问题描述
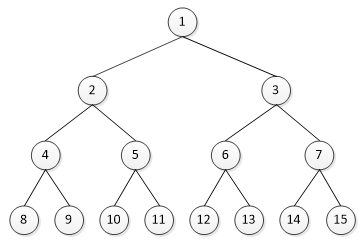
对于普通的二叉树,求指定两节点的最短距离。两节点间的最短距离即指连接两节点需要的边的最小数量,对于下图:
有如下结果:
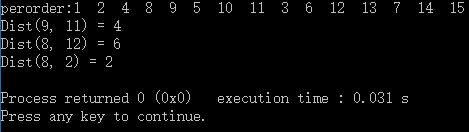
Dist(9, 11) = 4
Dist(8, 12) = 6
Dist(8, 2) = 2分析与实现
两节点之间node1与node2主要存在两种关系,即:
1)node1为node2的祖先节点(或反过来),此时node1与node2在同一条直线上;
2)node1与node2不在同一直线上,但是存在共同的祖先节点。比如上图中节点8与节点3的共同祖先节点为节点1。
根据上面的分析,如果能够找到最低的共同祖先节点(LCA),再根据各自相对该祖先节点的深度,即可求出两节点间的最短距离。假如对于节点n1与节点n2,其LCA为lca,则有如下公式:
Dist(n1, n2) = Depth(lca, n1) + Depth(lca, n2) C++ 实现代码如下,这里假定给定节点未超出范围,并且使用key值指定节点。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef struct Node
{
Node *left;
Node *right;
int key;
} Node, *pNode;
class BinaryTree
{
public:
Node *root;
public:
// 求节点1和2的最短距离
int Dist(int, int);
// 找到最小的共同节点
Node *findLCA(pNode node, int key1, int key2);
// 求节点1相对于节点2的深度
int FindDepth(pNode, int);
// 打印(先序遍历打印)
void Print();
// 先序遍历
void PreOrder(pNode);
// 创建模拟的完全二叉树
static BinaryTree *CreatSimulationTree(const int SIZE);
};
int BinaryTree::Dist(int key1, int key2)
{
pNode node = this->findLCA(this->root, key1, key2);
int d1 = FindDepth(node, key1);
int d2 = FindDepth(node, key2);
return d1 + d2;
}
Node *BinaryTree::findLCA(pNode lcaRoot, int key1, int key2)
{
if (!lcaRoot)
{
return NULL;
}
// 找到其中一个节点即返回
if (lcaRoot->key == key1 || lcaRoot->key == key2)
{
return lcaRoot;
}
// 分别在左子树与右子树种查找
pNode left_lca = findLCA(lcaRoot->left, key1, key2);
pNode right_lca = findLCA(lcaRoot->right, key1, key2);
// 如果左右分别有值,则说明两个节点分别在左子树与右子树中,那么此节点即为LAC节点
if (left_lca && right_lca)
{
return lcaRoot;
}
// 如果只找到其中一个节点,则另一个节点必然在其子节点内(不讨论节点不存在的情况)
return left_lca ? left_lca : right_lca;
}
int BinaryTree::FindDepth(pNode lcaRoot, int key)
{
int depth = 0;
if (!lcaRoot)
{
return -1;
}
if (lcaRoot->key == key) {
return 0;
}
// 在左子树中查找
depth = FindDepth(lcaRoot->left, key);
// 左子树中没有则在右子树中查找
if (depth == -1)
{
depth = FindDepth(lcaRoot->right, key);
}
// 如果depth1=-1,则说明在root节点下找到了节点键为key的节点
if (depth != -1)
{
return depth += 1;
}
return -1;
}
void BinaryTree::Print()
{
cout << "perorder:";
this->PreOrder(this->root);
cout << endl;
}
void BinaryTree::PreOrder(pNode node)
{
if (node != NULL)
{
cout << node->key << " ";
PreOrder(node->left);
PreOrder(node->right);
}
}
BinaryTree *BinaryTree::CreatSimulationTree(const int SIZE)
{
BinaryTree *bt = new BinaryTree;
pNode nodeArr[SIZE];
for (int n = 0; n < SIZE; n ++)
{
nodeArr[n] = new Node;
nodeArr[n]->key = n + 1;
}
// 循环设置各节点之间的关系
for (int n = 0; n < SIZE; n ++) {
int leftKey = 2 * n + 1;
int rightKey = 2 * n + 2;
if (leftKey < SIZE)
{
nodeArr[n]->left = nodeArr[leftKey];
} else {
nodeArr[n]->left = NULL;
}
if (rightKey < SIZE)
{
nodeArr[n]->right = nodeArr[rightKey];
} else {
nodeArr[n]->right = NULL;
}
}
bt->root = nodeArr[0];
return bt;
}
int main()
{
BinaryTree *bt = BinaryTree::CreatSimulationTree(15);
bt->Print();
cout << "Dist(9, 11) = " << bt->Dist(9, 11) << endl;
cout << "Dist(8, 12) = " << bt->Dist(8, 12) << endl;
cout << "Dist(8, 2) = " << bt->Dist(8, 2) << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果如下(请忽略最后两行代码):
在上面的代码中,最重要的两个方法为findLCA(pNode, int, int)与FindDepth(pNode, int)。其中使用先序遍历的方法打印二叉树是为了方便测试生成的二叉树是否正确,可以去掉。BinaryTree::CreatSimulationTree(int)是为了生成模拟的二叉树,这里是生成的完全二叉树,但实际中此算法对于非完全二叉树也同样适用。






















 3683
3683

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








