1、简介
在Java中创建线程的2种方式,一种是直接继承Thread,另外一种就是实现Runnable接口。这2种方式都有一个缺陷就是:在执行完任务之后无法获取执行结果。
2、需求
在Java中,如果需要获取执行结果,就必须通过共享变量或者使用线程通信的方式来达到效果,这样使用起来就比较麻烦。而自从Java 1.5开始,就提供了Callable和Future,通过它们可以在任务执行完毕之后得到任务执行结果。
3、Callable、FutureTask简介
在学习Callable和FutureTask之前,我们先看一下java.lang.Runnable吧,它是一个接口,在它里面只声明了一个run()方法:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Runnable {
/**
* When an object implementing interface <code>Runnable</code> is used
* to create a thread, starting the thread causes the object's
* <code>run</code> method to be called in that separately executing
* thread.
* <p>
* The general contract of the method <code>run</code> is that it may
* take any action whatsoever.
*
* @see java.lang.Thread#run()
*/
public abstract void run();
}由于run()方法返回值为void类型,所以在执行完任务之后无法返回任何结果。
Callable位于java.util.concurrent包下,它也是一个接口,在它里面也只声明了一个方法,只不过这个方法叫做call():
package java.util.concurrent;
/**
* A task that returns a result and may throw an exception.
* Implementors define a single method with no arguments called
* {@code call}.
*
* <p>The {@code Callable} interface is similar to {@link
* java.lang.Runnable}, in that both are designed for classes whose
* instances are potentially executed by another thread. A
* {@code Runnable}, however, does not return a result and cannot
* throw a checked exception.
*
* <p>The {@link Executors} class contains utility methods to
* convert from other common forms to {@code Callable} classes.
*
* @see Executor
* @since 1.5
* @author Doug Lea
* @param <V> the result type of method {@code call}
*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Callable<V> {
/**
* Computes a result, or throws an exception if unable to do so.
*
* @return computed result
* @throws Exception if unable to compute a result
*/
V call() throws Exception;
}可以看到,这是一个泛型接口,call()函数返回的类型就是传递进来的V类型。
那么怎么使用Callable呢?一般情况下是配合ExecutorService来使用的,在ExecutorService接口中声明了若干个submit方法的重载版本:
<T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task);
<T> Future<T> submit(Runnable task, T result);
Future<?> submit(Runnable task);- 第一个submit方法里面的参数类型就是Callable。
- Callable一般是和ExecutorService配合来使用的,具体的使用方法讲在后面讲述。
- 一般情况下我们使用第一个submit方法和第三个submit方法,第二个submit方法很少使用。
- Future就是对于具体的Runnable或者Callable任务的执行结果进行取消、查询是否完成、获取结果。必要时可以通过get方法获取执行结果,该方法会阻塞直到任务返回结果。
Future类位于java.util.concurrent包下,它是一个接口:
public interface Future<V> {
boolean cancel( boolean mayInterruptIfRunning);
boolean isCancelled();
boolean isDone();
V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException;
V get( long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException;
}在Future接口中声明了5个方法,下面依次解释每个方法的作用:
