以下出自http://www.open-open.com/lib/view/open1328837587484.html
LayoutInflater作用是将layout的xml布局文件实例化为View类对象。
获取LayoutInflater的方法有如下三种:
LayoutInflater inflater=(LayoutInflater)context.getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
View layout = inflater.inflate(R.layout.main,
null
);
LayoutInflater inflater = LayoutInflater.from(context); (该方法实质就是第一种方法,可参考源代码)
View layout = inflater.inflate(R.layout.main,
null
);
LayoutInflater inflater = getLayoutInflater();(在Activity中可以使用,实际上是View子类下window的一个函数)
View layout = inflater.inflate(R.layout.main,
null
);
getLayoutInflater():
Activity的getLayoutInflater()方法是调用PhoneWindow的getLayoutInflater()方法,看一下该源代码:
publicPhoneWindow(Contextcontext) {
super(context);
mLayoutInflater= LayoutInflater.from(context);
}
可以看出它其实是调用LayoutInflater.from(context)。
LayoutInflater.from(context):
public static LayoutInflaterfrom(Context context) {
LayoutInflaterLayoutInflater = (LayoutInflater)context.getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
if(LayoutInflater== null){
thrownew AssertionError("LayoutInflaternot found.");
}
returnLayoutInflater;
}
可以看出它其实调用context.getSystemService()。
|
一直有点纠结setContentView和inflate的区别找了一些资料。写了个小程序看了下:
public
class
MyInflate
extends
Activity{
private
TextView tv;
public
void
OnCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState){
super
.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
//setContentView(R.layout.main);
//tv = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv);
LayoutInflater inflate = LayoutInflater.from(
this
);
View view = inflate.inflate(R.layout.main,
null
);
setContentView(view);
}
}
|
上述注释掉的代码和没有注释掉的代码两种情况是相同的。
区别:
setContentView()一旦调用, layout就会立刻显示UI;而inflate只会把Layout形成一个以view类实现成的对象,有需要时再用setContentView(view)显示出来。一般在activity中通过setContentView()将界面显示出来,但是如果在非activity中如何对控件布局设置操作了,这就需要LayoutInflater动态加载。
public View inflate(int Resourece,ViewGroup root)
作用:填充一个新的视图层次结构从指定的XML资源文件中
reSource:View的layout的ID
root: 生成的层次结构的根视图
return 填充的层次结构的根视图。如果参数root提供了,那么root就是根视图;否则填充的XML文件的根就是根视图。
其余几个重载的inflate函数类似。
在实际开发种LayoutInflater这个类的作用类似于 findViewById(),
不同点是LayoutInflater是用来找layout下xml布局文件,并且实例化!而findViewById()是找具体xml下的具体 widget控件(如:Button,TextView等)。
为了让大家容易理解我做了一个简单的Demo,主布局main.xml里有一个TextView和一个Button,当点击Button,出现 Dialog,而这个Dialog的布局方式是我们在layout目录下定义的custom_dialog.xml文件(里面左右分布,左边 ImageView,右边TextView)。
效果图如下:
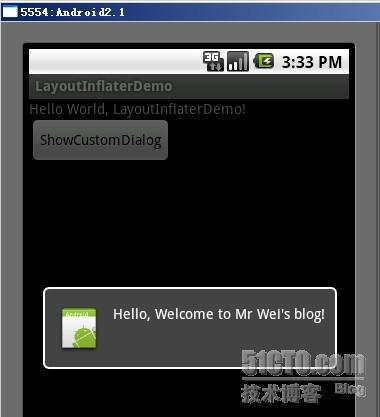
下面我将详细的说明Demo的实现过程:
1、新建一个 Android工程,我们命名为LayoutInflaterDemo.
2、修改main.xml布局,里面主要在原来基础上增加了一个Button.代码如下:
- view plaincopy to clipboardprint?
- <?xml version="1.0"
- encoding="utf-8"?>
- <LinearLayout
- xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- android:orientation="vertical"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="fill_parent"
- >
- <TextView
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:text="@string/hello"
- />
- <Button
- android:id="@+id/button"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:text="ShowCustomDialog"
- />
- </LinearLayout>
- <?xml version="1.0"
- encoding="utf-8"?>
- <LinearLayout
- xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- android:orientation="vertical"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="fill_parent"
- >
- <TextView
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:text="@string/hello"
- />
- <Button
- android:id="@+id/button"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:text="ShowCustomDialog"
- />
- </LinearLayout>
3.定义对话框的布局方式,我们在layout目录下,新建一个名为 custom_dialog.xml文件具体代码如下:
- view plaincopy to clipboardprint?
- <?xml version="1.0"
- encoding="utf-8"?>
- <LinearLayout
- xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- android:orientation="horizontal"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="fill_parent"
- android:padding="10dp"
- >
- <ImageView android:id="@+id/image"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="fill_parent"
- android:layout_marginRight="10dp"
- />
- <TextView android:id="@+id/text"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="fill_parent"
- android:textColor="#FFF"
- />
- </LinearLayout>
- <?xml version="1.0"
- encoding="utf-8"?>
- <LinearLayout
- xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- android:orientation="horizontal"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="fill_parent"
- android:padding="10dp"
- >
- <ImageView android:id="@+id/image"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="fill_parent"
- android:layout_marginRight="10dp"
- />
- <TextView android:id="@+id/text"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="fill_parent"
- android:textColor="#FFF"
- />
- </LinearLayout>
4.修改主程序LayouInflaterDemo.java代码如下:
- view plaincopy to clipboardprint?
