很多场景下我们需要根据已有的数据库表,生成对应的java bean,而且还希望生成的java类格式正确、命名规范。
使用idea可以轻松的完成这个功能。
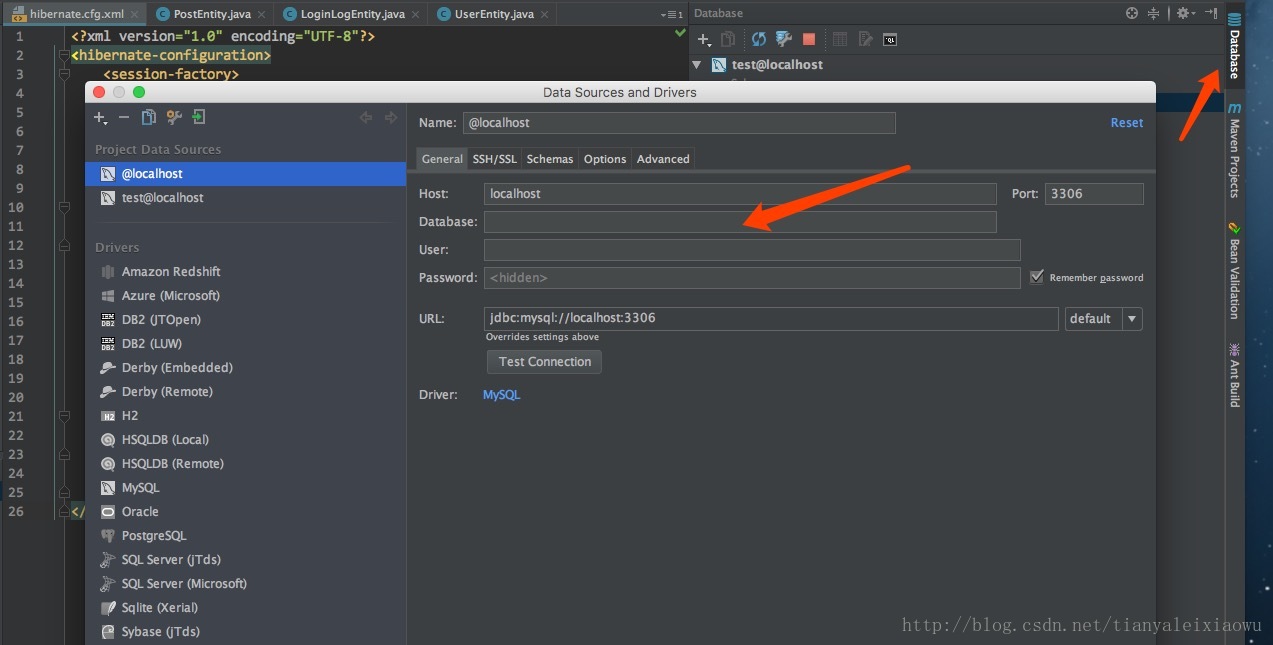
举例,我新建一个springboot项目,勾选mysql、jpa即可,在idea找到Database界面,新建Data source——MySQL,填写数据连接信息后即可。
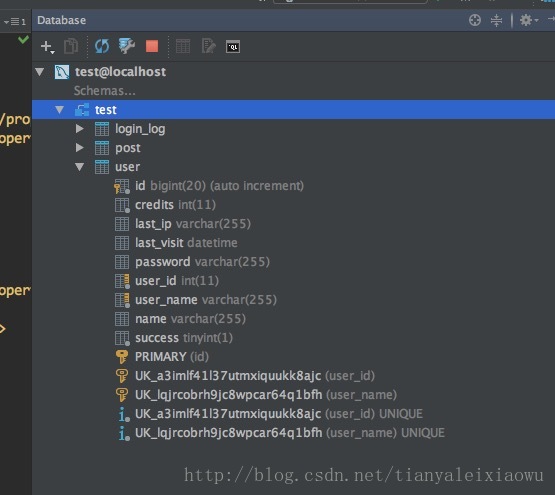
此时就可以生成简单的pojo类了,注意,此时还没有使用hibernate呢,就是idea的这个Database功能就可以生成pojo类了,只不过无格式。在界面上数据库名右键,出来下面的界面。
点Generate POJOs.clj即可
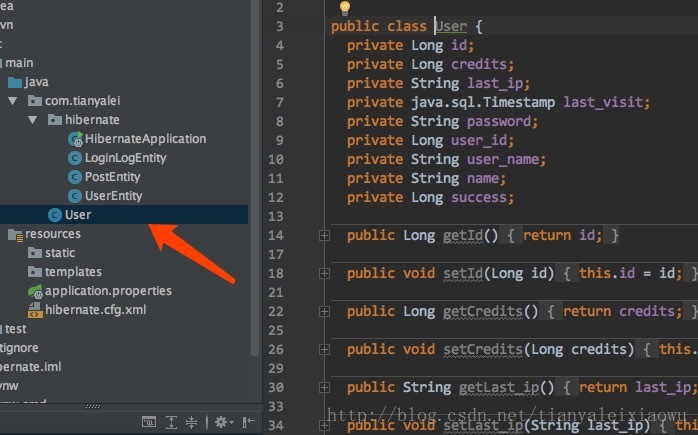
可以看到生成类很粗糙,就是把列名复制,完全照搬,我们希望的更格式化的pojo类,所以我们要使用hibernate来反向生成。
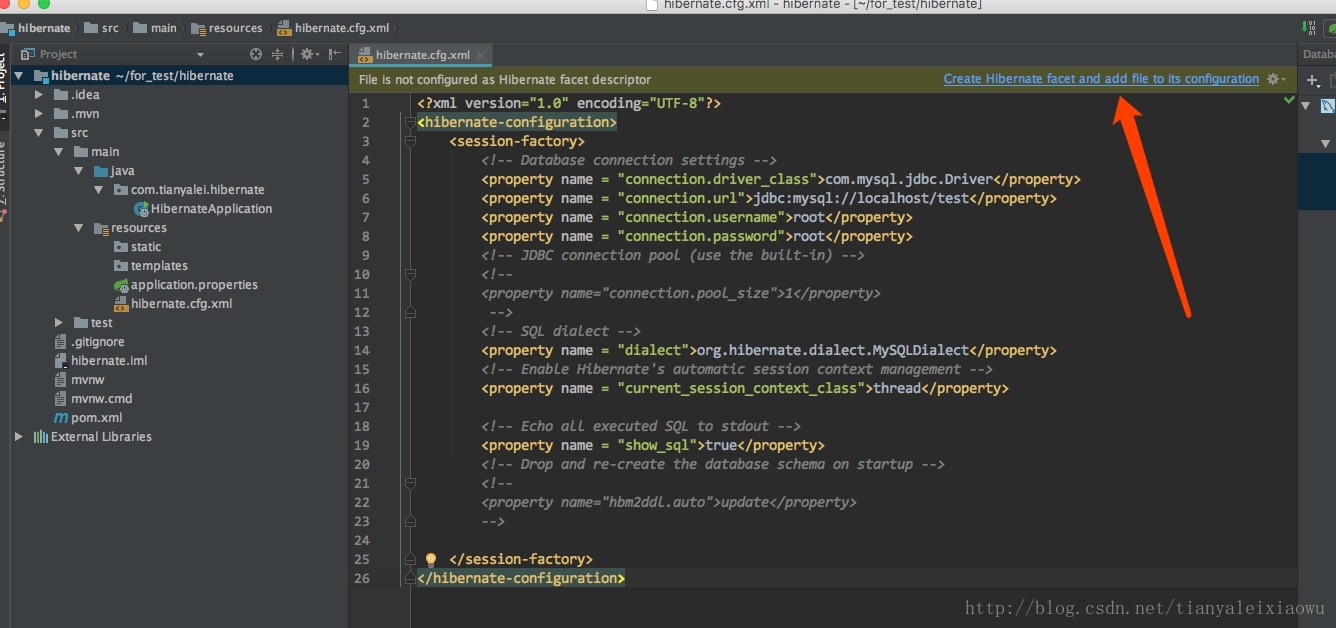
在resource文件夹下创建hibernate.cfg.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<!-- Database connection settings -->
<property name = "connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name = "connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost/test</property>
<property name = "connection.username">root</property>
<property name = "connection.password">root</property>
<!-- JDBC connection pool (use the built-in) -->
<!--
<property name="connection.pool_size">1</property>
