Dijkstra算法不能解决权值为负的情况。
Bellman-Ford算法能在更一般的情况下解决最短路径问题,即:允许权值为负。
注意,最短路径问题实际上均不允许有负值回路(当然是从源点可达的),因为这时不存在最短路径。总会有更短的办法-多绕负边回路走几趟就是了。
首先介绍一下松弛技术(Relaxation)
对每个顶点,都设置一个属性d[v], 用来描述从源点s到v的最短路径上权值的上界。
一步松弛操作的结果可以看作是对约束 d[v]<=d[u] + w(u,v)的松弛,即:每次比较dv和du+w(u,v)及更新dv叫做一次
松弛操做。
通俗来说,松弛可以认为是求最短路径时,每一次优化路径的过程。
总结来看,引入松弛概念其实主要是为了抽象一类步骤优化操作,为了思考问题,写伪代码方便。比如Dijkstra写成含有Relax的算法形式为:
void
Dijkstra(Graph& g, VertexNode& s)
{
for each vertex v in g
{
{
v.distance = INFINITY;
v.known = false;
v.path = NULL;
}
s.distance = 0;
for (int i=0; i<g.vertexnum; i++)
{
vertex v = smallest unknown distance vertex;
if (v==NULL)
break;
else
v.known = true;
for each w adjacent to v
{
if (!w.known)
{
Relax(w,v);
}
}
}
}
这样,Relax部分优化操作可以独立思考具体书写步骤。
回到原话题为什么Dijkstra算法不起作用,Dijkstra算法实际上相当于对每条边执行
一次Relax操作,所以其算法复杂度为O(|E|+×)。也就是说,顶点known标记的改变,记录了每条边的松弛操作。而对于含有负边的图,known顶点会出现标记过早的情况,即一次Relax操作是不够的。
Bellman-Ford算法的核心则是对每条边执行多次Relax操作,从而可以取消known的标记,因为顶点的known意向可能被之后的Relax操作改变。
Relax操作有一个非常重要的性质-路径松弛性质:如果p<v0,v1,v2,...,vk>是一个从v0到vk的最短路径,而p的边是按照<v0,v1>,<v1,v2>...<vk-1,vk>的顺序进行松弛的,那么d[vk]就是最短路径长度。这个性质的保持不受其他松弛操作的影响,即使他们与p的边上的松弛操作混在一起。
利用这个性质,我们很容易得出结论:对于一个图所有边均进行|V|-1次松弛操作,一定能得到最短路径。
所以可以得到伪代码:
BellmanFord(g, s)
{
for (int i=0; i < g.VertexNum; i++)
for each edge(u, v) in g
Relax(u, v);
}
算法复杂度为O(|E||V|)
另外还有一种利用类似广度优先搜索算法实现该算法:
这里其实相当于对上面的算法做了一个优化:如果某次对所有边进行Relax操作,没有任何d值变化,则可以立即退出迭代而不需要|V|-1次迭代都做完。
void BellmanFord(Graph& g, Vertex& s)
{
queue<vertex> q;
for each vertex v in g
{
v.distance = INFINITY;
v.path = NULL;
}
s.distance = 0;
q.enqueue(s);
while (!q.Empty())
{
v = dequeue(q);
for each w adjenct to v
{
Relax(w,v)
{
if (w not in q)
q.enqueue(w);
}
}
}
}
{
queue<vertex> q;
for each vertex v in g
{
v.distance = INFINITY;
v.path = NULL;
}
s.distance = 0;
q.enqueue(s);
while (!q.Empty())
{
v = dequeue(q);
for each w adjenct to v
{
Relax(w,v)
{
if (w not in q)
q.enqueue(w);
}
}
}
}
代码实现:
#include <iostream>
#include <deque>//双向队列
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define MAX_VERTEX_NUM 20
#define INFINITY 2147483647
struct adjVertexNode
{
int adjVertexPosition;
int weight;
adjVertexNode * next;
};
struct VertexNode
{
char data [ 2 ];
int distance;
VertexNode * path;
adjVertexNode * list;
};
struct Graph
{
VertexNode VertexNode [ MAX_VERTEX_NUM ];
int vertexNum;
int edgeNum;
};
void CreateGraph ( Graph & g)
{
int i , j , edgeStart , edgeEnd , edgeWeight;
adjVertexNode * adjNode;
cout << "Please input vertex and edge num (vnum enum):" << endl;
cin >> g . vertexNum >> g . edgeNum;
cout << "Please input vertex information (v1)\ n note: every vertex info end with Enter" << endl;
for ( i = 0; i < g . vertexNum; i ++)
{
cin >> g . VertexNode [ i ]. data; // vertex data info.
