Fragment:
碎片,是一种可以嵌在活动中的UI片段.
1.静态:在布局文件定义一个
<fragment
android:id="@+id/fragment1"
android:name="com.example.gp08_day23_fragment2.fragment.TestFragment"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
//获取碎片管理器----可以直接在 activity获取到
manager = getFragmentManager();
//使用碎片管理器得到需要的碎片对象
Fragment fragment = manager.findFragmentById(R.id.fragment1);
//得到碎片对象中的布局对象
View view = fragment.getView();2.动态:
—-FragmentManager
—-事务的使用
—-activity给fragment传值(Bundle对象)
2.1动态添加fragment步骤:
1)在布局文件中给fragment占个位,一般用FrameLayout
2)创建fragment实例
3)获取到FragmentManager,在活动中可以直接调用getFragmentManager()
4)开启一个事务,通过调用beginTransaction方法开启
5)向容器内加入fragment,一般使用replace()方法实现,需要传入容器的id(就是在布局文件中占的位置)和fragment实例
6)提交事务,调用commit()方法完成。
2.2先介绍一下传值
传值:
//使用碎片管理器对象得到事务对象
FragmentTransaction transaction = manager.beginTransaction();//开启事务
// Fragment f = manager.findFragmentByTag("flag");
// if(f==null)
// {
// TestFragment fragment = new TestFragment();
// transaction.add(R.id.container, fragment, "flag");
// }
TestFragment fragment = new TestFragment();
//activity给fragment传参数
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putString("msg", "hehe"+new Date());
fragment.setArguments(bundle);
//replace是替换掉之前的fragment对象(remove--->add)
transaction.replace(R.id.container, fragment);
//提交事务
transaction.commit();//事务只能提交一次
接收:
public class TestFragment extends Fragment {
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
TextView textView = new TextView(getActivity());
textView.setTextSize(20);
//获取传递过来的参数
Bundle bundle = getArguments();
String value = bundle.getString("msg");
textView.setText(value);
return textView;
}
}关键是这个:
//activity给fragment传参数
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putString(“msg”, “hehe”+new Date());
fragment.setArguments(bundle);
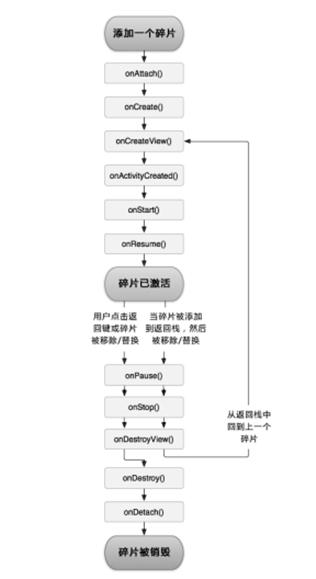
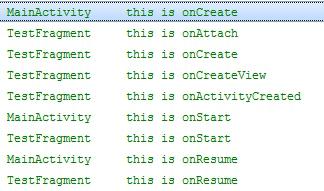
3.生命周期
Fragment的生命周期:11个方法
* 1):初始化:对应于 activity的onCreate()