-->
<!-- SQL dialect -->
<property name = "dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property>
<!-- Enable Hibernate's automatic session context management -->
<property name = "current_session_context_class">thread</property>
<!-- Echo all executed SQL to stdout -->
<property name = "show_sql">true</property>
<!-- Drop and re-create the database schema on startup -->
<!--
<property name="hbm2ddl.auto">update</property>
-->
</session-factory>
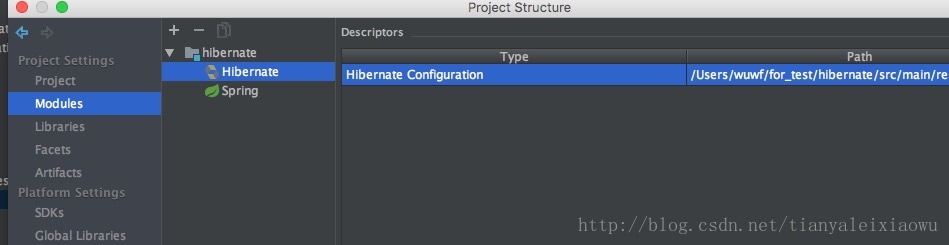
</hibernate-configuration>我们点击箭头处,或者在project structure里如下图,添加hibernate configuration
只有配置了hibernate,才能使用hibernate的反向生成功能。
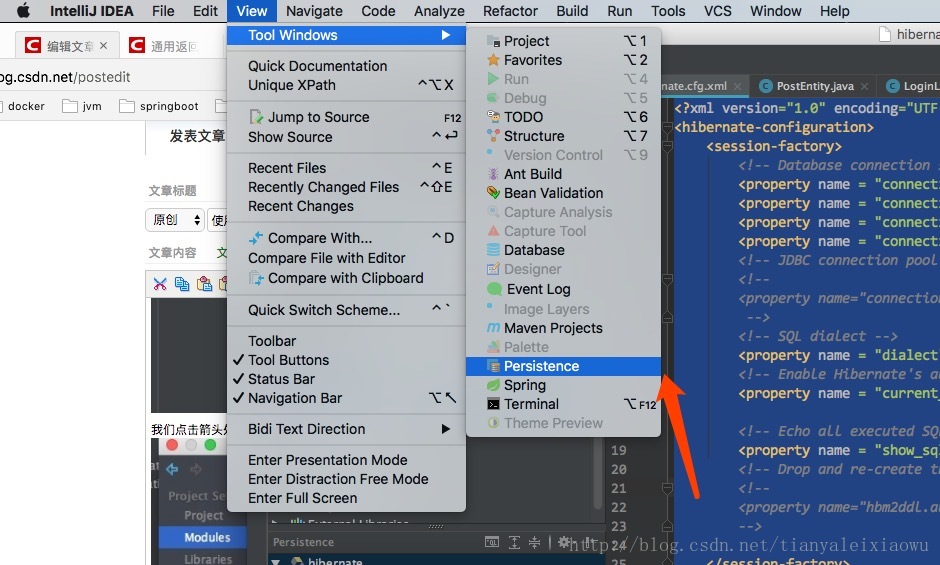
然后点击View-Tool Windows-Persistence,注意,如果没有配置hibernate的话,是没有Persistence这个选项的。
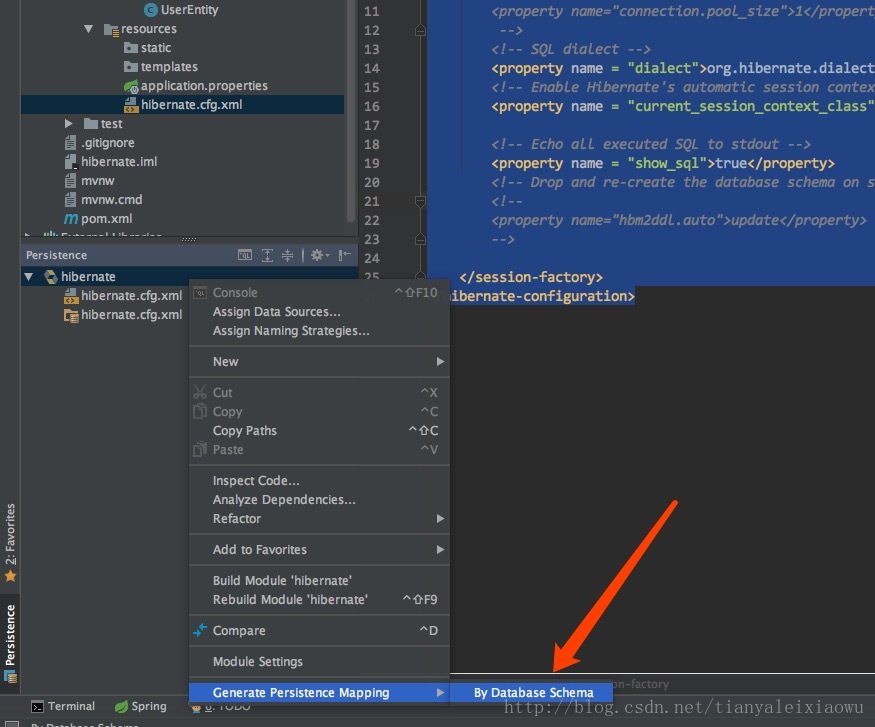
然后如下图操作,右键点击后会弹出下图界面。
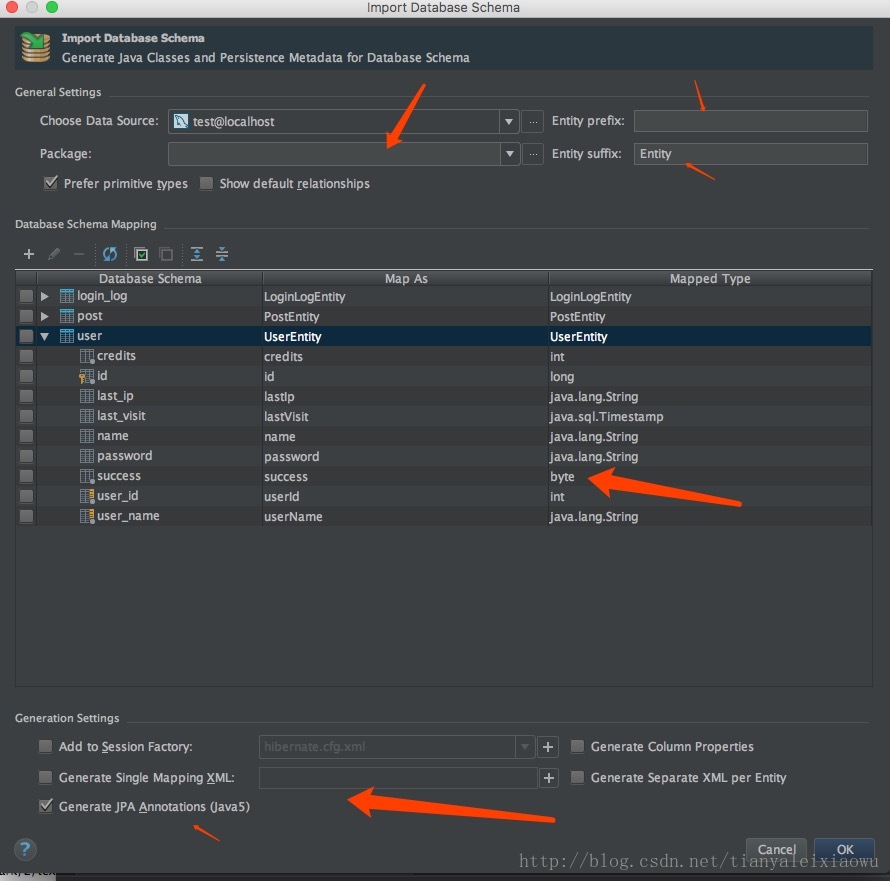
然后就可以设置要生成的类所在的包名,前缀、后缀,还可以修改pojo类的类型,譬如success字段可以修改为boolean,最下面勾选JPA注解。点击OK就行了。
package com.tianyalei.hibernate;