g . VertexNode [ i ]. list = NULL;
}
cout << "input edge information(start end weight):" << endl;
for ( j = 0; j < g . edgeNum; j ++)
{
cin >> edgeStart >> edgeEnd >> edgeWeight;
adjNode = new adjVertexNode;
adjNode -> weight = edgeWeight;
adjNode -> adjVertexPosition = edgeEnd - 1; // because array begin from 0, so it is j-1
// 将邻接点信息插入到顶点Vi的边表头部,注意是头部!!!不是尾部。
adjNode -> next = g . VertexNode [ edgeStart - 1 ]. list;
g . VertexNode [ edgeStart - 1 ]. list = adjNode;
}
}
void PrintAdjList( const Graph & g)
{
for ( int i = 0; i < g . vertexNum; i ++)
{
cout << g . VertexNode [ i ]. data << "->";
adjVertexNode * head = g . VertexNode [ i ]. list;
if ( head == NULL)
cout << "NULL";
while ( head != NULL)
{
cout << head -> adjVertexPosition + 1 << " ";
head = head -> next;
}
cout << endl;
}
}
void DeleteGraph( Graph & g)
{
for ( int i = 0; i < g . vertexNum; i ++)
{
adjVertexNode * tmp = NULL;
while( g . VertexNode [ i ]. list != NULL)
{
tmp = g . VertexNode [ i ]. list;
g . VertexNode [ i ]. list = g . VertexNode [ i ]. list -> next;
delete tmp;
tmp = NULL;
}
}
}
void BellmanFord( Graph & g , VertexNode & s)
{
deque < VertexNode *> q;
for ( int i = 0; i < g . vertexNum; i ++)
{
g . VertexNode [ i ]. distance = INFINITY;
g . VertexNode [ i ]. path = NULL;
}
s . distance = 0;
q . push_back( &s);
int counter = 0;
while( ! q . empty())
{
VertexNode * v = q . front();
q . pop_front();
if( v == NULL)
break;
adjVertexNode * head = v -> list;
while ( head != NULL)
{
VertexNode * w = & g . VertexNode [ head -> adjVertexPosition ];
if( v -> distance + head -> weight < w -> distance)
{
w -> distance = v -> distance + head -> weight;
w -> path = v;
if ( find( q . begin (), q . end (), w) == q . end())
{
q . push_back( w);
}
}
head = head -> next;
}
counter ++;
if ( counter > g . vertexNum * g . edgeNum)
{
cout << "This graph has minus value loop!" << endl;
exit( 1);
}
}
}
void PrintPath( Graph & g , VertexNode * source , VertexNode * target)
{
if ( source != target && target -> path == NULL)
{
cout << "There is no shortest path from " << source -> data << " to " << target -> data << endl;
}
else
{
if ( target -> path != NULL)
{
PrintPath( g , source , target -> path);
cout << " ";
}
cout << target -> data ;
}
}
int main( int argc , const char ** argv)
{
Graph g;
CreateGraph( g);
PrintAdjList( g);
VertexNode & start = g . VertexNode [ 0 ];
VertexNode & end = g . VertexNode [ 6 ];
BellmanFord( g , start);
cout << "print the shortest path from v1 to v7" << endl;
PrintPath( g , & start , & end);
cout << endl;
DeleteGraph( g);
return 0;
}
#include <deque>//双向队列
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define MAX_VERTEX_NUM 20
#define INFINITY 2147483647
struct adjVertexNode
{
int adjVertexPosition;
int weight;
adjVertexNode * next;
};
struct VertexNode
{
char data [ 2 ];
int distance;
VertexNode * path;
adjVertexNode * list;
};
struct Graph
{
VertexNode VertexNode [ MAX_VERTEX_NUM ];
int vertexNum;
int edgeNum;
};
void CreateGraph ( Graph & g)
{
int i , j , edgeStart , edgeEnd , edgeWeight;
adjVertexNode * adjNode;
cout << "Please input vertex and edge num (vnum enum):" << endl;
cin >> g . vertexNum >> g . edgeNum;
cout << "Please input vertex information (v1)\ n note: every vertex info end with Enter" << endl;
for ( i = 0; i < g . vertexNum; i ++)
{
cin >> g . VertexNode [ i ]. data; // vertex data info.
