首先Android框架架构图:(来自网上,我觉得这张图看起来很清晰)

Linux内核启动之后就到Android Init进程,进而启动Android相关的服务和应用。
启动的过程如下图所示:(图片来自网上,后面有地址)
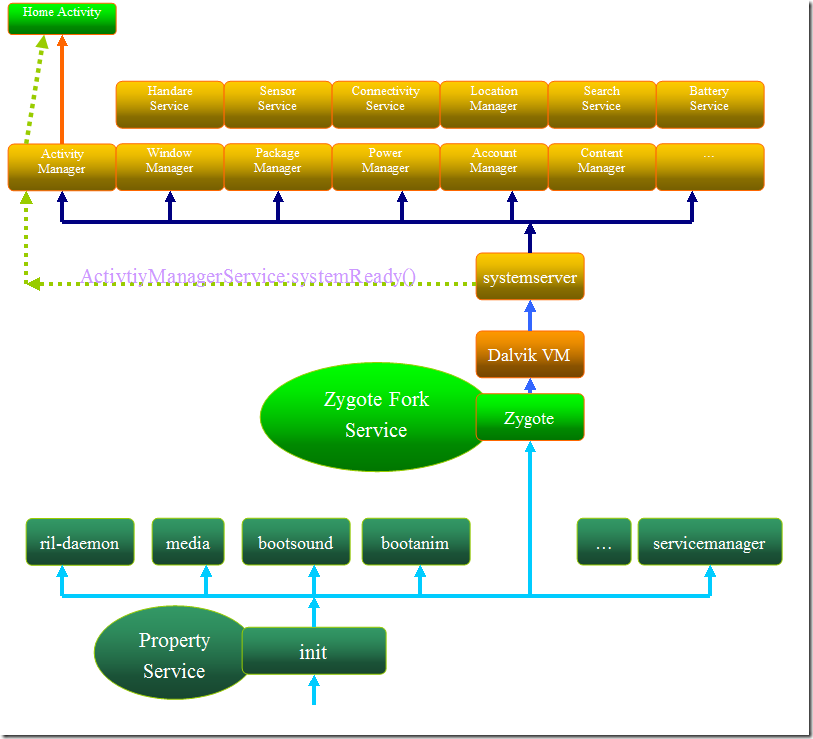
下面将从Android4.0源码中,和网络达人对此的总结中,对此过程加以学习了解和总结,
以下学习过程中代码片段中均有省略不完整,请参照源码。
一 Init进程的启动
init进程,它是一个由内核启动的用户级进程。内核自行启动(已经被载入内存,开始运行,
并已初始化所有的设备驱动程序和数据结构等)之后,就通过启动一个用户级程序init的方式,完成引导进程。init始终是第一个进程。
启动过程就是代码init.c中main函数执行过程:system\core\init\init.c
在函数中执行了:文件夹建立,挂载,rc文件解析,属性设置,启动服务,执行动作,socket监听……
下面看两个重要的过程:rc文件解析和服务启动。
1 rc文件解析
.rc文件是Android使用的初始化脚本文件 (System/Core/Init/readme.txt中有描述:
four broad classes of statements which are Actions, Commands, Services, and Options.)