- cancel方法用来取消任务,如果取消任务成功则返回true,如果取消任务失败则返回false。参数mayInterruptIfRunning表示是否允许取消正在执行却没有执行完毕的任务,如果设置true,则表示可以取消正在执行过程中的任务。如果任务已经完成,则无论mayInterruptIfRunning为true还是false,此方法肯定返回false,即如果取消已经完成的任务会返回false;如果任务正在执行,若mayInterruptIfRunning设置为true,则返回true,若mayInterruptIfRunning设置为false,则返回false;如果任务还没有执行,则无论mayInterruptIfRunning为true还是false,肯定返回true。
- isCancelled方法表示任务是否被取消成功,如果在任务正常完成前被取消成功,则返回 true。
- isDone方法表示任务是否已经完成,若任务完成,则返回true;
- get()方法用来获取执行结果,这个方法会产生阻塞,会一直等到任务执行完毕才返回;
- get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)用来获取执行结果,如果在指定时间内,还没获取到结果,就直接返回null。
Future提供了三种功能:
- 判断任务是否完成;
- 能够中断任务;
- 能够获取任务执行结果。
因为Future只是一个接口,所以是无法直接用来创建对象使用的,因此就有了下面的FutureTask。
4、Callable、FutureTask使用
4.1简单使用
CallableTask.java
public class CallableTask implements Callable<Integer> {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
int hours=5;
int amount = 0;
while(hours>0){
System.out.println("我正在工作,剩余时间 "+hours+"小时");
amount++;
hours--;
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
return amount;
}
}
TestDemo.java
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) throws ExecutionException {
CallableTask worker = new CallableTask();
FutureTask<Integer> jiangong = new FutureTask<Integer>(worker);
new Thread(jiangong).start();
while(!jiangong.isDone()){
try {
System.out.println("获取结果"+jiangong.get());
System.out.println("任务是否取消"+jiangong.isCancelled());
System.out.println("任务是否执行"+jiangong.isDone());
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
int amount;
try {
amount = jiangong.get();
System.out.println("工作做完了,上交了"+amount);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
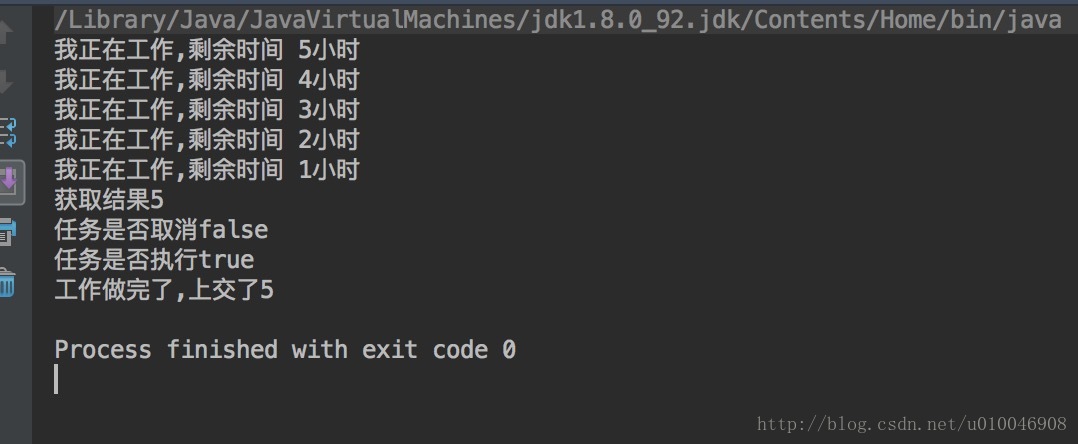
}运行的结果:
4.2并发的实现
package com.lidong.demo;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
/**
* @项目名称:lidong-dubbo
* @类名:Task
* @类的描述:
* @作者:lidong
* @创建时间:2017/2/21 下午3:42
* @公司:chni
* @QQ:1561281670
* @邮箱:lidong1665@163.com
*/
public class Task implements Callable<Integer> {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 子线程在进行计算开始");
Thread.sleep(3000);
int sum = 0;
for(int i=0;i<100;i++)
sum += i;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 子线程在进行计算结束");
return sum;
}
}Test.java
package com.lidong.demo;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
Task task = new Task();
FutureTask<Integer> futureTask = new FutureTask<Integer>(task);
executor.submit(futureTask);
executor.shutdown();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 主线程在执行任务");
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ " task运行结果"+futureTask.get());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ " 所有任务执行完毕");
}
}
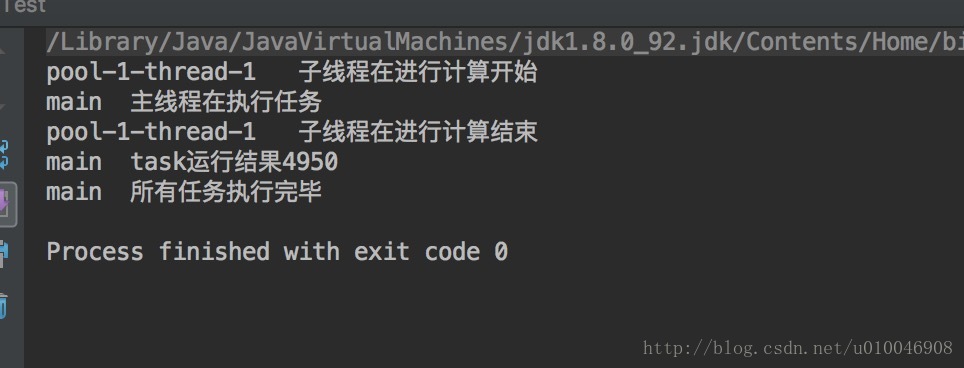
运行结果:






















 955
955

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








