异常处理机制
Java的异常处理机制主要依赖于try、catch、finally、throw和throws五个关键字。
- try后面紧跟花括号括起来的代码块,里面放置可能引起异常的代码块
- catch后面对应异常类型的代码块,用于表明该catch块用于处理这种类型的代码块。
- 多个catch后面还可以跟一个finally块,用于回收try块里打开的物理资源,异常机制保证finally块总会被执行。
- throws关键字主要在方法签名中使用,用于声明该方法可能抛出的异常。
- throw用于抛出一个实际异常,可以单独作为语句使用,抛出一个具体的异常对象。
使用try…catch捕获异常
- try块被执行一次,则try块后面只有一个catch块被执行
- try和catch后面的花括号都不可以省略
- try块里面声明的变量是代码块内局部变量,只在try块里有效
- 应把所有父类异常的catch块排在子类异常catch块的后面
public class DivTest {
public static void main(String[] args){
try{
int a = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
int b = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
int c = a / b;
System.out.println("相除的结果:"+ c);
}
catch(IndexOutOfBoundsException ie){
System.out.println("数组越界");
}
catch(NumberFormatException ne){
System.out.println("数字格式异常");
}
catch(ArithmeticException ae){
System.out.println("算数异常");
}
catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("未知异常");
}
}
}Java 7提供的多异常捕获
从Java 7开始,一个catch块可以捕获多种类型的异常。需要注意:
- 捕获多种类型的异常时,多种一场类型之间用竖线(|)隔开。
- 捕获多种类型的异常时,异常变量有隐式的final修饰,因此程序不能对异常变量重新赋值。
public class MultiExceptionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
int a = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
int b = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
int c = a / b;
System.out.println("相除的结果:"+ c);
}
catch(IndexOutOfBoundsException | NumberFormatException |ArithmeticException ie){
System.out.println("数组越界 或 数字格式异常 或 算数异常");
//捕获多异常时,异常变量默认有final修饰
//ie = new NumberFormatException();
}
catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("未知异常");
//捕获一种异常时,异常变量没有final修饰
e = new NumberFormatException();
}
}
}访问异常信息
所有异常对象都包含了如下几个常用方法:
- getMessage():返回该异常的详细描述字符串
- printStackTrace():将该异常的跟踪栈信息输出到标准错误输出中
- printStackTrace(PrintStream s):将该异常的跟踪栈信息输出到指定输出流
- getStackTrace():返回该异常的跟踪栈信息
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
public class AccessExceptionMsg {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("a.txt");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}java.io.FileNotFoundException: a.txt (系统找不到指定的文件。)
at java.io.FileInputStream.open0(Native Method)
at java.io.FileInputStream.open(Unknown Source)
at java.io.FileInputStream.<init>(Unknown Source)
at java.io.FileInputStream.<init>(Unknown Source)
at exceptionHandlingMechanism.AccessExceptionMsg.main(AccessExceptionMsg.java:10)
a.txt (系统找不到指定的文件。)使用finally回收资源
在程序try块中打开的物理资源必须在finally显示回收,如数据库连接,网络连接和磁盘文件等。
不管 那个catch块被执行,设置在try块或catch块中执行了return语句,finally块总会被执行。
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FinallyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream fis = null;
try
{
fis = new FileInputStream("a.txt");
}
catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
return;//执行finally
//System.exit(1);不执行finally
}
finally{
if(fis != null){
try{
fis.close();
}
catch(IOException io){
io.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("执行finally块");
}
}
}在通常情况下,不要在finally块中使用return或throw等导致方法终止的语句,一旦使用,将会导致try块和catch块中的return和throw语句失效。
public class FinallyFlowTest {
public static void main(String[] args){
boolean a = test();
System.out.println(a);//false
}
public static boolean test(){
try{
return true;
}
finally{
return false;
}
}
}Java 7自动关闭资源的try语句
Java 7允许在try关键字后紧跟一对圆括号,圆括号可以声明、初始化一个或多个资源,此处的资源指的是那些必须在程序结束时显示关闭的资源,try语句在结束时会自动关闭。
为了保证try语句可以正常关闭资源,这些资源实现类必须实现AutoCloseable或Closeable接口。
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintStream;
public class AutoCloseTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
try(
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("src/exceptionHandlingMechanism/AutoCloseTest.java"));
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream("a.txt"))
){
System.out.println(br.readLine());
ps.println("abcdefg");
}
}
}自动关闭资源的try块相当于包含了隐式的finally块。
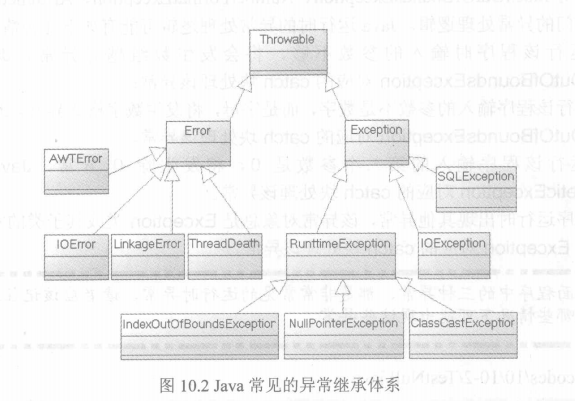
Checked异常和Runtime异常体系
JAVA异常分为Checked异常和Runtime异常(运行时异常)。
所有的RuntimeException类及其子类的实例被称为Runtime异常。
不是RuntimeException类及其子类的异常实例则被称为Checked异常。
throws声明抛出异常
当前方法不知道如何处理这种类型的异常,该异常应该由上一级调用者处理。
如果main方法也不知道如何处理这种类型的异常,也可以使用throws声明抛出异常,交给JVM处理。
JVM对异常的处理方法是,打印异常的跟踪栈信息,并终止程序运行。
一旦使用throws声明抛出该异常,程序就无需使用try…catch块来捕获该异常。
子类方法声明抛出的异常类型应该是父类方法声明抛出的异常类型的子类或相同。
throws声明抛出的语法格式如下:
throws ExceptionClass1 , ExceptionClass2...使用throw抛出异常
Java允许程序自行抛出异常,自行抛出异常使用throw语句来完成。
public class ThrowTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
throwChecked(-3);
}
catch(Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
throwRuntime(3);
}
public static void throwChecked(int a) throws Exception{
if(a > 0){
throw new Exception("a的值大于0,不符合要求");
}
}
public static void throwRuntime(int a){
if(a > 0){
throw new RuntimeException("a的值大于0,不符合要求");
}
}
}






















 399
399

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