其中Command 就是系统支持的一系列命令,如:export,hostname,mkdir,mount,等等,其中一部分是 linux 命令,
还有一些是 android 添加的,如:class_start <serviceclass>: 启动服务,class_stop <serviceclass>:关闭服务,等等。
其中Options是针对 Service 的选项的。
系统初始化要触发的动作和要启动的服务及其各自属性都在rc脚本文件中定义。 具体看一下启动脚本:\system\core\rootdir\init.rc
在解析rc脚本文件时,将相应的类型放入各自的List中:
\system\core\init\Init_parser.c :init_parse_config_file( )存入到
action_queue、 action_list、 service_list中,解析过程可以看一下parse_config函数,类似状态机形式挺有意思。
这其中包含了服务:adbd、servicemanager、vold、ril-daemon、debuggerd、surfaceflinger、zygote、media……
2 服务启动
文件解析完成之后将service放入到service_list中。
文件解析完成之后将service放入到service_list中。
\system\core\init\builtins.c
Service的启动是在do_class_start函数中完成:
int do_class_start(int nargs, char **args)
{
service_for_each_class(args[1], service_start_if_not_disabled);
return 0;
}
遍历所有名称为classname,状态不为SVC_DISABLED的Service启动
void service_for_each_class(const char *classname,
void (*func)(struct service *svc))
{
……
}
static void service_start_if_not_disabled(struct service *svc)
{
if (!(svc->flags & SVC_DISABLED)) {
service_start(svc, NULL);
}
}
do_class_start对应的命令:
KEYWORD(class_start, COMMAND, 1, do_class_start)
init.rc文件中搜索class_start:class_start main 、class_start core、……
main、core即为do_class_start参数classname
init.rc文件中Service class名称都是main:
service drm /system/bin/drmserver
class main
service surfaceflinger /system/bin/surfaceflinger
class main
于是就能够通过main名称遍历到所有的Service,将其启动。
do_class_start调用:
init.rc中
on boot //action
class_start core //执行command 对应 do_class_start
class_start main
Init进程main函数中:
system/core/init/init.c中:
int main(){
//挂在文件
//解析配置文件:init.rc……
//初始化化action queue
……
for(;;){
execute_one_command();
restart_processes();
for (i = 0; i < fd_count; i++) {
if (ufds[i].revents == POLLIN) {
if (ufds[i].fd == get_property_set_fd())
handle_property_set_fd();
else if (ufds[i].fd == get_keychord_fd())
handle_keychord();
else if (ufds[i].fd == get_signal_fd())
handle_signal();
}
}
}
}
循环调用service_start,将状态SVC_RESTARTING启动, 将启动后的service状态设置为SVC_RUNNING。
pid=fork();
execve();
在消息循环中:Init进程执行了Android的Command,启动了Android的NativeService,监听Service的变化需求,Signal处理。
Init进程是作为属性服务(Property service),维护这些NativeService。
二 ServiceManager启动
在.rc脚本文件中zygote的描述:
service servicemanager /system/bin/servicemanager
class core
user system
group system
critical
onrestart restart zygote
onrestart restart media
onrestart restart surfaceflinger
onrestart restart drm
ServiceManager用来管理系统中所有的binder service,不管是本地的c++实现的还是java语言实现的都需要
这个进程来统一管理,最主要的管理就是,注册添加服务,获取服务。所有的Service使用前都必须先在servicemanager中进行注册。
do_find_service( )
do_add_service( )
svcmgr_handler( )
代码位置:frameworks\base\cmds\servicemanager\Service_manager.c
三 Zygote进程的启动
Zygote这个进程是非常重要的一个进程,Zygote进程的建立是真正的Android运行空间,初始化建立的Service都是Navtive service.
(1) 在.rc脚本文件中zygote的描述:
service zygote /system/bin/app_process -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --start-system-server
class main
socket zygote stream 666
onrestart write /sys/android_power/request_state wake
onrestart write /sys/power/state on
onrestart restart media
onrestart restart netd
参数:--zygote --start-system-server
代码位置:frameworks/base/cmds/app_process/app_main.cpp
上面的参数在这里就会用上,决定是否要启动和启动那些进程。
int main( ){
AppRuntime runtime;
if (zygote) {
runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit",
startSystemServer ? "start-system-server" : "");
}
}
class AppRuntime : public AndroidRuntime{};
(2) 接着到了AndroidRuntime类中:
frameworks\base\core\jni\AndroidRuntime.cpp
void start(const char* className, const char* options){
// start the virtual machine Java在虚拟机中运行的
JNIEnv* env;
if (startVm(&mJavaVM, &env) != 0) {
return;
}
//向刚刚新建的虚拟机注册JNI本地接口
if (startReg(env) < 0) {
return;
}
// jni 调用 java 方法,获取对应类的静态main方法
jmethodID startMeth = env->GetStaticMethodID(startClass,
"main","([Ljava/lang/String;)V");
// jni调用 java方法,调用到ZygoteInit类的main函数
jclass startClass = env->FindClass(className);
env->CallStaticVoidMethod(startClass, startMeth, strArray);
}
到了ZygoteInit.java中的静态main函数中,从C++ ——》JAVA
(3)ZygoteInit
真正Zygote进程:
frameworks\base\core\java\com\android\internal\os\ZygoteInit.java
public static void main(String argv[]) {
//Registers a server socket for zygote command connections
registerZygoteSocket();
//Loads and initializes commonly used classes and
//used resources that can be shared across processes
preload();
// Do an initial gc to clean up after startup
gc();
if (argv[1].equals("start-system-server")) {
startSystemServer();
}
/**
* Runs the zygote process's select loop. Accepts new connections as
* they happen, and reads commands from connections one spawn-request's
* worth at a time.
