TCP编程底层都有粘包和拆包机制,因为我们在C/S这种传输模型下,以TCP协议传输的时候,在网络中的byte其实就像是河水,TCP就像一个搬运工,将这流水从一端转送到另一端,这时又分两种情况:
1)如果客户端的每次制造的水比较多,也就是我们常说的客户端给的包比较大,TCP这个搬运工就会分多次去搬运。
2)如果客户端每次制造的水比较少的话,TCP可能会等客户端多次生产之后,把所有的水一起再运输到另一端
上述第一种情况,就是需要我们进行粘包,在另一端接收的时候,需要把多次获取的结果粘在一起,变成我们可以理解的信息,第二种情况,我们在另一端接收的时候,就必须进行拆包处理,因为每次接收的信息,可能是另一个远程端多次发送的包,被TCP粘在一起的
我们进行上述两种情况给出具体的场景:
1)单次发送的包内容过多的情况,拆包的现象:
我们先写客户端的bootstrap:
客户端的handler:
服务端的serverBootstrap:
服务端的handler:
照例,我们先运行服务器端:
我们再运行客户端,客户端启动后,我们再看看服务器端的控制台打印输出:
我们可以看到服务器端分三次接收到了客户端两次发送的那段很长的信息
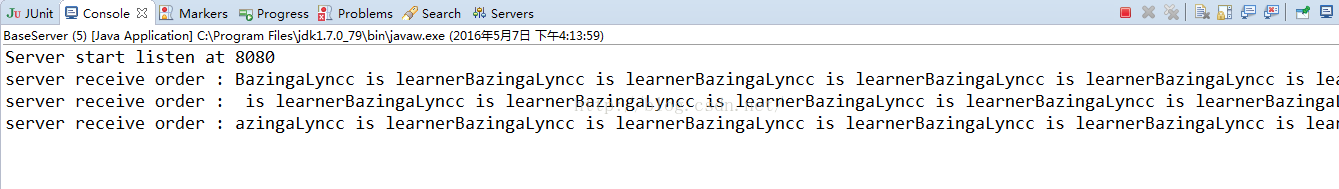
2)单次发送的包内容过多的情况,粘包的现象:
客户端和服务端的bootstrap不改变,我们修改一下,客户端发送信息的channelActive的代码:
我们再次启动服务器端:
启动客户端后,依旧看服务器端的控制台:
可以看出,客户端发送100次的信息,被服务器端分三次就接收了,这就发生了粘包的现象
以上就是典型的粘包和拆包的场景
2.4 粘包问题的解决办法
粘包的解决办法有很多,可以归纳如下。
- 消息定长,例如每个报文的大小为固定长度200字节,如果不够,空位补空格。
- 在包尾增加回车换行符进行分割,例如FTP协议。
- 将消息分为消息头和消息体,消息头中包含消息长度的字段,通常设计思路为消息头的第一个字段使用int32来表示消息的总长度
在本案例中,我使用的是第2个解决办法在包尾增加回车换行符进行分割。
自定义协议实现
1、什么是粘包/拆包
一般所谓的TCP粘包是在一次接收数据不能完全地体现一个完整的消息数据。TCP通讯为何存在粘包呢?主要原因是TCP是以流的方式来处理数据,再加上网络上MTU的往往小于在应用处理的消息数据,所以就会引发一次接收的数据无法满足消息的需要,导致粘包的存在。处理粘包的唯一方法就是制定应用层的数据通讯协议,通过协议来规范现有接收的数据是否满足消息数据的需要。
2、解决办法
2.1、消息定长,报文大小固定长度,不够空格补全,发送和接收方遵循相同的约定,这样即使粘包了通过接收方编程实现获取定长报文也能区分。
2.2、包尾添加特殊分隔符,例如每条报文结束都添加回车换行符(例如FTP协议)或者指定特殊字符作为报文分隔符,接收方通过特殊分隔符切分报文区分。
2.3、将消息分为消息头和消息体,消息头中包含表示信息的总长度(或者消息体长度)的字段
3、自定义协议,来实现TCP的粘包/拆包问题
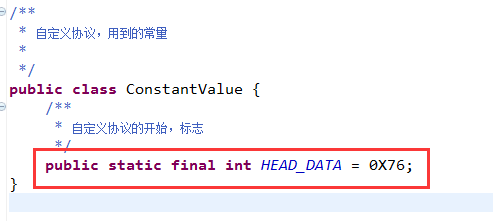
3.0 自定义协议,开始标记
3.1 自定义协议的介绍
3.2 自定义协议的类的封装
3.3 自定义协议的编码器
3.4 自定义协议的解码器
4、协议相关的实现
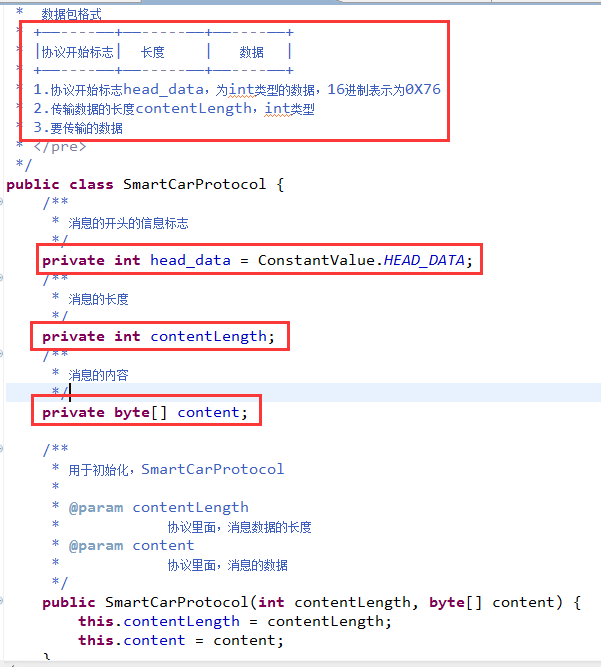
4.1 协议的封装
- import java.util.Arrays;
- /**
- * <pre>
- * 自己定义的协议
- * 数据包格式
- * +——----——+——-----——+——----——+
- * |协议开始标志| 长度 | 数据 |
- * +——----——+——-----——+——----——+
- * 1.协议开始标志head_data,为int类型的数据,16进制表示为0X76
- * 2.传输数据的长度contentLength,int类型
- * 3.要传输的数据
- * </pre>
- */
- public class SmartCarProtocol {
- /**
- * 消息的开头的信息标志
- */
- private int head_data = ConstantValue.HEAD_DATA;
- /**
- * 消息的长度
- */
- private int contentLength;
- /**
- * 消息的内容
- */
- private byte[] content;
- /**
- * 用于初始化,SmartCarProtocol
- *
- * @param contentLength
- * 协议里面,消息数据的长度
- * @param content
- * 协议里面,消息的数据
- */
- public SmartCarProtocol(int contentLength, byte[] content) {
- this.contentLength = contentLength;
- this.content = content;
- }
- public int getHead_data() {
- return head_data;
- }
- public int getContentLength() {
- return contentLength;
- }
- public void setContentLength(int contentLength) {
- this.contentLength = contentLength;
- }
- public byte[] getContent() {
- return content;
- }
- public void setContent(byte[] content) {
- this.content = content;
- }
- @Override
- public String toString() {
- return "SmartCarProtocol [head_data=" + head_data + ", contentLength="
- + contentLength + ", content=" + Arrays.toString(content) + "]";
- }
- }
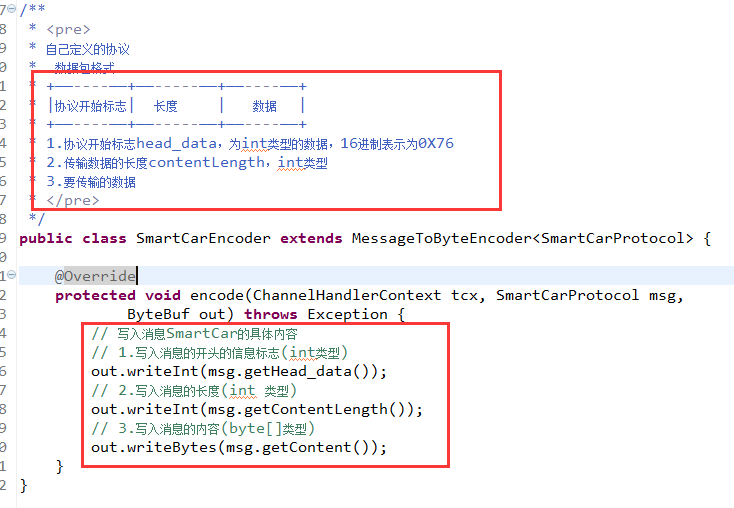
4.2 协议的编码器
- /**
- * <pre>
- * 自己定义的协议
- * 数据包格式
- * +——----——+——-----——+——----——+
