1.为什么要使用memcache
MemCache是一个自由、源码开放、高性能、分布式的分布式内存对象缓存系统,用于动态Web应用以减轻数据库的负载。 MemCaChe是一个存储键值对的HashMap,在内存中对任意的数据(比如字符串、对象等)所使用的key-value存储。 通常把数据库查询的结果保存到Memcache中,下次访问时直接从memcache中读取。 保存在memcache中的对象实际放置在 内存 中,这也是memcache如此高效的原因。

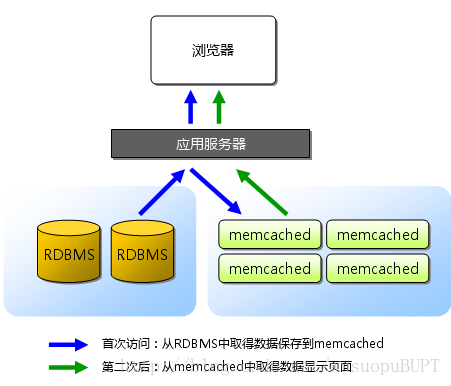
MemCache虽然被称为”分布式缓存”,但是MemCache本身完全不具备分布式的功能,MemCache集群之间不会相互通信(与之形成对比的,比如JBoss Cache,某台服务器有缓存数据更新时,会通知集群中其他机器更新缓存或清除缓存数据),所谓的”分布式”,完全依赖于客户端程序的实现,就像上面这张图的流程一样。
2.基于libevent的事件处理
libevent是个程序库,它将Linux的 epoll、BSD类操作系统的kqueue等事件处理功能 封装成统一的接口。即使对服务器的连接数增加,也能发挥O(1)的性能。memcached使用这个libevent库,因此能在 Linux、BSD、Solaris等 操作系统上发挥其高性能。
3.memcache如何支持高并发
memcache使用多路复用I/O模型,如(epoll, select等),传统I/O中,系统可能会因为某个用户连接还没做好I/O准备而一直等待,知道这个连接做好I/O准备。这时如果有其他用户连接到服务器,很可能会因为系统阻塞而得不到响应。而多路复用I/O是一种消息通知模式,用户连接做好I/O准备后,系统会通知我们这个连接可以进行I/O操作,这样就不会阻塞在某个用户连接。因此,memcache才能支持高并发。memcache使用了多线程机制。可以同时处理多个请求。
4、MemCache实现原理

这张图片里面涉及了slab_class、slab、page、chunk四个概念,它们之间的关系是:
1、MemCache将内存空间分为一组slab
2、每个slab下又有若干个page,每个page默认是1M,如果一个slab占用100M内存的话,那么这个slab下应该有100个page
3、每个page里面包含一组chunk,chunk是真正存放数据的地方,同一个slab里面的chunk的大小是固定的
4、有相同大小chunk的slab被组织在一起,称为slab_class
MemCache内存分配的方式称为allocator,slab的数量是有限的,几个、十几个或者几十个,这个和启动参数的配置相关。