*/
runSelectLoopMode(); //loop中
/**
* Close and clean up zygote sockets. Called on shutdown and on the
* child's exit path.
*/
closeServerSocket();
}
Zygote就建立好了,利用Socket通讯,接收请求,Fork应用程序进程,进入Zygote进程服务框架中。
四 SystemServer启动
(1)在Zygote进程进入循环之前,调用了startSystemServer( );
private static boolean startSystemServer(){
/* Request to fork the system server process 孵化新的进程 */
ZygoteConnection.Arguments parsedArgs = null;
pid = Zygote.forkSystemServer(
parsedArgs.uid, parsedArgs.gid,
parsedArgs.gids,
parsedArgs.debugFlags,
null,
parsedArgs.permittedCapabilities,
parsedArgs.effectiveCapabilities);
/* For child process 对新的子进程设置 */
if (pid == 0) {
handleSystemServerProcess(parsedArgs);
}
}
void handleSystemServerProcess(parsedArgs){
closeServerSocket();
//"system_server"
Process.setArgV0(parsedArgs.niceName);
//Pass the remaining arguments to SystemServer.
RuntimeInit.zygoteInit(parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion,
parsedArgs.remainingArgs);
/* should never reach here */
}
(2)RuntimeInit中:
frameworks\base\core\java\com\android\internal\os\RuntimeInit.java
//The main function called when started through the zygote process.
void zygoteInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv){
applicationInit(targetSdkVersion, argv);
}
void applicationInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv){
// Remaining arguments are passed to the start class's static main
invokeStaticMain(args.startClass, args.startArgs);
}
void invokeStaticMain(String className, String[] argv){
Class<?> cl;
cl = Class.forName(className);
//获取SystemServer的main方法,抛出MethodAndArgsCaller异常
Method m;
m = cl.getMethod("main", new Class[] { String[].class });
int modifiers = m.getModifiers();
throw new ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller(m, argv);
}
(3)从startSystemServer开始执行并没有去调用SystemServer的任何方法,
只是通过反射获取了main方法,付给了MethodAndArgsCaller,并抛出了MethodAndArgsCaller异常。
此异常是在哪里处理的呢?
回到startSystemServer( )函数的调用处:
在ZygoteInit的main函数中:
public static void main(String argv[]) {
try {
……
if (argv[1].equals("start-system-server")) {
startSystemServer(); //这里如果抛出异常,跳过下面流程
}
runSelectLoopMode(); //loop中
……
} catch (MethodAndArgsCaller caller) {
caller.run(); //处理的异常
}
}
如果startSystemServer抛出了异常,跳过执行ZygoteInit进程的循环,这是怎么回事呢?
在startSystemServer中异常是由handleSystemServerProcess抛出,而
pid = Zygote.forkSystemServer( )
/* For child process 仅对新的子进程设置 */
if (pid == 0) {
handleSystemServerProcess(parsedArgs);
}
// Zygote.forkSystemServer根据参数fork 出一个子进程,若成功调用,则返回两次:
一次返回的是 zygote 进程的 pid ,值大于0;一次返回的是子进程 pid,值等于0否则,出错返回-1;
caller.run();
MethodAndArgsCaller run函数:调用前面所提到的
//SystemServer main方法
m = cl.getMethod("main", new Class[] { String[].class });
启动了进程SystemServer。
(4)SystemServer的执行 init1( )
//frameworks\base\services\java\com\android\server\SystemServer.java
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.loadLibrary("android_servers");
/*
* This method is called from Zygote to initialize the system.