- * |协议开始标志| 长度 | 数据 |
- * +——----——+——-----——+——----——+
- * 1.协议开始标志head_data,为int类型的数据,16进制表示为0X76
- * 2.传输数据的长度contentLength,int类型
- * 3.要传输的数据
- * </pre>
- */
- public class SmartCarEncoder extends MessageToByteEncoder<SmartCarProtocol> {
- @Override
- protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext tcx, SmartCarProtocol msg,
- ByteBuf out) throws Exception {
- // 写入消息SmartCar的具体内容
- // 1.写入消息的开头的信息标志(int类型)
- out.writeInt(msg.getHead_data());
- // 2.写入消息的长度(int 类型)
- out.writeInt(msg.getContentLength());
- // 3.写入消息的内容(byte[]类型)
- out.writeBytes(msg.getContent());
- }
- }
4.3 协议的解码器
- import java.util.List;
- import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
- import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
- import io.netty.handler.codec.ByteToMessageDecoder;
- /**
- * <pre>
- * 自己定义的协议
- * 数据包格式
- * +——----——+——-----——+——----——+
- * |协议开始标志| 长度 | 数据 |
- * +——----——+——-----——+——----——+
- * 1.协议开始标志head_data,为int类型的数据,16进制表示为0X76
- * 2.传输数据的长度contentLength,int类型
- * 3.要传输的数据,长度不应该超过2048,防止socket流的攻击
- * </pre>
- */
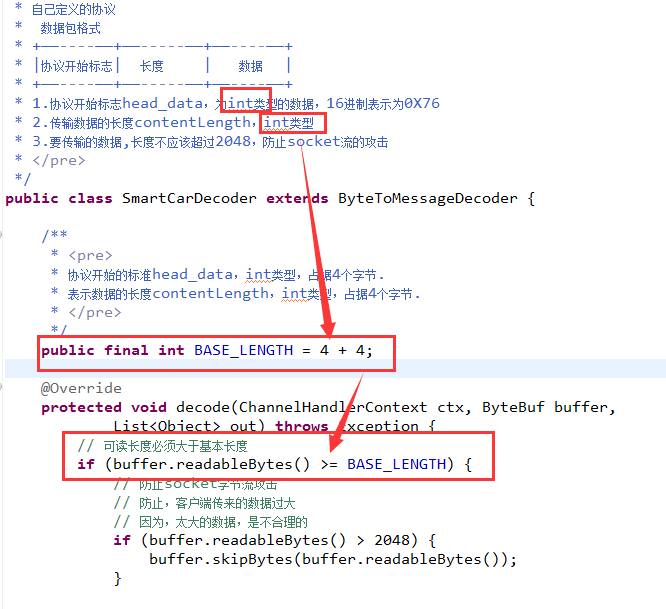
- public class SmartCarDecoder extends ByteToMessageDecoder {
- /**
- * <pre>
- * 协议开始的标准head_data,int类型,占据4个字节.
- * 表示数据的长度contentLength,int类型,占据4个字节.
- * </pre>
- */
- public final int BASE_LENGTH = 4 + 4;
- @Override
- protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf buffer,
- List<Object> out) throws Exception {
- // 可读长度必须大于基本长度
- if (buffer.readableBytes() >= BASE_LENGTH) {
- // 防止socket字节流攻击
- // 防止,客户端传来的数据过大
- // 因为,太大的数据,是不合理的
- if (buffer.readableBytes() > 2048) {
- buffer.skipBytes(buffer.readableBytes());
- }
- // 记录包头开始的index
- int beginReader;
- while (true) {
- // 获取包头开始的index
- beginReader = buffer.readerIndex();
- // 标记包头开始的index
- buffer.markReaderIndex();
- // 读到了协议的开始标志,结束while循环
- if (buffer.readInt() == ConstantValue.HEAD_DATA) {
- break;
- }
- // 未读到包头,略过一个字节
- // 每次略过,一个字节,去读取,包头信息的开始标记
- buffer.resetReaderIndex();
- buffer.readByte();
- // 当略过,一个字节之后,
- // 数据包的长度,又变得不满足
- // 此时,应该结束。等待后面的数据到达
- if (buffer.readableBytes() < BASE_LENGTH) {
- return;
- }
- }
- // 消息的长度
- int length = buffer.readInt();
- // 判断请求数据包数据是否到齐
- if (buffer.readableBytes() < length) {
- // 还原读指针
- buffer.readerIndex(beginReader);
- return;
- }
- // 读取data数据
- byte[] data = new byte[length];
- buffer.readBytes(data);
- SmartCarProtocol protocol = new SmartCarProtocol(data.length, data);
- out.add(protocol);
- }
- }
- }
4.4 服务端加入协议的编/解码器
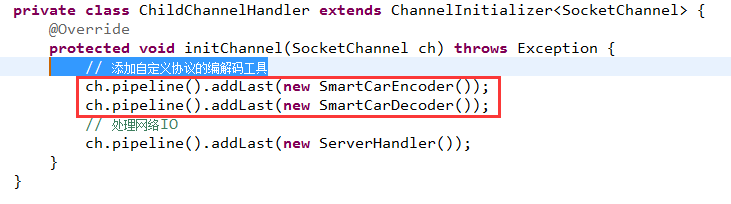
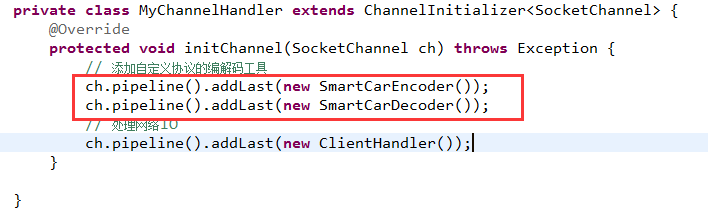
4.5 客户端加入协议的编/解码器
5、服务端的实现
- import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
- import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
- import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
- import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
