原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/lee353086/article/details/39937139 作者:kagula
C++ AMP 介绍(二)
最后更新日期:2014-05-02
阅读前提:《C++ AMP介绍(一)》
环境:Windows 8.1 64bit英文版,Visual Studio 2013 Update1英文版,Nvidia QuadroK600 显卡
内容简介
介绍C++ AMP的 array、array_view、extent类和平铺的知识。
正文
数据的移动
array和 array_view两个数据容器(模板类)用于把数据从运行时库(CPU)移到加速器(显卡或通用计算卡)上,array类在构造时建立数据的深拷贝,把数据复制到加速器(GPU)上,而array_view类是个包装类,仅仅当核心函数(kernel function)要用到数据时,才把源数据复制到加速器上。
array_view同array之间几乎有相同的成员,但是它们底层的行为不一样,所以当你建立两个指向同一个数据源的array_view实例时,实际上它们指向同一个内存地址,数据只有当需要的时候才会被复制到加速器中,所以你得注意数据的同步,array_view类的主要好处是数据仅当要被加速器用到的时候才会被移动。
共享内存是能被CPU和GPU访问的内存,array类可以控制共享内存的存取方式,但是首先我们需要测试加速器是不是支持共享内存,下面是array使用共享内存的示例代码。
index 类
index类指定元素在array或array_view对象中的位置,下面是index类的使用示例代码
extent类
虽然extent类在很多场合下不是必要的,但是微软的部分示例代码使用到了extent class,所以有必要介绍下extent class。
extentclass用来指定array或array_view各个维度的元素数量,你可以使用extent class建立array或array_view对象,也可以从array或array_view对象中存取extent,下面的例子演示了extent class的使用。
parallel_for_each函数
我们在上篇文章中调用过parallel_for_each函数,它有两个入口参数,第一个入口参数为计算域,是个extent或tiled_extent对象,定义了要在加速器上并发运行的线程集合,它会为每个元素生成一根用于计算的线程。第二个参数是lambda表达式,定义了要在每根线程上运行的代码。
加速代码: 砖面(Tiles )和边界(Barriers)
将全体线程划分为若干个具有相等数量矩形(M*N根)线程集合,每个集合称为tile(砖面),多个tile(砖面)组成全体线程,叫做平铺(tiling)。
若要使用平铺,在parallel_for_each 方法中的计算域上调用 extent::tile 方法,并在 lambda 表达式中使用 tiled_index 对象。
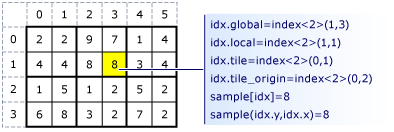
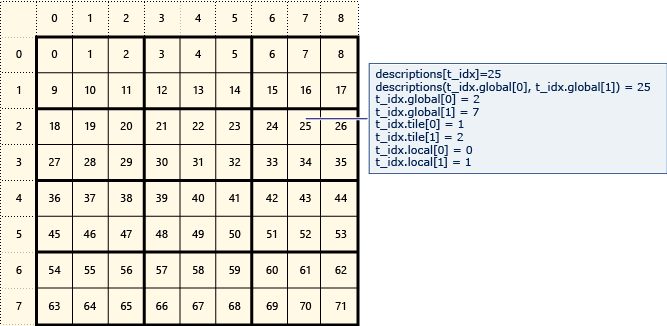
下面是两张来自微软官网的砖面(tile)的组织图,可以看到如何索引元素。
图中的idx是index类,sample是全局空间(array或array_view对象)
下图中的t_idx是index类,descriptions是全局空间(array或array_view对象)
下面这个来自微软官方的例子,每2*2=4根线程组成一个砖面(tile),计算砖面(tile)中元素的平均值。
使用平铺的好处是,从tile_static变量存取数据要比从全局空间(array和array_view对象)要快。为了从平铺中得到性能优势,我们的算法必须把计算域拆分为tile(砖面)然后把数据放到tile_static变量中加快数据存取速度。
注意不要使用类似下面的代码来累加tile(砖面)中的数据,
tile_static float total;
total += matrix[t_idx];‘
原因[1]total的初始值是不确定的,所以第二句代码的运算没有意义。
原因[2]由于tile(砖面)中的多根线程竞争同一个title_static变量,计算结果会不确定。
内存屏障(MemoryFences)
在restrict(amp)限定中,有两种内存必须要同步:
全局内存:array或array_view实例
tile_static内存:tile(砖面)内存
内存屏障确保两种内存的线程同步,要调用内存屏障可以使用下面三种方法:
tile_barrier::wait(或tile_barrier::wait_with_all_memory_fence)方法: 建立全局内存和tile_static内存的屏障。
tile_barrier::wait_with_global_memory_fence方法 : 仅建立全局内存的屏障
tile_barrier::wait_with_tile_static_memory_fence 方法 :仅建立tile_static内存的屏障
调用特定类型的屏障(fence)可以提高你应用的性能,在下面的例子中 tile_barrier::wait_with_tile_static_memory_fence 方法的调用代替tile_barrier::wait方法的调用提高了应用的性能。
restrict(amp)修饰的代码段是在加速器(GPU)上运行的,默认在里面的代码段,下断点不会Break(进入),在[Solution Explorer]窗口中点击项目名称,快捷键[Alt]+[Enter],打开当前项目属性页,[Configuration Properties]->[Debugging]->[Debugger Type]默认为“Auto”,改为“GPU Only”就可以Debug当前项目加速器(GPU)上运行的代码了。
据官网介绍,无符号整数的处理速度要比带符号整数快,所以尽量用无符号整数吧。
参考资料
《Using Tiles》
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/vstudio/hh873135.aspx
《使用平铺》
http://msdn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/library/vstudio/hh873135.aspx





















 2876
2876











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