* This will cause the native services (SurfaceFlinger, AudioFlinger, etc..)
* to be started. After that it will call back
* up into init2() to start the Android services.
*/
init1(args); //native 完了回调init2( )
}
//init1:
frameworks/base/services/jni/com_android_server_SystemServer.cpp:: android_server_SystemServer_init1( )
中调用:system_init
extern "C" status_t system_init()
{
sp<ProcessState> proc(ProcessState::self());
sp<IServiceManager> sm = defaultServiceManager();
//启动SurfaceFlinger 和传感器
property_get("system_init.startsurfaceflinger", propBuf, "1");
SurfaceFlinger::instantiate();
property_get("system_init.startsensorservice", propBuf, "1");
SensorService::instantiate();
// And now start the Android runtime. We have to do this bit
// of nastiness because the Android runtime initialization requires
// some of the core system services to already be started.
// All other servers should just start the Android runtime at
// the beginning of their processes's main(), before calling
// the init function.
AndroidRuntime* runtime = AndroidRuntime::getRuntime();
//回调 com.android.server.SystemServer init2 方法
JNIEnv* env = runtime->getJNIEnv();
jclass clazz = env->FindClass("com/android/server/SystemServer");
jmethodID methodId = env->GetStaticMethodID(clazz, "init2", "()V");
env->CallStaticVoidMethod(clazz, methodId);
//启动线程池 做为binder 服务
ProcessState::self()->startThreadPool();
IPCThreadState::self()->joinThreadPool();
return NO_ERROR;
}
ProcessState:
每个进程在使用binder 机制通信时,均需要维护一个ProcessState 实例来描述当前进程在binder 通信时的binder 状态。
ProcessState 有如下2 个主要功能:
1. 创建一个thread, 该线程负责与内核中的binder 模块进行通信,称该线程为Pool thread ;
2. 为指定的handle 创建一个BpBinder 对象,并管理该进程中所有的BpBinder 对象。
Pool thread:
在Binder IPC 中,所有进程均会启动一个thread 来负责与BD 来直接通信,也就是不停的读写BD ,
这个线程的实现主体是一个IPCThreadState 对象,下面会介绍这个类型。
下面是Pool thread 的启动方式:
ProcessState::self()->startThreadPool();
IPCThreadState :
IPCThreadState 也是以单例模式设计的。由于每个进程只维护了一个ProcessState 实例,同时ProcessState 只启动一个Pool thread ,
也就是说每一个进程只会启动一个Pool thread ,因此每个进程则只需要一个IPCThreadState 即可。
Pool thread 的实际内容则为:
IPCThreadState::self()->joinThreadPool();
(5)SystemServer的执行 init2( )
public static final void init2() {
//建立线程来处理
Thread thr = new ServerThread();
thr.setName("android.server.ServerThread");
thr.start();
}
//看看线程ServerThread里面都做了什么事情?
public void run() {
addBootEvent(new String("Android:SysServerInit_START"));
Looper.prepare();
android.os.Process.setThreadPriority(
android.os.Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_FOREGROUND);
//初始化服务,创建各种服务实例,如:电源、网络、Wifi、蓝牙,USB等,
//初始化完成以后加入到 ServiceManager中,
//事我们用 Context.getSystemService (String name) 才获取到相应的服务
PowerManagerService power = null;
NetworkManagementService networkManagement = null;
WifiP2pService wifiP2p = null;
WindowManagerService wm = null;
BluetoothService bluetooth = null;
UsbService usb = null;
NotificationManagerService notification = null;
StatusBarManagerService statusBar = null;
……
power = new PowerManagerService();
ServiceManager.addService(Context.POWER_SERVICE, power);
……
// ActivityManagerService作为ApplicationFramework最重要的服务
ActivityManagerService.setSystemProcess();
ActivityManagerService.installSystemProviders();
ActivityManagerService.self().setWindowManager(wm);
// We now tell the activity manager it is okay to run third party
// code. It will call back into us once it has gotten to the state
// where third party code can really run (but before it has actually
// started launching the initial applications), for us to complete our
// initialization.