- import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
- import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
- import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
- import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
- import io.netty.handler.logging.LogLevel;
- import io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler;
- public class Server {
- public Server() {
- }
- public void bind(int port) throws Exception {
- // 配置NIO线程组
- EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
- EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
- try {
- // 服务器辅助启动类配置
- ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
- b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
- .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
- .handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))
- .childHandler(new ChildChannelHandler())//
- .option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 1024) // 设置tcp缓冲区 // (5)
- .childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true); // (6)
- // 绑定端口 同步等待绑定成功
- ChannelFuture f = b.bind(port).sync(); // (7)
- // 等到服务端监听端口关闭
- f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
- } finally {
- // 优雅释放线程资源
- workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
- bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
- }
- }
- /**
- * 网络事件处理器
- */
- private class ChildChannelHandler extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> {
- @Override
- protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
- // 添加自定义协议的编解码工具
- ch.pipeline().addLast(new SmartCarEncoder());
- ch.pipeline().addLast(new SmartCarDecoder());
- // 处理网络IO
- ch.pipeline().addLast(new ServerHandler());
- }
- }
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
- new Server().bind(9999);
- }
- }
6、服务端Handler的实现
- import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerAdapter;
- import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
- public class ServerHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
- // 用于获取客户端发送的信息
- @Override
- public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg)
- throws Exception {
- // 用于获取客户端发来的数据信息
- SmartCarProtocol body = (SmartCarProtocol) msg;
- System.out.println("Server接受的客户端的信息 :" + body.toString());
- // 会写数据给客户端
- String str = "Hi I am Server ...";
- SmartCarProtocol response = new SmartCarProtocol(str.getBytes().length,
- str.getBytes());
- // 当服务端完成写操作后,关闭与客户端的连接
- ctx.writeAndFlush(response);
- // .addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE);
- // 当有写操作时,不需要手动释放msg的引用
- // 当只有读操作时,才需要手动释放msg的引用
- }
- @Override
- public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause)
- throws Exception {
- // cause.printStackTrace();
- ctx.close();
- }
- }
7、客户端的实现
- import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