- package com.android.tutor;
- import android.app.Activity;
- import android.app.AlertDialog;
- import android.content.Context;
- import android.os.Bundle;
- import android.view.LayoutInflater;
- import android.view.View;
- import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
- import android.widget.Button;
- import android.widget.ImageView;
- import android.widget.TextView;
- public class LayoutInflaterDemo extends Activity implements
- OnClickListener {
- private Button button;
- public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- setContentView(R.layout.main);
- button = (Button)findViewById(R.id.button);
- button.setOnClickListener(this);
- }
- @Override
- public void onClick(View v) {
- showCustomDialog();
- }
- public void showCustomDialog()
- {
- AlertDialog.Builder builder;
- AlertDialog alertDialog;
- Context mContext = LayoutInflaterDemo.this;
- //下面俩种方法都可以
- LayoutInflater inflater = getLayoutInflater();
- LayoutInflater inflater = (LayoutInflater)
- mContext.getSystemService(LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
- View layout = inflater.inflate(R.layout.custom_dialog,null);
- TextView text = (TextView) layout.findViewById(R.id.text);
- text.setText("Hello, Welcome to Mr Wei's blog!");
- ImageView image = (ImageView) layout.findViewById(R.id.image);
- image.setImageResource(R.drawable.icon);
- builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(mContext);
- builder.setView(layout);
- alertDialog = builder.create();
- alertDialog.show();
- }
- }
- package com.android.tutor;
- import android.app.Activity;
- import android.app.AlertDialog;
- import android.content.Context;
- import android.os.Bundle;
- import android.view.LayoutInflater;
- import android.view.View;
- import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
- import android.widget.Button;
- import android.widget.ImageView;
- import android.widget.TextView;
- public class LayoutInflaterDemo extends Activity implements
- OnClickListener {
- private Button button;
- public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- setContentView(R.layout.main);
- button = (Button)findViewById(R.id.button);
- button.setOnClickListener(this);
- }
- @Override
- public void onClick(View v) {
- showCustomDialog();
- }
- public void showCustomDialog()
- {
- AlertDialog.Builder builder;
- AlertDialog alertDialog;
- Context mContext = LayoutInflaterDemo.this;
- //下面俩种方法都可以
- LayoutInflater inflater = getLayoutInflater();
- LayoutInflater inflater = (LayoutInflater)
- mContext.getSystemService(LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
- View layout = inflater.inflate(R.layout.custom_dialog,null);
- TextView text = (TextView) layout.findViewById(R.id.text);
- text.setText("Hello, Welcome to Mr Wei's blog!");
- ImageView image = (ImageView) layout.findViewById(R.id.image);
- image.setImageResource(R.drawable.icon);
- builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(mContext);
- builder.setView(layout);
- alertDialog = builder.create();
- alertDialog.show();
- }
- }
另外getSystemService()是Android很重要的一个API,它是Activity的一个方法,根据传入的NAME来取得对应的Object,然后转换成相应的服务对象。以下介绍系统相应的服务。
传入的Name
返回的对象
说明
WINDOW_SERVICE
WindowManager
管理打开的窗口程序
LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE
LayoutInflater
取得xml里定义的view
ACTIVITY_SERVICE
ActivityManager
管理应用程序的系统状态
POWER_SERVICE
PowerManger
电源的服务
ALARM_SERVICE
AlarmManager
闹钟的服务
NOTIFICATION_SERVICE
NotificationManager
状态栏的服务
KEYGUARD_SERVICE
KeyguardManager
键盘锁的服务
LOCATION_SERVICE
LocationManager
位置的服务,如GPS
SEARCH_SERVICE
SearchManager
搜索的服务
VEBRATOR_SERVICE
Vebrator
手机震动的服务
CONNECTIVITY_SERVICE
Connectivity
网络连接的服务
WIFI_SERVICE
WifiManager
Wi-Fi服务
TELEPHONY_SERVICE
TeleponyManager
电话服务
inflate 方法
通过 sdk 的 api 文档,可以知道该方法有以下几种过载形式,返回值均是 View 对象,如下:
public View inflate (int resource, ViewGroup root)
public View inflate (XmlPullParser parser, ViewGroup root)
public View inflate (XmlPullParser parser, ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot)
public View inflate (int resource, ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot)
示意代码:
LayoutInflater inflater = (LayoutInflater)getSystemService(LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.custom, (ViewGroup)findViewById(R.id.test));
//EditText editText = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.content);// error
EditText editText = (EditText)view.findViewById(R.id.content);
对于上面代码,指定了第二个参数 ViewGroup root,当然你也可以设置为 null 值。
注意:
·inflate 方法与 findViewById 方法不同;
·inflater 是用来找 res/layout 下的 xml 布局文件,并且实例化;
·findViewById() 是找具体 xml 布局文件中的具体 widget 控件(如:Button、TextView 等)。





















 857
857

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








