSingleObject failed: %d\n", GetLastError());
ExitProcess(-1);
}
// Retrieve the first buffer from this connection's queue
BuffObj = DequeueBufferObj(ConnObj);
//
// If the this receive by the receive thread indicated zero bytes then
// the connection has been gracefully closed. Otherwise, if an error
// was indicated then the connection was aborted.
//
if ((gProtocol == IPPROTO_TCP ) && ((BuffObj->buflen == 0) || (BuffObj->buflen == SOCKET_ERROR)))
{
FreeBufferObj(BuffObj);
BuffObj = NULL;
break;
}
if (gProtocol == IPPROTO_UDP)
{
// For UDP we send the packet back to the source address
rc = sendto(
ConnObj->s,
BuffObj->buf,
BuffObj->buflen,
0,
(SOCKADDR *)&BuffObj->addr,
BuffObj->addrlen
);
if (BuffObj->buflen == 0)
{
FreeBufferObj(BuffObj);
BuffObj = NULL;
break;
}
}
else if (gProtocol == IPPROTO_TCP)
{
// Otherwise send the buffer on the connection socket
nleft = BuffObj->buflen;
idx = 0;
printf("SendThread Send data: %s\n",BuffObj->buf);
while (nleft > 0)
{
rc = send(
ConnObj->s,
&BuffObj->buf[idx],
nleft,
0
);
if (rc == SOCKET_ERROR)
{
break;
}
else
{
nleft -= rc;
idx += rc;
}
}
}
if (rc == SOCKET_ERROR)
{
printf("SendThread: send(to) failed: %d\n", WSAGetLastError());
break;
}
else if (rc > 0)
{
// Increment the statistics
InterlockedExchangeAdd(&gBytesSent, rc);
InterlockedExchangeAdd(&gBytesSentLast, rc);
}
FreeBufferObj(BuffObj);
BuffObj = NULL;
}
// Close the connection's socket
closesocket(ConnObj->s);
FreeConnectionObj(ConnObj);
ExitThread(0);
return 0;
}
//
// Funtion: ServerListenThread
//
// Description:
// This function is spawned for each listening or receive thread
// depending on whether the server is started for UDP or TCP. In
// reality there will only be two server threads, one for IPv4
// and one for IPv6.
//
DWORD WINAPI ServerListenThread(LPVOID lpParam)
{
CONNECTION_OBJ *ConnObj=NULL;
HANDLE hThread = NULL;
SOCKET s;
int rc;
s = (SOCKET) lpParam;
if (gProtocol == IPPROTO_UDP)
{
// If we're UDP we don't have any "connections" to handle. we just have to
// receive UDP packets and send them back. Hence we only need 1 receiver
// thread and 1 sender thread for the whole thing.
//
ConnObj = GetConnectionObj(s);
hThread = CreateThread(NULL, 0, ReceiveThread, (LPVOID)ConnObj, 0, NULL);
if (hThread == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "ServerListenThread: CreateThread failed: %d\n", GetLastError());
ExitThread(-1);
}
SendThread((LPVOID)ConnObj);
}
else if (gProtocol == IPPROTO_TCP)
{
SOCKADDR_STORAGE saAccept; // client address
SOCKET ns; // client socket
int acceptlen = sizeof(SOCKADDR_STORAGE);
rc = listen(s, 200);
if (rc == SOCKET_ERROR)
{
fprintf(stderr, "listen failed: %d\n", WSAGetLastError());
ExitThread(-1);
}
while (1)
{
// Wait for an incoming client connection
ns = accept(s, (SOCKADDR *)&saAccept, &acceptlen);
if (ns == INVALID_SOCKET)
{
fprintf(stderr, "accept failed: %d\n", WSAGetLastError());
return -1;
}
InterlockedIncrement(&gConnectedClients);
/*
printf("Accepted connection from: ");
PrintAddress((SOCKADDR *)&saAccept, acceptlen);
printf("\n");
*/
// Allocate a connection object for this client
ConnObj = GetConnectionObj(ns);
// Create a receiver thread for this connection
hThread = CreateThread(NULL, 0, ReceiveThread, (LPVOID)ConnObj, 0, NULL);
if (hThread == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "CreateThread failed: %d\n", GetLastError());
ExitThread(-1);
}
CloseHandle(hThread);
// Create a sender thread for this connection
hThread = CreateThread(NULL, 0, SendThread, (LPVOID)ConnObj, 0, NULL);
if (hThread == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "CreateThread failed: %d\n", GetLastError());
ExitThread(-1);
}
CloseHandle(hThread);
}
}
closesocket(s);
ExitThread(0);
return 0;
}
//
// Function: main
//
// Description:
// This is the main program. It parses the command line and creates
// the main socket. For UDP this socket is used to receive datagrams.