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.sql.Timestamp;
/**
* Created by wuweifeng on 2017/10/11.
*/
@Entity
@Table(name = "user", schema = "test", catalog = "")
public class UserEntity {
private long id;
private int credits;
private String lastIp;
private Timestamp lastVisit;
private String password;
private int userId;
private String userName;
private String name;
private boolean success;
@Id
@Column(name = "id")
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(long id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Basic
@Column(name = "credits")
public int getCredits() {
return credits;
}
public void setCredits(int credits) {
this.credits = credits;
}
@Basic
@Column(name = "last_ip")
public String getLastIp() {
return lastIp;
}
public void setLastIp(String lastIp) {
this.lastIp = lastIp;
}
@Basic
@Column(name = "last_visit")
public Timestamp getLastVisit() {
return lastVisit;
}
public void setLastVisit(Timestamp lastVisit) {
this.lastVisit = lastVisit;
}
@Basic
@Column(name = "password")
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@Basic
@Column(name = "user_id")
public int getUserId() {
return userId;
}
public void setUserId(int userId) {
this.userId = userId;
}
@Basic
@Column(name = "user_name")
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
@Basic
@Column(name = "name")
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Basic
@Column(name = "success")
public boolean isSuccess() {
return success;
}
public void setSuccess(boolean success) {
this.success = success;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
UserEntity that = (UserEntity) o;
if (id != that.id) return false;
if (credits != that.credits) return false;
if (userId != that.userId) return false;
if (success != that.success) return false;
if (lastIp != null ? !lastIp.equals(that.lastIp) : that.lastIp != null) return false;
if (lastVisit != null ? !lastVisit.equals(that.lastVisit) : that.lastVisit != null) return false;
if (password != null ? !password.equals(that.password) : that.password != null) return false;
if (userName != null ? !userName.equals(that.userName) : that.userName != null) return false;
if (name != null ? !name.equals(that.name) : that.name != null) return false;
return true;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
int result = (int) (id ^ (id >>> 32));
result = 31 * result + credits;
result = 31 * result + (lastIp != null ? lastIp.hashCode() : 0);
result = 31 * result + (lastVisit != null ? lastVisit.hashCode() : 0);
result = 31 * result + (password != null ? password.hashCode() : 0);
result = 31 * result + userId;
result = 31 * result + (userName != null ? userName.hashCode() : 0);
result = 31 * result + (name != null ? name.hashCode() : 0);
result = 31 * result + (success ? 1 : 0);
return result;
}
}
可以看到这个就是生成的类,注解很完整,驼峰式命名,有特殊情况的话只需稍微修改就可以直接来用了。譬如把索引注解也加上去。




























 1078
1078

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