g . VertexNode [ i ]. list = NULL;
}
cout << "input edge information(start end weight):" << endl;
for ( j = 0; j < g . edgeNum; j ++)
{
cin >> edgeStart >> edgeEnd >> edgeWeight;
adjNode = new adjVertexNode;
adjNode -> weight = edgeWeight;
adjNode -> adjVertexPosition = edgeEnd - 1; // because array begin from 0, so it is j-1
// 将邻接点信息插入到顶点Vi的边表头部,注意是头部!!!不是尾部。
adjNode -> next = g . VertexNode [ edgeStart - 1 ]. list;
g . VertexNode [ edgeStart - 1 ]. list = adjNode;
}
}
void PrintAdjList( const Graph & g)
{
for ( int i = 0; i < g . vertexNum; i ++)
{
cout << g . VertexNode [ i ]. data << "->";
adjVertexNode * head = g . VertexNode [ i ]. list;
if ( head == NULL)
cout << "NULL";
while ( head != NULL)
{
cout << head -> adjVertexPosition + 1 << " ";
head = head -> next;
}
cout << endl;
}
}
void DeleteGraph( Graph & g)
{
for ( int i = 0; i < g . vertexNum; i ++)
{
adjVertexNode * tmp = NULL;
while( g . VertexNode [ i ]. list != NULL)
{
tmp = g . VertexNode [ i ]. list;
g . VertexNode [ i ]. list = g . VertexNode [ i ]. list -> next;
delete tmp;
tmp = NULL;
}
}
}
void BellmanFord( Graph & g , VertexNode & s)
{
deque < VertexNode *> q;
for ( int i = 0; i < g . vertexNum; i ++)
{
g . VertexNode [ i ]. distance = INFINITY;
g . VertexNode [ i ]. path = NULL;
}
s . distance = 0;
q . push_back( &s);
int counter = 0;
while( ! q . empty())
{
VertexNode * v = q . front();
q . pop_front();
if( v == NULL)
break;
adjVertexNode * head = v -> list;
while ( head != NULL)
{
VertexNode * w = & g . VertexNode [ head -> adjVertexPosition ];
if( v -> distance + head -> weight < w -> distance)
{
w -> distance = v -> distance + head -> weight;
w -> path = v;
if ( find( q . begin (), q . end (), w) == q . end())
{
q . push_back( w);
}
}
head = head -> next;
}
counter ++;
if ( counter > g . vertexNum * g . edgeNum)
{
cout << "This graph has minus value loop!" << endl;
exit( 1);
}
}
}
void PrintPath( Graph & g , VertexNode * source , VertexNode * target)
{
if ( source != target && target -> path == NULL)
{
cout << "There is no shortest path from " << source -> data << " to " << target -> data << endl;
}
else
{
if ( target -> path != NULL)
{
PrintPath( g , source , target -> path);
cout << " ";
}
cout << target -> data ;
}
}
int main( int argc , const char ** argv)
{
Graph g;
CreateGraph( g);
PrintAdjList( g);
VertexNode & start = g . VertexNode [ 0 ];
VertexNode & end = g . VertexNode [ 6 ];
BellmanFord( g , start);
cout << "print the shortest path from v1 to v7" << endl;
PrintPath( g , & start , & end);
cout << endl;
DeleteGraph( g);
return 0;
}
其中判断含有负值回路的方法很多,这里采用认为最多会有|V|×|E|次操作,否则存在负值回路。
使用 queue也是可以的,但要注意 relax 内部判断要写成:
if (find(q._Get_container().begin(), q._Get_container().end(), w) == q._Get_container().end())
略显臃肿。 而实际上 queue也是一个container adapter,他内部封装了deque。
运行示例:
1 含有负值权边,但不含负值回路。
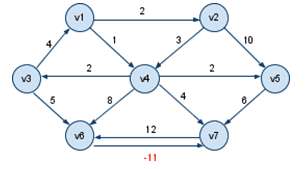
运行结果
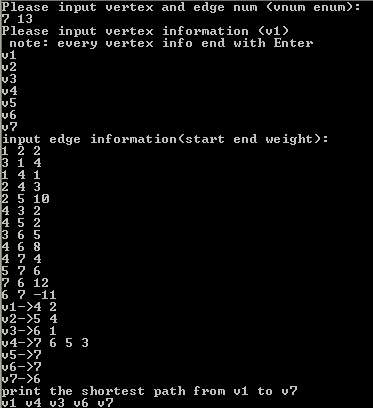
2 含有负值回路:v6->v7->v6 (-10)
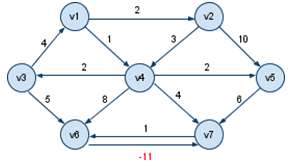
运行结果
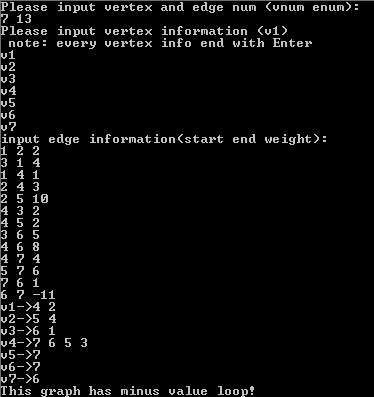






















 491
491

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








