堆
堆数据结构是一种数组对象,他也可以被视为是一棵完全二叉树。
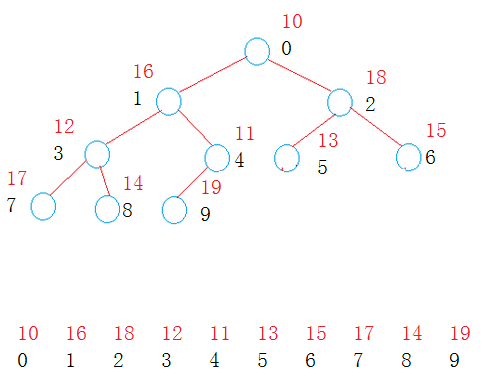
堆数据结构的二叉树存储结构如下:
堆的特点:
最大堆:每个父节点都大于他的孩子节点。
最小堆:每个父节点都小于他的孩子节点。
以下是自己写的堆代码(以小堆为例):
#pragma once
#include <vtor>
#include <assert.h>
using namespace std;
//仿函数
template <class T>
struct Greater
{
bool operator() (const T& l,const T& r) const
{
return l > r;
}
};
template <class T>
struct Less
{
bool operator() (const T& l,const T& r) const
{
return l < r;
}
};
template<class T, class Compare = Less<T> >
class Heap
{
public:
Heap()
{}
Heap(const T* array, size_t size)
{
assert(array);
for (int i = 0; i< size; ++i)
{
_v.push_back(array[i]);
}
for (int i = _v.size()/2 - 1; i >=0; --i)
{
_AdjustDown(_v, i, _v.size());
}
}
Heap(const vtor<T>& v)
{
_v.swap(v);
for (int i = _v.size()/2 - 1; i >=0; --i)
{
_AdjustDown(_v, i, _v.size());
}
}
// 插入一个数据x到最小堆中
void Push(const T& x)
{
_v.push_back(x);
if (_v.size() > 1)
{
_AdjustUp(_v, _v.size() - 1);
}
}
// 删除堆顶元素
void Pop()
{
int size = _v.size();
assert(size > 0);
swap(_v[0], _v[size - 1]);
_v.pop_back();
if (_v.size() > 1)
{
_AdjustDown(_v, 0, _v.size());
}
}
const T& Top()
{
return _v[0];
}
// 将根节点向下调整(小堆举例)
void _AdjustDown(vtor<T>& v, int root, int size)
{
// 1.child指向左孩子节点
int child = root * 2 + 1;
while (child < size)
{
// 2.child指向左右孩子中小的节点
if (child + 1 < size && Compare()(v[child + 1], v[child]))
{
++child;
}
// 3.若child小于根节点,则交换child和root节点,并继续向下调整
if (Compare()(v[child], v[root]))
//if (v[child] < v[root])
{
swap(v[child], v[root]);
root = child;
child = root*2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
// 一个节点向上调整(小堆举例说明)
void _AdjustUp(vtor<T>& v, int pos)
{
// 1.parent指向父节点
int child = pos;
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
// 当child==0时,则上调完成。不能使用parent来判断,parent不会小于0
//while(parent >= 0)
while(child > 0)
{
// 2.若child小于父节点,则交换父子节点,并继续向上调整,直到根节点
if (Compare()(v[child], v[parent]))
//if (v[child] < v[parent])
{
swap(v[child], v[parent]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
// 判断是否为空
bool Empty()
{
return _v.empty();
}
size_t Size()
{
return _v.size();
}
private:
vtor<T> _v;
};
// 测试堆
void TestHeap()
{
Heap<int, Greater<int>> heap;
heap.Push(3);
heap.Push(5);
heap.Push(1);
heap.Push(4);
heap.Push(5);
heap.Push(1);
heap.Push(8);
while (!heap.Empty())
{
cout<<heap.Top()<<" ";
heap.Pop();
}
cout<<endl;
//int array[10] = {9,1,3,5,6,7,8,0,2,4};
int array[10] = {10,16,18,12,11,13,15,17,14,19};
Heap<int> heap1(array, 10);
while (!heap1.Empty())
{
cout<<heap1.Top()<<" ";
heap1.Pop();
}
cout<<endl;
}堆的应用:
- 优先级队列。
- 100w个数中找出最大的前K个数(建小堆)。
- 堆排序。






















 23万+
23万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