MemCache中的value过来存放的地方是由value的大小决定的,value总是会被存放到与chunk大小最接近的一个slab中,比如slab[1]的chunk大小为80字节、slab[2]的chunk大小为100字节、slab[3]的chunk大小为128字节(相邻slab内的chunk基本以1.25为比例进行增长,MemCache启动时可以用-f指定这个比例),那么过来一个88字节的value,这个value将被放到2号slab中。放slab的时候,首先slab要申请内存,申请内存是以page为单位的,所以在放入第一个数据的时候,无论大小为多少,都会有1M大小的page被分配给该slab。申请到page后,slab会将这个page的内存按chunk的大小进行切分,这样就变成了一个chunk数组,最后从这个chunk数组中选择一个用于存储数据。
如果这个slab中没有chunk可以分配了怎么办,如果MemCache启动没有追加-M(禁止LRU,这种情况下内存不够会报Out Of Memory错误),那么MemCache会把这个slab中最近最少使用的chunk中的数据清理掉,然后放上最新的数据。针对MemCache的内存分配及回收算法,总结三点:
1、MemCache的内存分配chunk里面会有内存浪费,88字节的value分配在128字节(紧接着大的用)的chunk中,就损失了30字节,但是这也避免了管理内存碎片的问题
2、MemCache的LRU算法不是针对全局的,是针对slab的
3、应该可以理解为什么MemCache存放的value大小是限制的,因为一个新数据过来,slab会先以page为单位申请一块内存,申请的内存最多就只有1M,所以value大小自然不能大于1M了
再总结MemCache的特性和限制
上面已经对于MemCache做了一个比较详细的解读,这里再次总结MemCache的限制和特性:
1、MemCache中可以保存的item数据量是没有限制的,只要内存足够
2、MemCache单进程在32位机中最大使用内存为2G,这个之前的文章提了多次了,64位机则没有限制
3、Key最大为250个字节,超过该长度无法存储
4、单个item最大数据是1MB,超过1MB的数据不予存储
5、MemCache服务端是不安全的,比如已知某个MemCache节点,可以直接telnet过去,并通过flush_all让已经存在的键值对立即失效
6、不能够遍历MemCache中所有的item,因为这个操作的速度相对缓慢且会阻塞其他的操作
