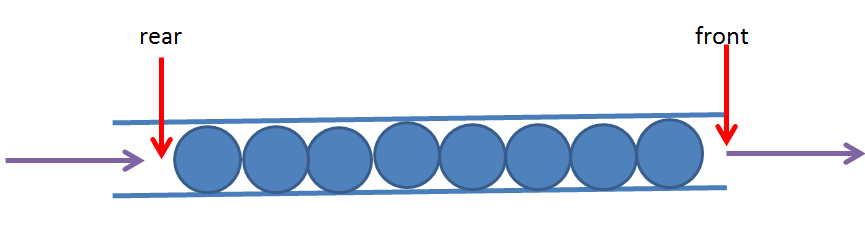
栈是“后进先出”(LIFO,Last InFirst Out)的数据结构,与之相反,队列是“先进先出”(FIFO,First InFirst Out)的数据结构。
队列特性:
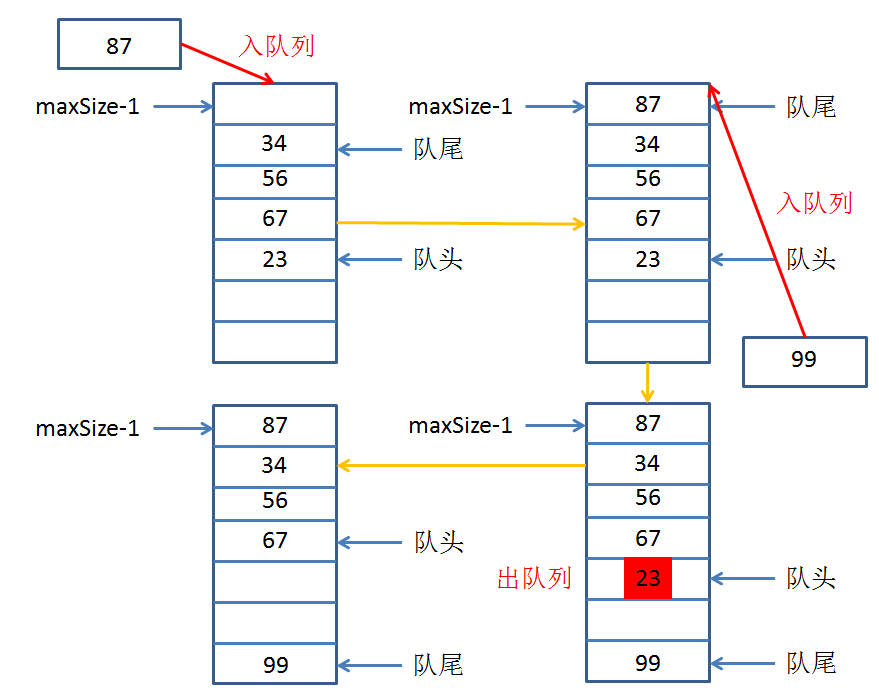
下面我们使用数组作为底层容器来实现一个队列的操作封装,与栈不同的是,队列的数据项并不都是从数组的第一个下标开始,因为数据项在数组的下标越小代表其在队列中的排列越靠前,移除数据项只能从队头移除,然后队头指针后移。
队列有下面几个操作:
InitQueue() ——初始化队列
EnQueue() ——进队列
DeQueue() ——出队列
IsEmpty() ——判断队列是否为空
IsFull() ——判断队列是否已满
下面是用一般的数组实现的队列:
package com.cn;
//底层数据结构是数组,用数组实现队列
public class ArrayQueue {
private int [] Array; //底层数组
private int maxSize;
public int front; //存储队头元素的下标
public int rear; //存储队尾元素的下标
private int length; //队列长度
//构造方法,初始化队列
public ArrayQueue(int maxSize){
this.maxSize = maxSize;
Array = new int [maxSize];
front = 0;
rear = -1;
length = 0;
}
//入队列
public void EnQueue(int element) throws Exception{
if(isFull()){
throw new Exception("队列已满,不能进行入队列操作!");
}
//如果队尾指针已到达数组的末端,插入到数组的第一个位置
if(rear == maxSize-1){
rear = -1;
}
Array[++rear] = element;
length++;
}
//出队列
public int DeQueue() throws Exception{
if(isEmpty()){
throw new Exception("队列为空,不能进行出队列操作!");
}
int element = Array[front++]; //所谓的出队列只是,指针不在指着原数据,也就是原数据不再被访问
//如果队头指针已到达数组末端,则移到数组第一个位置
if(front == maxSize){
front = 0;
}
length--;
return element;
}
//查看队头元素 ,但不出队列
public int peek() throws Exception{
if(isEmpty()){
throw new Exception("队列内没有元素!");
}
return Array[front];
}
//获取队列长度
public int size(){
return length;
}
//判空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return (length == 0);
}
//判满
public boolean isFull(){
return (length == maxSize);
}
}
package com.cn;
public class TestArrayQueue {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ArrayQueue theQueue = new ArrayQueue(5); // 队列有5个元素
theQueue.EnQueue(10); // 添加4个元素
theQueue.EnQueue(20);
theQueue.EnQueue(30);
theQueue.EnQueue(40);
theQueue.DeQueue(); // 移除3个元素
theQueue.DeQueue(); // (10, 20, 30)
theQueue.DeQueue();
theQueue.EnQueue(50); // 添加4个元素
theQueue.EnQueue(60);
theQueue.EnQueue(70);
theQueue.EnQueue(80);
while( !theQueue.isEmpty() ) // 遍历队列并移除所有元素
{
long n = theQueue.DeQueue(); // (40, 50, 60, 70, 80)
System.out.print(n);
System.out.print(" ");
}
System.out.println("");
}
}
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class MyQueue<E> {
private LinkedList<E> list=new LinkedList<E>();//用链表实现队列
//入队列从列表尾
public void enqueue(E e){
list.addLast(e);
}
//出队列从列表头
public E dequeue(){
return list.removeFirst();
}
public int getSize(){
return list.size();
}
public String toString(){
return list.toString();
}
}
在java5中新增加了java.util.Queue接口,用以支持队列的常见操作。该接口扩展了java.util.Collection接口。
Queue使用时要尽量避免Collection的add()和remove()方法,而是要使用offer()来加入元素,使用poll()来获取并移出元素。它们的优点是通过返回值可以判断成功与否,add()和remove()方法在失败的时候会抛出异常。 如果要使用前端而不移出该元素,使用element()或者peek()方法。
值得注意的是LinkedList类实现了Queue接口,因此我们可以把LinkedList当成Queue来用。
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class TestQueue {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue queue = new LinkedList();
queue.offer("北京"); //使用offer在队尾添加元素
queue.offer("上海");
queue.offer("广州");
System.out.println(queue.size());
String str;
while((str=queue.poll())!=null){
System.out.println(str); //北京 上海 广州
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println(queue.size());//0
}
}

























 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








