二叉搜索树
概述
随着计算机算力的提升和对数据结构的深入研究,二叉搜索树也不断被优化和扩展,例如AVL树、红黑树等。
特性
二叉搜索树(也称二叉排序树)是符合下面特征的二叉树:
- 树节点增加 key 属性,用来比较谁大谁小,key 不可以重复;
- 对于任意一个树节点,它的 key 比左子树的 key 都大,同时也比右子树的 key 都小。
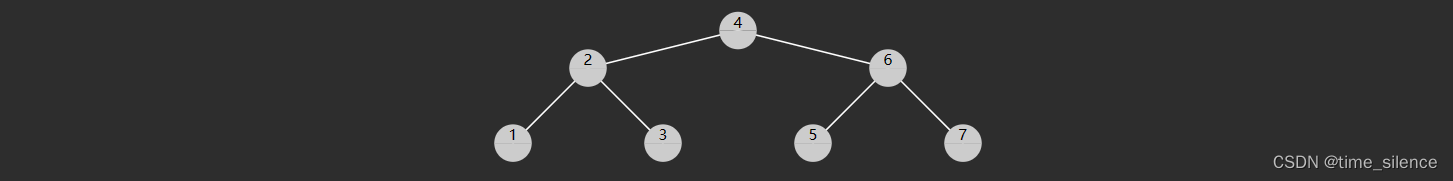
查找的时间复杂度与树高相关,插入、删除也是如此。
注:
- 二叉搜索树 - 英文 binary search tree,简称 BST
- 二叉排序树 - 英文 binary ordered tree 或 binary sorted tree
代码
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Binary Search Tree 二叉搜索树
*/
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class BSTTree1 {
BSTNode root; // 根节点
static class BSTNode {
int key;
Object value;
BSTNode left;
BSTNode right;
public BSTNode(int key) {
this.key = key;
}
public BSTNode(int key, Object value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
public BSTNode(int key, Object value, BSTNode left, BSTNode right) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
/**
* <h3>查找关键字对应的值</h3>
*
* @param key 关键字
* @return 关键字对应的值
*/
public Object get(int key) {
BSTNode node = root;
while (node != null) {
if (key < node.key) {
node = node.left;
} else if (node.key < key) {
node = node.right;
} else {
return node.value;
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* <h3>查找最小关键字对应值</h3>
*
* @return 关键字对应的值
*/
public Object min() {
return min(root);
}
private Object min(BSTNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
BSTNode p = node;
while (p.left != null) {
p = p.left;
}
return p.value;
}
/**
* <h3>查找最大关键字对应值</h3>
*
* @return 关键字对应的值
*/
public Object max() {
return max(root);
}
private Object max(BSTNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
BSTNode p = node;
while (p.right != null) {
p = p.right;
}
return p.value;
}
/**
* <h3>存储关键字和对应值</h3>
*
* @param key 关键字
* @param value 值
*/
public void put(int key, Object value) {
root = doPut(root, key, value);
}
private BSTNode doPut(BSTNode node, int key, Object value) {
if (node == null) {
return new BSTNode(key, value);
}
if (key < node.key) {
node.left = doPut(node.left, key, value);
} else if (node.key < key) {
node.right = doPut(node.right, key, value);
} else {
node.value = value;
}
return node;
}
/**
* <h3>查找关键字的前任值</h3>
*
* @param key 关键字
* @return 前任值
*/
public Object predecessor(int key) {
BSTNode p = root;
BSTNode ancestorFromLeft = null;
while (p != null) {
if (key < p.key) {
p = p.left;
} else if (p.key < key) {
ancestorFromLeft = p;
p = p.right;
} else {
break;
}
}
// 没找到节点
if (p == null) {
return null;
}
// 找到节点 情况1:节点有左子树,此时前任就是左子树的最大值
if (p.left != null) {
return max(p.left);
}
// 找到节点 情况2:节点没有左子树,若离它最近的、自左而来的祖先就是前任
return ancestorFromLeft != null ?
ancestorFromLeft.value : null;
}
/**
* <h3>查找关键字的后任值</h3>
*
* @param key 关键字
* @return 后任值
*/
public Object successor(int key) {
BSTNode p = root;
BSTNode ancestorFromRight = null;
while (p != null) {
if (key < p.key) {
ancestorFromRight = p;
p = p.left;
} else if (p.key < key) {
p = p.right;
} else {
break;
}
}
// 没找到节点
if (p == null) {
return null;
}
// 找到节点 情况1:节点有右子树,此时后任就是右子树的最小值
if (p.right != null) {
return min(p.right);
}
// 找到节点 情况2:节点没有右子树,若离它最近的、自右而来的祖先就是后任
return ancestorFromRight != null ?