//系统服务初始化准备就绪,通知各个模块
ActivityManagerService.self().systemReady(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
startSystemUi(contextF);
batteryF.systemReady();
networkManagementF.systemReady();
usbF.systemReady();
……
// It is now okay to let the various system services start their
// third party code...
appWidgetF.systemReady(safeMode);
wallpaperF.systemReady();
}
});
//
//BOOTPROF
addBootEvent(new String("Android:SysServerInit_END"));
Looper.loop();
}
到这里系统ApplicationFramework层的XxxServiceManager准备就绪,可以开始跑上层应用了,我们的第一个上层应用HomeLauncher。
HomeActivity又是如何启动的呢?
Activity的启动必然和ActivityManagerService有关,我们需要去看看
ActivityManagerService.systemReady( )中都干了些什么。
五 Home界面启动
public void systemReady(final Runnable goingCallback) {
……
//ready callback
if (goingCallback != null)
goingCallback.run();
synchronized (this) {
// Start up initial activity.
// ActivityStack mMainStack;
mMainStack.resumeTopActivityLocked(null);
}
……
}
final boolean resumeTopActivityLocked(ActivityRecord prev) {
// Find the first activity that is not finishing.
ActivityRecord next = topRunningActivityLocked(null);
if (next == null) {
// There are no more activities! Let's just start up the
// Launcher...
if (mMainStack) {
//ActivityManagerService mService;
return mService.startHomeActivityLocked();
}
}
……
}
然后就启动了Home界面,完成了整个Android启动流程。
整个过程如下:

Android开机启动流程初探
l Init进程
Android系统在启动时首先会启动Linux系统,引导加载Linux Kernel并启动init进程。Init进程是一个由内核启动的用户级进程,是Android系统的第一个进程。该进程的相关代码在platform\system\core\init\init.c。在main函数中,有如下代码:
open_devnull_stdio();
log_init();
INFO("reading config file\n");
init_parse_config_file("/init.rc");
/* pull the kernel commandline and ramdisk properties file in */
import_kernel_cmdline(0);
get_hardware_name(hardware, &revision);
snprintf(tmp, sizeof(tmp), "/init.%s.rc", hardware);
init_parse_config_file(tmp);
这里会加载解析init.rc和init.hardware.rc两个初始化脚本。*.rc文件定义了在init进程中需要启动哪些进程服务和执行哪些动作。其详细说明参见platform\system\core\init\reademe.txt。init.rc见如下定义:
service servicemanager /system/bin/servicemanager
user system
critical
onrestart restart zygote
onrestart restart media
service vold /system/bin/vold
socket vold stream 0660 root mount
ioprio be 2
service netd /system/bin/netd
socket netd stream 0660 root system
socket dnsproxyd stream 0660 root inet
service debuggerd /system/bin/debuggerd
service ril-daemon /system/bin/rild
socket rild stream 660 root radio
socket rild-debug stream 660 radio system
user root
group radio cache inet misc audio sdcard_rw
service zygote /system/bin/app_process -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --start-system-server
socket zygote stream 666
onrestart write /sys/android_power/request_state wake
onrestart write /sys/power/state on
onrestart restart media
onrestart restart netd
service drm /system/bin/drmserver
user drm
group system root inet
具体解析过程见platform\system\core\init\Init_parser.c。解析所得服务添加到service_list中,动作添加到action_list中。
接下来在main函数中执行动作和启动进程服务:
execute_one_command();
restart_processes()
通常init过程需要创建一些系统文件夹并启动USB守护进程、Android Debug Bridge守护进程、Debug守护进程、ServiceManager进程、Zygote进程等。
l ServiceManager进程
ServiceManager进程是所有服务的管理器。由init.rc对ServiceManager的描述service servicemanager /system/bin/servicemanager可知servicemanager进程从platform\frameworks\base\cmd\servicemanager\Service_manager.cpp启动。在main函数中有如下代码:
int main(int argc, char **argv) { struct binder_state *bs; void *svcmgr = BINDER_SERVICE_MANAGER; bs = binder_open(128*1024); if (binder_become_context_manager(bs)) { LOGE("cannot become context manager (%s)\n", strerror(errno)); return -1; } svcmgr_handle = svcmgr; binder_loop(bs, svcmgr_handler); return 0; }