- import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
- import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
- import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
- import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
- import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
- import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
- import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
- public class Client {
- /**
- * 连接服务器
- *
- * @param port
- * @param host
- * @throws Exception
- */
- public void connect(int port, String host) throws Exception {
- // 配置客户端NIO线程组
- EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
- try {
- // 客户端辅助启动类 对客户端配置
- Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap();
- b.group(group)//
- .channel(NioSocketChannel.class)//
- .option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true)//
- .handler(new MyChannelHandler());//
- // 异步链接服务器 同步等待链接成功
- ChannelFuture f = b.connect(host, port).sync();
- // 等待链接关闭
- f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
- } finally {
- group.shutdownGracefully();
- System.out.println("客户端优雅的释放了线程资源...");
- }
- }
- /**
- * 网络事件处理器
- */
- private class MyChannelHandler extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> {
- @Override
- protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
- // 添加自定义协议的编解码工具
- ch.pipeline().addLast(new SmartCarEncoder());
- ch.pipeline().addLast(new SmartCarDecoder());
- // 处理网络IO
- ch.pipeline().addLast(new ClientHandler());
- }
- }
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
- new Client().connect(9999, "127.0.0.1");
- }
- }
8、客户端Handler的实现
- import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerAdapter;
- import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
- import io.netty.util.ReferenceCountUtil;
- //用于读取客户端发来的信息
- public class ClientHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
- // 客户端与服务端,连接成功的售后
- @Override
- public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
- // 发送SmartCar协议的消息
- // 要发送的信息
- String data = "I am client ...";
- // 获得要发送信息的字节数组
- byte[] content = data.getBytes();
- // 要发送信息的长度
- int contentLength = content.length;
- SmartCarProtocol protocol = new SmartCarProtocol(contentLength, content);
- ctx.writeAndFlush(protocol);
- }
- // 只是读数据,没有写数据的话
- // 需要自己手动的释放的消息
- @Override
- public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg)
- throws Exception {
- try {
- // 用于获取客户端发来的数据信息
- SmartCarProtocol body = (SmartCarProtocol) msg;
- System.out.println("Client接受的客户端的信息 :" + body.toString());
- } finally {
- ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg);
- }
- }
- @Override
- public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause)
- throws Exception {
- ctx.close();
- }
- }
























 1157
1157

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








