1.File类的理解
1.File类的一个对象,代表一个文件或一个文件目录(俗称:文件夹)
2.File类声明在Java.io包下
3.File类中涉及到关于文件或文件目录的创建、删除、重命名、修改时间、文件大小等方法,
并未涉及到写入和读取文件内容的操作,如果需要读取或写入文件内容,必须使用IO流完成。
4.后续File类的对象常会作为参数传递到流的构造器中,指明读取或写入的节点。
2.File的实例化
2.1 常用构造器
File(string filePath)
File(string parentPath, string chiLdPath)
File(File parentFile,String childPath)
2.2路径的分类
相对路径:相较于某个路径下指明的路径。
绝对路径:包含盘符在内的文件或文件目录的路径。
2.3路径分隔符
Windows:
unix:/
3.常用方法
public String getAbsolutePath():获取绝对路径
public string getPath():获取路径
public string getName() :获取名称
public string getParent():获取上层文件目录路径。若无,返回null
public long length() :获取文件长度(即:字节数)。不能获取目录的长度。
public longlastModified():获取最后一次的修改时间,毫秒值 如下的两个方法适用于文件目录
public string[]list():获取指定目录下的所有文件或者文件目录的名称数组
public File[]listFiles():获取指定目录下的所有文件或者文件目录的FiLle数组 File类的重命名功能
public boolean renameTo(File dest):把文件重命名为指定的文件路径
public booLean isDirectory():判断是否是文件目录
public booLean isFile() :判断是否是文件
public booLean exists() :判断是否存在
public booLean canRead() :判断是否可读
public booLean canwrite() :判断是否可写
public booLean isHidden() :判断是否隐藏
创建硬盘中对应的文件或文件目录
public boolean createNewFile():创建文件。若文件存在,则不创建,返回false
public boolean mkdir() :创建文件目录。如果此文件目录存在,就不创建了。如果此文件目录的上层目录不存在,也不创建。
public boolean mkdirs():创建文件目录。如果上层文件目录不存在,一并创建
注意事项:如果你创建文件或者文件目录没有写盘符路径,那么,默认在项目路径下。
删除硬盘中的文件或文件目录
public boolean delete():删除文件或文件夹 注意:删除不走回收站
@Test
public void test1() {
File file = new File("hello.txt");
System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath());
System.out.println(file.getPath());
System.out.println(file.getName());
System.out.println(file.getParent());
System.out.println(file.length());
System.out.println(new Date(file.lastModified()));
String[] list = file.list();
System.out.println(list);
File[] listFiles = file.listFiles();
System.out.println(listFiles);
File file1 = new File("hello.txt");
File file2 = new File("D:\\Thunder\\hi.txt");
boolean renameTo = file2.renameTo(file1);
System.out.println(renameTo);
System.out.println(file1.isDirectory());
System.out.println(file1.isFile());
System.out.println(file1.exists());
System.out.println(file1.canRead());
System.out.println(file1.canWrite());
System.out.println(file1.isHidden());
System.out.println("-------------");
System.out.println(file2.isDirectory());
System.out.println(file2.isFile());
System.out.println(file2.exists());
System.out.println(file2.canRead());
System.out.println(file2.canWrite());
System.out.println(file2.isHidden());
}
@Test
public void test2() throws IOException {
// 文件的创建与删除
File file1 = new File("hi.txt");
if (!file1.exists()) {
file1.createNewFile();
System.out.println("创建成功");
} else {
// 文件存在
file1.delete();
System.out.println("删除成功");
}
}
@Test
public void test3() throws IOException {
// 文件目录的创建
File file1 = new File("D:\\Thunder\\Brook\\Brook3");
boolean mkdir = file1.mkdir();
if (mkdir) {
System.out.println("创建成功1");
}
File file2 = new File("D:\\Thunder\\Brook\\Brook4");
boolean mkdirs = file2.mkdirs();
if (mkdirs) {
System.out.println("创建成功2");
}
}
4.Java IO原理
I/O是Input/Output的缩写,I/O技术是非常实用的技术,用于处理设备之间的数据传输。如读/写文件,网络通讯等。
Java程序中,对于数据的输入/输出操作以“流(stream)”的方式进行。
java.io包下提供了各种“流”类和接口,用以获取不同种类的数据,并通过标准的方法输入或输出数据。
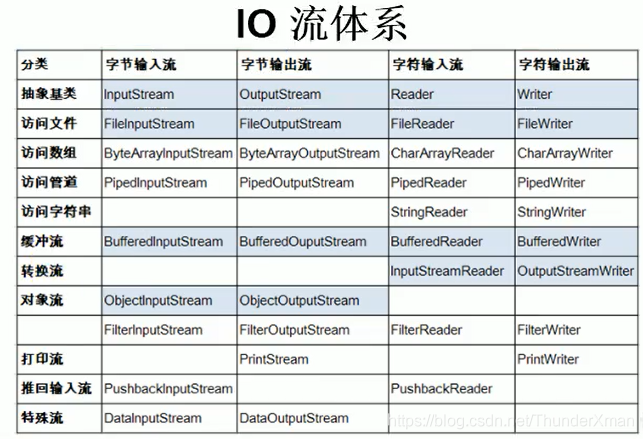
5.流的分类
JavaIO流共涉及40多个类,实际上非常规则,都是从如下四个抽象基类派生的
由这四个类派生出来的子类名称都是以其父类名作为子类名后缀.

按操作数据单位不同分为:字节流(8 bit),字符流(16bit)
按数据流向不同分为:输入流,输出流
按流的角色的不同分为:节点流,处理流
6.使用缓冲流复制a.jpg为b.jpg
@Test
public void copyBuffered() {
BufferedInputStream bis = null;
BufferedOutputStream bos = null;
try{
//1.造文件,造流
bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(new File("a.jpg")));
bos = new BufferedOutputStream (new FileOutputStream(new File("b.jpg")));
//2.读入写出文件
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = bis.read(buffer)) != -1){
bos.write(buffer,0,len);
}
}catch(FileNotFoundException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
//3.关闭流
if(bis != null){
try{
bis.close();
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(bos != null){
try{
bos.close();
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
7.转换流使用的是那两个类,分别的作用是什么,请分别创建两个类的对象.
/*
转换流 InputStreamReader : 将输入的字节流转换为输入的字符流 解码
OutputStreamWriter: 将输出的字符流转换为输出的字节流 编码
*/
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("a.txt","GBK"));
//构造参数的参数一为 文本文件,参数2为文本文件编写时所用的编码格式
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("a.txt","uft-8"));
/*
* 综合使用InputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter
*
*/
@Test
public void test2() {
InputStreamReader isr = null;
OutputStreamWriter osw = null;
try {
File file1 = new File("dbcp.txt");
File file2 = new File("dbcp_GBK.txt");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file1);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file2);
isr = new InputStreamReader(fis,"utf-8");
osw = new OutputStreamWriter(fos,"gbk");
//读写过程
char[] cbuf = new char[20];
int len;
while ((len = isr.read(cbuf)) != -1) {
osw.write(cbuf, 0, len);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if (isr != null) {
try {
isr.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if ( osw != null) {
try {
osw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}























 16万+
16万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