首先调用binder_open()打开Binder设备(/dev/binder),调用binder_become_context_manager()把当前进程设置为ServiceManager。ServiceManager本身就是一个服务。
int binder_become_context_manager(struct binder_state *bs) { return ioctl(bs->fd, BINDER_SET_CONTEXT_MGR, 0); }
最后binder_loop()进入循环状态,并设置svcmgr_handler回调函数等待添加、查询、获取服务等请求。
l Zygote进程
Zygote进程用于产生其他进程。由init.rc对zygote的描述service zygot /system/bin/app_process可知zygote进程从platfrom\frameworks\base\cmds\app_process\App_main.cpp启动。在main函数中有如下代码:
if (0 == strcmp("--zygote", arg)) { bool startSystemServer = (i < argc) ? strcmp(argv[i], "--start-system-server") == 0 : false; setArgv0(argv0, "zygote"); set_process_name("zygote"); runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit", startSystemServer); } else { set_process_name(argv0); runtime.mClassName = arg; // Remainder of args get passed to startup class main() runtime.mArgC = argc-i; runtime.mArgV = argv+i; LOGV("App process is starting with pid=%d, class=%s.\n", getpid(), runtime.getClassName()); runtime.start(); }
首先创建AppRuntime,即AndroidRuntime,建立了一个Dalvik虚拟机。通过这个runtime传递com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit参数,从而由Dalvik虚拟机运行ZygoteInit.java的main(),开始创建Zygote进程。在其main()中,如下所示:
registerZygoteSocket();
EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_START,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
preloadClasses();
//cacheRegisterMaps();
preloadResources();
EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_END,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
// Finish profiling the zygote initialization.
SamplingProfilerIntegration.writeZygoteSnapshot();
// Do an initial gc to clean up after startup
gc();
// If requested, start system server directly from Zygote
if (argv.length != 2) {
throw new RuntimeException(argv[0] + USAGE_STRING);
}
if (argv[1].equals("true")) {
startSystemServer();
} else if (!argv[1].equals("false")) {
throw new RuntimeException(argv[0] + USAGE_STRING);
}
首先通过registerZygoteSocket()登记端口,接着preloadClasses()装载相关类。这里大概要装载1000多个类,具体装载类见platform\frameworks\base\preloaded-classes。这个文件有WritePreloadedClassFile类自动生成。分析该类的main函数,有如下一段筛选类的代码:
// Preload classes that were loaded by at least 2 processes. Hopefully, // the memory associated with these classes will be shared. for (LoadedClass loadedClass : root.loadedClasses.values()) { Set<String> names = loadedClass.processNames(); if (!Policy.isPreloadable(loadedClass)) { continue; } if (names.size() >= MIN_PROCESSES || (loadedClass.medianTimeMicros() > MIN_LOAD_TIME_MICROS && names.size() > 1)) { toPreload.add(loadedClass); } } int initialSize = toPreload.size(); System.out.println(initialSize + " classses were loaded by more than one app."); // Preload eligable classes from applications (not long-running // services). for (Proc proc : root.processes.values()) { if (proc.fromZygote() && !Policy.isService(proc.name)) { for (Operation operation : proc.operations) { LoadedClass loadedClass = operation.loadedClass; if (shouldPreload(loadedClass)) { toPreload.add(loadedClass); } } } }
其中MIN_LOAD_TIME_MICROS等于1250,当类的装载时间大于1.25ms,则需要预装载。
Policy.isPreloadable()定于如下:
/**Reports if the given class should be preloaded. */ public static boolean isPreloadable(LoadedClass clazz) { return clazz.systemClass && !EXCLUDED_CLASSES.contains(clazz.name); }
其中EXCLUDED_CLASSES如下定义:
/** * Classes which we shouldn't load from the Zygote. */ private static final Set<String> EXCLUDED_CLASSES = new HashSet<String>(Arrays.asList( // Binders "android.app.AlarmManager", "android.app.SearchManager", "android.os.FileObserver", "com.android.server.PackageManagerService$AppDirObserver", // Threads "android.os.AsyncTask", "android.pim.ContactsAsyncHelper", "java.lang.ProcessManager" ));