7、MemCache的高性能源自于两阶段哈希结构:第一阶段在客户端,通过Hash算法根据Key值算出一个节点;第二阶段在服务端,通过一个内部的Hash算法,查找真正的item并返回给客户端。从实现的角度看,MemCache是一个非阻塞的、基于事件的服务器程序。
6.使用Slab分配算法保存数据
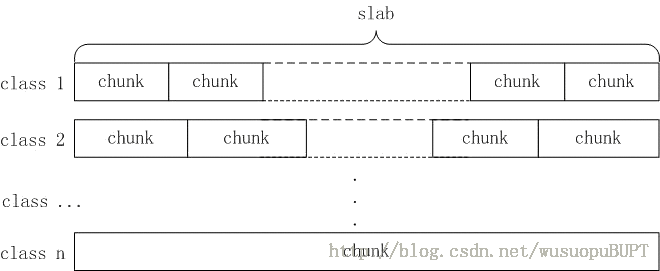
slab分配算法的原理是:把固定大小(1MB)的内存分为n小块,如下图所示:
slab分配算法把每1MB大小的内存称为一个slab页,每次向系统申请一个slab页,然后再通过分隔算法把这个slab页分割成若干个小块的chunk(如上图所示),然后把这些chunk分配给用户使用,分割算法如下(在slabs.c文件中):
(注:memcache的github项目地址:https://github.com/wusuopubupt/memcached)
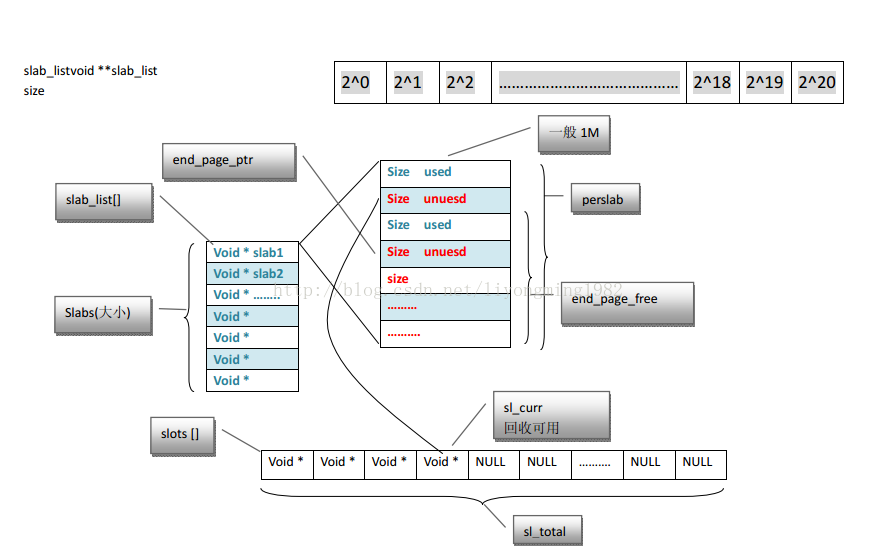
上面代码中的slabclass是一个类型为slabclass_t结构的数组,其定义如下:
借用别人的一张图说明slabclass_t结构:
由分割算法的源代码可知,slab算法按照不同大小的chunk分割slab页,而不同大小的chunk以factor(默认是1.25)倍增大。
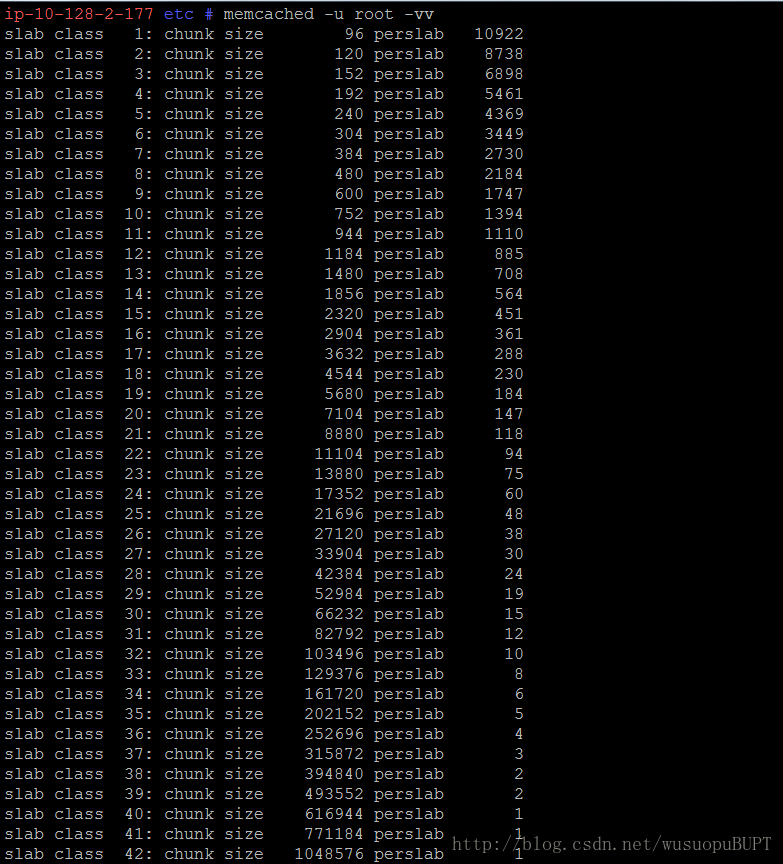
使用memcache -u root -vv 命令查看内存分配情况(8字节对齐):
找到大小最合适的chunk分配给请求缓存的数据:
内存分配:
(此处参考:http://slowsnail.com.cn/?p=20)
do_slabs_allc()函数首先尝试从slot列表(被回收的chunk)中获取可用的chunk,如果有可用的就返回,否则从空闲的chunk列表中获取可用的chunk并返回。
删除过期item:
延迟删除过期item到查找时进行,可以提高memcache的效率,因为不必每时每刻检查过期item,从而提高CPU工作效率
使用LRU(last recently used)算法淘汰数据:
从item列表的尾部开始遍历,找到refcount==0的chunk,调用do_item_unlink()函数释放掉,另外,search->time+10800<current_time(即最近3小时没有被访问过的item),也释放掉--这就是LRU算法的原理。






















 165
165

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








