Problem Description
Ignatius被魔王抓走了,有一天魔王出差去了,这可是Ignatius逃亡的好机会.
魔王住在一个城堡里,城堡是一个A*B*C的立方体,可以被表示成A个B*C的矩阵,刚开始Ignatius被关在(0,0,0)的位置,离开城堡的门在(A-1,B-1,C-1)的位置,现在知道魔王将在T分钟后回到城堡,Ignatius每分钟能从一个坐标走到相邻的六个坐标中的其中一个.现在给你城堡的地图,请你计算出Ignatius能否在魔王回来前离开城堡(只要走到出口就算离开城堡,如果走到出口的时候魔王刚好回来也算逃亡成功),如果可以请输出需要多少分钟才能离开,如果不能则输出-1.
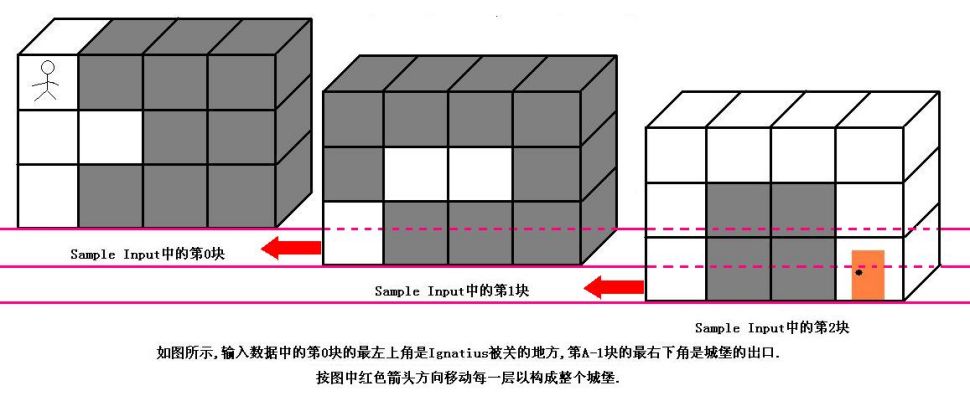
魔王住在一个城堡里,城堡是一个A*B*C的立方体,可以被表示成A个B*C的矩阵,刚开始Ignatius被关在(0,0,0)的位置,离开城堡的门在(A-1,B-1,C-1)的位置,现在知道魔王将在T分钟后回到城堡,Ignatius每分钟能从一个坐标走到相邻的六个坐标中的其中一个.现在给你城堡的地图,请你计算出Ignatius能否在魔王回来前离开城堡(只要走到出口就算离开城堡,如果走到出口的时候魔王刚好回来也算逃亡成功),如果可以请输出需要多少分钟才能离开,如果不能则输出-1.

Input
输入数据的第一行是一个正整数K,表明测试数据的数量.每组测试数据的第一行是四个正整数A,B,C和T(1<=A,B,C<=50,1<=T<=1000),它们分别代表城堡的大小和魔王回来的时间.然后是A块输入数据(先是第0块,然后是第1块,第2块......),每块输入数据有B行,每行有C个正整数,代表迷宫的布局,其中0代表路,1代表墙.(如果对输入描述不清楚,可以参考Sample Input中的迷宫描述,它表示的就是上图中的迷宫)
特别注意:本题的测试数据非常大,请使用scanf输入,我不能保证使用cin能不超时.在本OJ上请使用Visual C++提交.
特别注意:本题的测试数据非常大,请使用scanf输入,我不能保证使用cin能不超时.在本OJ上请使用Visual C++提交.
Output
对于每组测试数据,如果Ignatius能够在魔王回来前离开城堡,那么请输出他最少需要多少分钟,否则输出-1.
Sample Input
1 3 3 4 20 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0
Sample Output
11
代码:
//本题需要使用bfs进行搜索,使用dfs会超时
//下面是代码,随后附上bfs的模版
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int A,B,C,time,fu=1;
struct State
{
int x,y,z,Step_Counter;
} ;
struct node
{
int bc[55][55];
} aa[55],root[55];
bool CheckState(int a,int b,int c)
{
if(a<0||a>=A||b<0||b>=B||c<0||c>=C)
{
return 0;
}
else if(aa[a].bc[b][c]==1&&(a!=0||b!=0||c!=0)||root[a].bc[b][c]==1)
{
return 0;
}
else return 1;
}
int dir[6][3]= {0,-1,0,0,0,-1,0,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,0,-1,0,0};
void bfs(State st)
{
queue <State> q;
State now,next;
st.Step_Counter=0;
q.push(st);
root[st.x].bc[st.y][st.z]=1;
while(!q.empty())
{
now=q.front();
if(now.x==A-1&&now.y==B-1&&now.z==C-1)
{
if(now.Step_Counter<=time)
printf("%d\n",now.Step_Counter);
else printf("-1\n");
fu=0;
return;
}
for(int i=0; i<6; i++)
{
next.x=now.x+dir[i][0];
next.y=now.y+dir[i][1];
next.z=now.z+dir[i][2];
next.Step_Counter=now.Step_Counter+1;
if(CheckState(next.x,next.y,next.z))
{
q.push(next);
root[next.x].bc[next.y][next.z]=1;
}
}
q.pop();
}
return;
}
int main()
{
int t,i,j,k;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
scanf("%d%d%d%d",&A,&B,&C,&time);
for(i=0; i<A; i++)
for(j=0; j<B; j++)
for(k=0; k<C; k++)
scanf("%d",&aa[i].bc[j][k]);
if(aa[A-1].bc[B-1][C-1]==1||A+B+C-3>time)
{
printf("-1\n");
continue;
}
fu=1;
memset(root,0,sizeof(root));
State st;
st.x=st.y=st.z=0;
bfs(st);
if(fu) printf("-1\n");
}
return 0;
}
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=100;
bool vst[maxn][maxn]; // 访问标记
int dir[4][2]={0,1,0,-1,1,0,-1,0}; // 方向向量
struct State // BFS 队列中的状态数据结构
{
int x,y; // 坐标位置
int Step_Counter; // 搜索步数统计器
};
State a[maxn];
bool CheckState(State s) // 约束条件检验
{
if(!vst[s.x][s.y] && ...) // 满足条件
return 1;
else // 约束条件冲突
return 0;
}
void bfs(State st)
{
queue <State> q; // BFS 队列
State now,next; // 定义2 个状态,当前和下一个
st.Step_Counter=0; // 计数器清零
q.push(st); // 入队
vst[st.x][st.y]=1; // 访问标记
while(!q.empty())
{
now=q.front(); // 取队首元素进行扩展
if(now==G) // 出现目标态,此时为Step_Counter 的最小值,可以退出即可
{
...... // 做相关处理
return;
}
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
{
next.x=now.x+dir[i][0]; // 按照规则生成下一个状态
next.y=now.y+dir[i][1];
next.Step_Counter=now.Step_Counter+1; // 计数器加1
if(CheckState(next)) // 如果状态满足约束条件则入队
{
q.push(next);
vst[next.x][next.y]=1; //访问标记
}
}
q.pop(); // 队首元素出队
}
return;
}
int main()
{
......
return 0;
}






















 278
278

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