这几个Binders和Thread是不会被预加载的。
另外还有一些application需要装载,要求满足条件proc.fromZygote()且不是属于常驻内存的服务。SERVICES定义如下:
/** * Long running services. These are restricted in their contribution to the * preloader because their launch time is less critical. */ // TODO: Generate this automatically from package manager. private static final Set<String> SERVICES = new HashSet<String>(Arrays.asList( "system_server", "com.google.process.content", "android.process.media", "com.android.bluetooth", "com.android.calendar", "com.android.inputmethod.latin", "com.android.phone", "com.google.android.apps.maps.FriendService", // pre froyo "com.google.android.apps.maps:FriendService", // froyo "com.google.android.apps.maps.LocationFriendService", "com.google.android.deskclock", "com.google.process.gapps", "android.tts" ));
preloaded-classes是在下载源码的时候生成,WritePreloadedClassFile类并没有被用到,但可以通过这个类了解Android系统对预加载类的默认要求,参考修改preloaded-classes文件,减少开机初始化时要预加载的类,提高开机速度。
最后来通过startSystemServer()启动SystemServer进程。见如下代码:
/* Hardcoded command line to start the system server */ String args[] = { "--setuid=1000", "--setgid=1000", "--setgroups=1001,1002,1003,1004,1005,1006,1007,1008,1009,1010,1018,3001,3002,3003", "--capabilities=130104352,130104352", "--runtime-init", "--nice-name=system_server", "com.android.server.SystemServer", }; ZygoteConnection.Arguments parsedArgs = null; int pid; try { parsedArgs = new ZygoteConnection.Arguments(args); /* * Enable debugging of the system process if *either* the command line flags * indicate it should be debuggable or the ro.debuggable system property * is set to "1" */ int debugFlags = parsedArgs.debugFlags; if ("1".equals(SystemProperties.get("ro.debuggable"))) debugFlags |= Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_DEBUGGER; /* Request to fork the system server process */ pid = Zygote.forkSystemServer( parsedArgs.uid, parsedArgs.gid, parsedArgs.gids, debugFlags, null, parsedArgs.permittedCapabilities, parsedArgs.effectiveCapabilities)
Zygote包装了Linux的fork。forkSystemServer()调用forkAndSpecialize(),最终穿过虚拟机调用platform\dalvik\vm\native\dalvik_system_Zygote.c中Dalvik_dalvik_system_Zygote_forkAndSpecialize()。由dalvik完成fork新的进程。
main()最后会调用runSelectLoopMode(),进入while循环,由peers创建新的进程。
l SystemService进程
SystemService用于创建init.rc定义的服务之外的所有服务。在main()的最后有如下代码:
// The system server has to run all of the time, so it needs to be // as efficient as possible with its memory usage. VMRuntime.getRuntime().setTargetHeapUtilization(0.8f); System.loadLibrary("android_servers"); init1(args);
Init1()是在native空间实现的,用于启动native空间的服务,其实现在com_android_server_SystemServer.cpp中的android_server_SystemServer_init1():
static void android_server_SystemServer_init1(JNIEnv* env, jobject clazz) { system_init(); }
而system_init()服务初始化创建native层的各个服务:
// Start the sensor service SensorService::instantiate(); // On the simulator, audioflinger et al don't get started the // same way as on the device, and we need to start them here if (!proc->supportsProcesses()) { // Start the AudioFlinger AudioFlinger::instantiate(); // Start the media playback service MediaPlayerService::instantiate(); // Start the camera service CameraService::instantiate(); // Start the audio policy service AudioPolicyService::instantiate(); }
最后通过如下代码:
LOGI("System server: starting Android services.\n"); runtime->callStatic("com/android/server/SystemServer", "init2");
回到SystemServer.java,调用init2():
public static final void init2() { Slog.i(TAG, "Entered the Android system server!"); Thread thr = new ServerThread(); thr.setName("android.server.ServerThread"); thr.start(); }