ancestorFromRight.value : null;
}
/**
* <h3>根据关键字删除</h3>
*
* @param key 关键字
* @return 被删除关键字对应值
*/
// public Object remove(int key) {
// ArrayList<Object> result = new ArrayList<>(); // 保存被删除节点的值
// root = doRemove(root, key, result);
// return result.isEmpty() ? null : result.get(0);
// }
//
// /*
// 4
// / \
// 2 6
// / \
// 1 7
//
// node 起点
// 返回值 删剩下的孩子(找到) 或 null(没找到)
// */
// private BSTNode doRemove(BSTNode node, int key, ArrayList<Object> result) {
// if (node == null) {
// return null;
// }
// if (key < node.key) {
// node.left = doRemove(node.left, key, result);
// return node;
// }
// if (node.key < key) {
// node.right = doRemove(node.right, key, result);
// return node;
// }
// result.add(node.value);
// if (node.left == null) { // 情况1 - 只有右孩子
// return node.right;
// }
// if (node.right == null) { // 情况2 - 只有左孩子
// return node.left;
// }
// BSTNode s = node.right; // 情况3 - 有两个孩子
// while (s.left != null) {
// s = s.left;
// }
// s.right = doRemove(node.right, s.key, new ArrayList<>());
// s.left = node.left;
// return s;
// }
public Object remove(int key) {
BSTNode p = root;
BSTNode parent = null;
while (p != null) {
if (key < p.key) {
parent = p;
p = p.left;
} else if (p.key < key) {
parent = p;
p = p.right;
} else {
break;
}
}
if (p == null) {
return null;
}
// 删除操作
if (p.left == null) {
shift(parent, p, p.right); // 情况1
} else if (p.right == null) {
shift(parent, p, p.left); // 情况2
} else {
// 情况4
// 4.1 被删除节点找后继
BSTNode s = p.right;
BSTNode sParent = p; // 后继父亲
while (s.left != null) {
sParent = s;
s = s.left;
}
// 后继节点即为 s
if (sParent != p) { // 不相邻
// 4.2 删除和后继不相邻, 处理后继的后事
shift(sParent, s, s.right); // 不可能有左孩子
s.right = p.right;
}
// 4.3 后继取代被删除节点
shift(parent, p, s);
s.left = p.left;
}
return p.value;
}
/**
* 托孤方法
*
* @param parent 被删除节点的父亲
* @param deleted 被删除节点
* @param child 被顶上去的节点
*/
private void shift(BSTNode parent, BSTNode deleted, BSTNode child) {
if (parent == null) {
root = child;
} else if (deleted == parent.left) {
parent.left = child;
} else {
parent.right = child;
}
}
/*
4
/ \
2 6
/ \ / \
1 3 5 7
*/
// 找 < key 的所有 value
public List<Object> less(int key) { // key=6
ArrayList<Object> result = new ArrayList<>();
BSTNode p = root;
LinkedList<BSTNode> stack = new LinkedList<>();
while (p != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
if (p != null) {
stack.push(p);
p = p.left;
} else {
BSTNode pop = stack.pop();
// 处理值
if (pop.key < key) {
result.add(pop.value);
} else {
break;
}
p = pop.right;
}
}
return result;
}
// 找 > key 的所有 value
public List<Object> greater(int key) {
/*ArrayList<Object> result = new ArrayList<>();
BSTNode p = root;
LinkedList<BSTNode> stack = new LinkedList<>();
while (p != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
if (p != null) {
stack.push(p);
p = p.left;
} else {
BSTNode pop = stack.pop();
// 处理值
if (pop.key > key) {
result.add(pop.value);
}
p = pop.right;
}
}
return result;*/
ArrayList<Object> result = new ArrayList<>();
BSTNode p = root;
LinkedList<BSTNode> stack = new LinkedList<>();
while (p != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
if (p != null) {
stack.push(p);
p = p.right;
} else {
BSTNode pop = stack.pop();
// 处理值
if (pop.key > key) {
result.add(pop.value);
} else {
break;
}
p = pop.left;
}
}
return result;
}
// 找 >= key1 且 <= key2 的所有值
public List<Object> between(int key1, int key2) {
ArrayList<Object> result = new ArrayList<>();
BSTNode p = root;
LinkedList<BSTNode> stack = new LinkedList<>();
while (p != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
if (p != null) {
stack.push(p);
p = p.left;
} else {
BSTNode pop = stack.pop();
// 处理值
if (pop.key >= key1 && pop.key <= key2) {
result.add(pop.value);
} else if (pop.key > key2) {
break;
}
p = pop.right;
}
}
return result;
}
}
补充
如果希望让除 int 外更多的类型能够作为 key
- 一种方式是 key 必须实现 Comparable 接口;
- 还有一种做法不要求 key 实现 Comparable 接口,而是在构造 Tree 时把比较规则作为 Comparator 传入,将来比较 key 大小时都调用此 Comparator 进行比较,这种做法可以参考 Java 中的 java.util.TreeMap。
前驱后继
- 一个节点的前驱(前任)节点是指比它小的节点中,最大的那个;
- 一个节点的后继(后任)节点是指比它大的节点中,最小的那个。
力扣题目
- 450. 删除二叉搜索树中的节点
- 701. 二叉搜索树中的插入操作
- 700. 二叉搜索树中的搜索
- 98. 验证二叉搜索树
- 938. 二叉搜索树的范围和
- 1008. 前序遍历构造二叉搜索树
- 235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
来源
路漫漫其修远兮,吾将上下而求索。





















 123
123











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








