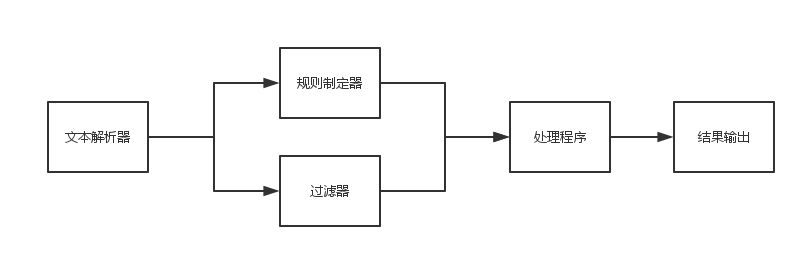
本练习根据《python基础教程》课后练习一——《即时标记》改编
分为四个模块(不包括输出部分):文本解析、规则制定、过滤、处理程序,顺序如下:
规则制定
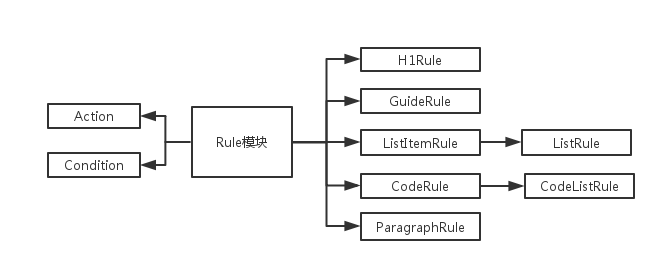
Rule模块由action和condition两部分实现,就是在遍历规则的时候通过调用condition这个东西来判断是否符合当前规则。
我们考虑了标题(H1Rule)、引用(GuideRule)、无序列表(ListItemRule&ListRule)、代码(CodeRule&CodeListRule)和普通段落(ParagraphRule),在处理程序(handlers)模块会有相应的实现。
过滤部分
采用正则表达式,对加粗、加斜和超链接做了相应的处理
self.addFilter(r'\*([^*].+?)\*','emphasis')
self.addFilter(r'\*{3}([^*].+?)\*{3}','bold')
self.addFilter(r'(http://[\.a-zA-Z1-9]+)','url')中文处理
#coding=utf-8
print data.decode('utf-8').encode('gbk')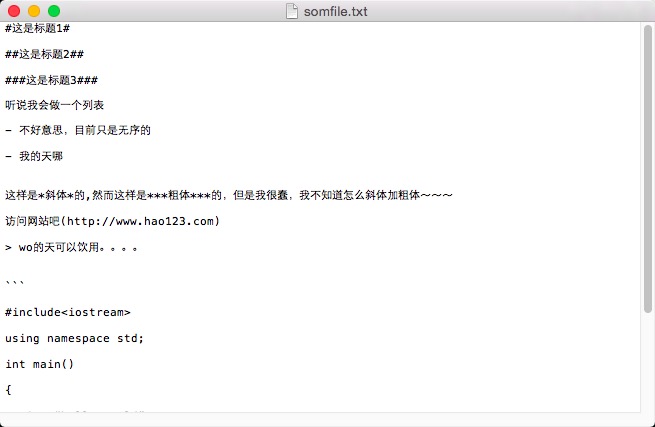
请忽略我丑丑的布局T^T

具体代码如下:
handlers.py
class Handler:
def callback(self,prefix,name,*args):
method = getattr(self,prefix+name,None)
if callable(method):
return method(*args)
def start(self,name):
self.callback('start_',name)
def end(self,name):
self.callback('end_',name)
def sub(self,name):
def subsitution(match):
result = self.callback('sub_',name,match)
if result is None:
match.group(0)
return result
return subsitution
class HTMLRenderer(Handler):
def start_document(self):
print '<html><head><title>...</title></head><body>'
def end_document(self):
print '</body></html>'
def start_paragraph(self):
print '<p>'
def end_paragraph(self):
print '</p>'
def start_guide(self):
print '<div style="background:#C0C0C0"><p>'
def end_guide(self):
print '</p></div>'
def start_code(self):
print '<div style="background:#F0F8FF"><ol>'
def end_code(self):
print '</ol></div>'
def start_h1(self):
print '<h1>'
def end_h1(self):
print '</h1>'
def start_h2(self):
print '<h2>'
def end_h2(self):
print '</h2>'
def start_h3(self):
print '<h3>'
def end_h3(self):
print '</h3>'
def start_list(self):
print '<ul>'
def end_list(self):
print '</ul>'
def start_listitem(self):
print '<li>'
def end_listitem(self):
print '</li>'
def start_title(self):
print '<h1>'
def end_title(self):
print '</h1>'
def sub_bold(self,match):
return '<b>%s</b>' %match.group(1)
def sub_emphasis(self,match):
return '<em>%s</em>' % match.group(1)
def sub_boldandemphasis(self,match):
return '<b>%s</b>' % match.group(1)
def sub_url(self,match):
return '<a href="%s">%s</a>' %(match.group(1),match.group(1))
def feed(self,data):
print data.decode('utf-8').encode('gbk')
rules.py
class Rule:
flag=True
def action(self,block,handler):
handler.start(self.type)
handler.feed(block)
handler.end(self.type)
return True
class H1Rule(Rule):
def condition(self,block):
return block[-1]=='#' and block[0]=='#'
def action(self,block,handler):
count=0;i=0;j=-1
while block[j]=='#' and block[i]=='#':
i=i+1;j=j-1;count=count+1
type='h'+str(count)
handler.start(type)
handler.feed(block[i:j+1].strip())
handler.end(type)
return True
class GuideRule(Rule):
type='guide'
def condition(self,block):
return block[0]=='>'
def action(self,block,handler):
handler.start(self.type)
handler.feed(block[1:].strip())
handler.end(self.type)
return True
class ListItemRule(Rule):
type='listitem'
def condition(self,block):
return block[0]=='-'
def action(self,block,handler):
handler.start(self.type)
handler.feed(block[1:].strip())
handler.end(self.type)
return True
class ListRule(ListItemRule):
type='list'
inside=False
def condition(self,block):
return True
def action(self,block,handler):
if not self.inside and ListItemRule.condition(self,block):
handler.start(self.type)
self.inside=True
elif self.inside and not ListItemRule.condition(self,block):
handler.end(self.type)
self.inside=False
return False
class CodeRule(Rule):
type='code'
def condition(self,block):
return block=='```'
def action(self,block,handler):
if self.flag==True:
handler.start(self.type)
self.flag=False
print self.flag
else:
handler.end(self.type)
self.flag=True
return True
class CodeListRule(CodeRule):
type='list'
def condition(self,block):
return True
def action(self,block,handler):
if self.flag==False and block!='```':
handler.start(self.type)
handler.feed(block)
handler.end(self.type)
return True
else:
return False
class ParagraphRule(Rule):
type='paragraph'
def condition(self,block):
return True
执行
$python makeup.py
























 549
549











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








