#include <iostream>
#include <typeinfo>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
Person(int x, int y=0, int z=0):mId(x), mAge(y), test(z){
print();
cout << "Person" << endl;
}
void operator = (const Person& per){
// mId = 1;
per.print();
cout << "operator = (const Person& per)" << endl; }
Person(const Person& per){
// mId = 1;
print();
cout << "Person(const Person& per)" << endl; }
virtual void print() const
{
cout << "id: " << mId
<< ", age: " << mAge << endl;
}
protected:
int mId;
int mAge;
int test;
};
int main()
{
Person p1 = {1,2,3};
Person p2 = {1};
Person p3 = p1;
Person p4(p1);
Person p5{1};
p5 = p1;
return 0;
}
输出:
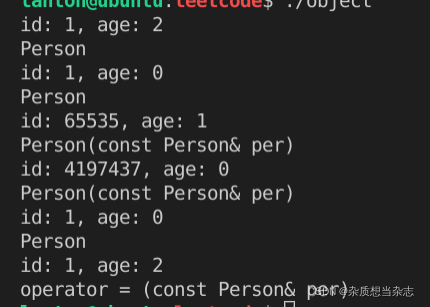
default constrctor
第一种的initialization list(初始化列表)构造比第二种inline expansion(内联展开)构造更高效:
- 初始化列表在构造函数时,把成员变量的值直接放进内存,最快。
而用内联展开的方式,在成员变量构造好后,再增加对成员变量的赋值操作,把初值放进内存中。慢!
Person(int x, int y=0, int z=0):mId(x), mAge(y), test(z){
}
// 或者(这两种等效)
Person(int x, int y=0, int z=0){
mId = x;
mAge = y;
test = z;
}
initialization list 调用方式:
Perso P1 = {1,2,3} //因为有两个默认参数,所以可以只传递一个参数:P1 = {1}
inline expansion 调用方式:
Perso P1(1);
copy construnctor
复制构造函数,调用方式:
Person p2(p1)
// 或者
Person p3 = p1;
copy assignment constructor
赋值构造函数,调用方式:
Person P1{1}, p2{2};
p1 = p2;





















 3094
3094











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