Init2启动一个线程,专门用来启动java空间的所有服务。如下代码所示启动部分服务:
Slog.i(TAG, "Content Manager"); ContentService.main(context, factoryTest == SystemServer.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL); Slog.i(TAG, "System Content Providers"); ActivityManagerService.installSystemProviders(); Slog.i(TAG, "Battery Service"); battery = new BatteryService(context); ServiceManager.addService("battery", battery); Slog.i(TAG, "Lights Service"); lights = new LightsService(context); Slog.i(TAG, "Vibrator Service"); ServiceManager.addService("vibrator", new VibratorService(context)); // only initialize the power service after we have started the // lights service, content providers and the battery service. power.init(context, lights, ActivityManagerService.getDefault(), battery); Slog.i(TAG, "Alarm Manager"); AlarmManagerService alarm = new AlarmManagerService(context); ServiceManager.addService(Context.ALARM_SERVICE, alarm);
并且把这些服务添加到ServiceManager中,以便管理和进程间通讯。
在该线程后半部分,ActivityManagerService会等待AppWidget、WallPaper、IMM等systemReady后调用自身的systemReady()。
((ActivityManagerService)ServiceManager.getService("activity")) .setWindowManager(wm); // Skip Bluetooth if we have an emulator kernel // TODO: Use a more reliable check to see if this product should // support Bluetooth - see bug 988521 if (SystemProperties.get("ro.kernel.qemu").equals("1")) { Slog.i(TAG, "Registering null Bluetooth Service (emulator)"); ServiceManager.addService(BluetoothAdapter.BLUETOOTH_SERVICE, null); } else if (factoryTest == SystemServer.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL) { Slog.i(TAG, "Registering null Bluetooth Service (factory test)"); ServiceManager.addService(BluetoothAdapter.BLUETOOTH_SERVICE, null); } else { Slog.i(TAG, "Bluetooth Service"); bluetooth = new BluetoothService(context); ServiceManager.addService(BluetoothAdapter.BLUETOOTH_SERVICE, bluetooth); bluetooth.initAfterRegistration(); bluetoothA2dp = new BluetoothA2dpService(context, bluetooth); ServiceManager.addService(BluetoothA2dpService.BLUETOOTH_A2DP_SERVICE, bluetoothA2dp); int bluetoothOn = Settings.Secure.getInt(mContentResolver, Settings.Secure.BLUETOOTH_ON, 0); if (bluetoothOn > 0) { bluetooth.enable(); } }
而在ActivityManagerService的systemReady()最后会执行如下代码:
mMainStack.resumeTopActivityLocked(null);
由于Activity管理栈为空,因此启动Launcher。
// Find the first activity that is not finishing. ActivityRecord next = topRunningActivityLocked(null); // Remember how we'll process this pause/resume situation, and ensure // that the state is reset however we wind up proceeding. final boolean userLeaving = mUserLeaving; mUserLeaving = false; if (next == null) { // There are no more activities! Let's just start up the // Launcher... if (mMainStack) { return mService.startHomeActivityLocked(); } }
在startHomeActivityLocked()中创建一个带Category为CATEGORY_HOME的Intent,由此去启动相应Activity,即Launcher。
Intent intent = new Intent( mTopAction, mTopData != null ? Uri.parse(mTopData) : null); intent.setComponent(mTopComponent); if (mFactoryTest != SystemServer.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL) { intent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_HOME); }
这样,Android系统便启动起来进入到待机界面。
参考文档:
http://blog.csdn.net/maxleng/article/details/5508372
http://www.cnblogs.com/linucos/archive/2012/05/22/2513760.html#commentform
http://www.cnblogs.com/idiottiger/archive/2012/05/25/2516295.html
Android系统启动流程 -- android:http://blog.csdn.net/lizhiguo0532/article/details/7028910























 705
705

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