// For TCP the socket is used to accept incoming client connections.
// Each client TCP connection is handed off to a worker thread which
// will receive any data on that connection until the connection is
// closed.
//
int __cdecl main(int argc, char **argv)
{
WSADATA wsd;
SOCKET s[MAX_LISTEN_SOCKETS];
HANDLE threads[MAX_LISTEN_SOCKETS];
int rc,
listencount=0,
i;
struct addrinfo *res=NULL,
*ptr=NULL;
ValidateArgs(argc, argv);
if (WSAStartup(MAKEWORD(2,2), &wsd) != 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "unable to load Winsock!\n");
return -1;
}
printf("Local address: %s; Port: %s; Family: %d\n",
gBindAddr, gBindPort, gAddressFamily);
res = ResolveAddress(gBindAddr, gBindPort, gAddressFamily, gSocketType, gProtocol);
if (res == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "ResolveAddress failed to return any addresses!\n");
return -1;
}
// For each local address returned, create a listening/receiving socket
ptr = res;
while (ptr)
{
if (listencount > MAX_LISTEN_SOCKETS)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Exceeded maximum listening sockets allowed\n");
return -1;
}
PrintAddress(ptr->ai_addr, ptr->ai_addrlen); printf("\n");
// create the socket
s[listencount] = socket(ptr->ai_family, ptr->ai_socktype, ptr->ai_protocol);
if (s[listencount] == INVALID_SOCKET)
{
fprintf(stderr,"socket failed: %d\n", WSAGetLastError());
return -1;
}
// bind the socket to a local address and port
rc = bind(s[listencount], ptr->ai_addr, ptr->ai_addrlen);
if (rc == SOCKET_ERROR)
{
fprintf(stderr, "bind failed: %d\n", WSAGetLastError());
return -1;
}
// Create a listen thread for each local address to listen on
threads[listencount] = CreateThread(
NULL,
0,
ServerListenThread,
(LPVOID)s[listencount],
0,
NULL
);
if (threads[listencount] == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "CreateThread failed: %d\n", GetLastError());
return -1;
}
listencount++;
ptr = ptr->ai_next;
}
gStartTime = gStartTimeLast = GetTickCount();
// free the addrinfo structure for the 'bind' address
freeaddrinfo(res);
while (1)
{
// Wait for the listening threads to exit, also print out statistics
// when the wait times out
rc = WaitForMultipleObjects(listencount, threads, TRUE, 5000);
if (rc == WAIT_FAILED)
{
fprintf(stderr, "WaitForMultipleObjects failed: %d\n", GetLastError());
return -1;
}
else if (rc == WAIT_TIMEOUT)
{
ULONG bps, tick, elapsed;
tick = GetTickCount();
elapsed = (tick - gStartTime) / 1000;
printf("\n");
bps = gBytesSent / elapsed;
printf("Average BPS sent: %lu [%lu]\n", bps, gBytesSent);
bps = gBytesRead / elapsed;
printf("Average BPS read: %lu [%lu]\n", bps, gBytesRead);
elapsed = (tick - gStartTimeLast) / 1000;
bps = gBytesSentLast / elapsed;
printf("Current BPS sent: %lu\n", bps);
bps = gBytesReadLast / elapsed;
printf("Current BPS read: %lu\n", bps);
InterlockedExchange(&gBytesSentLast, 0);
InterlockedExchange(&gBytesReadLast, 0);
printf("Current Connections: %lu\n", gConnectedClients);
gStartTimeLast = tick;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
// Close the thread handles opened
for (i=0; i < listencount ;i++)
{
CloseHandle(threads[i]);
}
WSACleanup();
return 0;
}





















 3298
3298

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