* onAttach(Activity) 和所属的activity关联
* onCreate(Bundle )fragment的初始化
* onCreateView()初始化fragment显示的UI视图
* onActivityCreated()当activity的 onCreate()方法执行完(说明 activity的初始化已经完成)
* 2):显示,隐藏
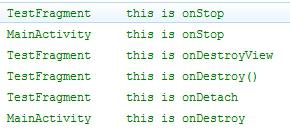
* onStart(),onResume(),onPause(),onStop()
* 3):销毁
* onDestroyView() 销毁fragment显示的UI视图(View 对象)
* onDestroy() 销毁的是fragment
* onDettach() 和所属的activity断开
实例:源码地址见后面
和Activity联动:
创建时:从外到内创建
关闭时:从内到外销毁
4.自定义模拟回退栈
// 作为回退栈
private LinkedList<Fragment> stack = new LinkedList<Fragment>();
public void addFragment(View v) {
TestFragment fragment = new TestFragment();
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putString("msg", "hahahaha" + new Date());
fragment.setArguments(bundle);
// 如果栈为空直接入栈,不为空则把当前的activity隐藏,然后加入新的fragment
if (stack.size() == 0)
getFragmentManager().beginTransaction()
.add(R.id.container, fragment).commit();
else getFragmentManager().beginTransaction().hide(stack.peek())// 隐藏栈顶的
.add(R.id.container, fragment).commit();
// 入栈
stack.push(fragment);
}
// 点击回退按钮显示上一个fragment
public void backFragment(View v) {
if (!stack.isEmpty()) {
getFragmentManager().beginTransaction().remove(stack.poll())
.commit();
}
if (!stack.isEmpty()) getFragmentManager().beginTransaction().show(stack.peek()).commit();
}效果图:
5.使用baskToStack(null);方法
public void addFragment(View v) {
TestFragment fragment = new TestFragment();
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putString("msg", "xixi" + new Date());
fragment.setArguments(bundle);
FragmentTransaction tran = getFragmentManager().beginTransaction();
tran.add(R.id.container, fragment);//remove1 add 2
tran.addToBackStack(null);//把事务加入当前的回退栈 回滚
tran.commit();
}
// 点击回退按钮显示上一个fragment
public void backFragment(View v) {
onBackPressed();
}效果和自定义回退栈相同。
–>使用回退栈的作用主要是返回时返回到上一个fragment
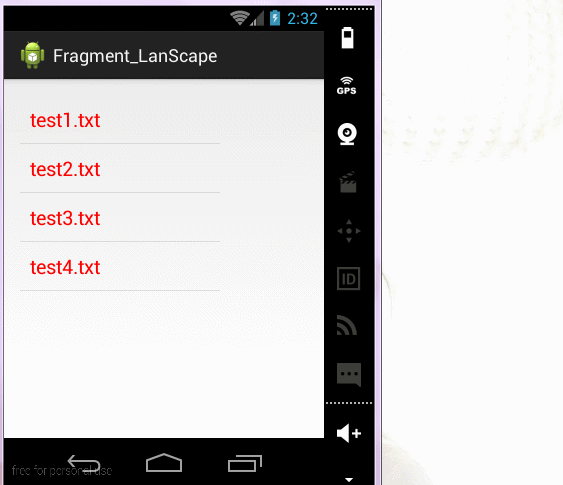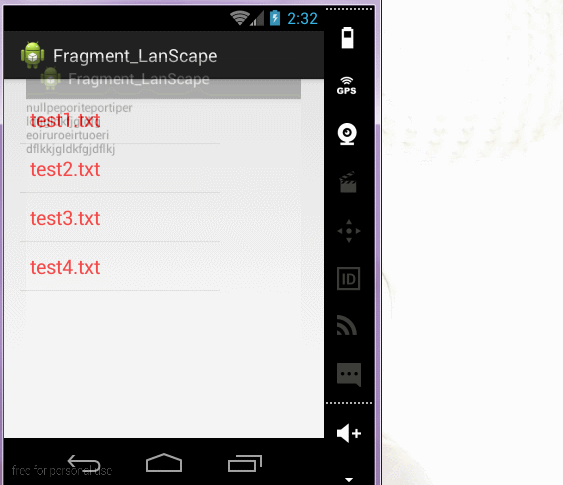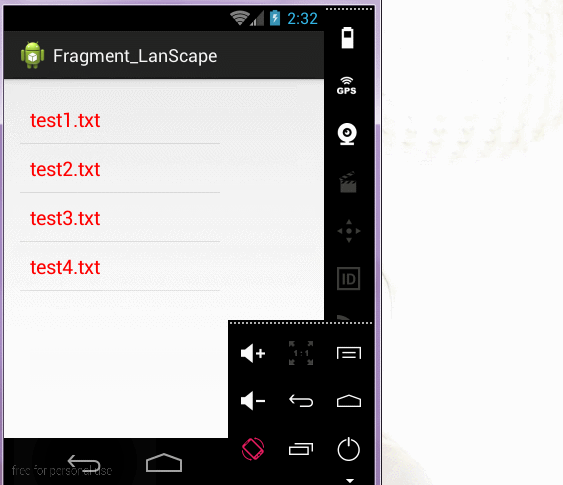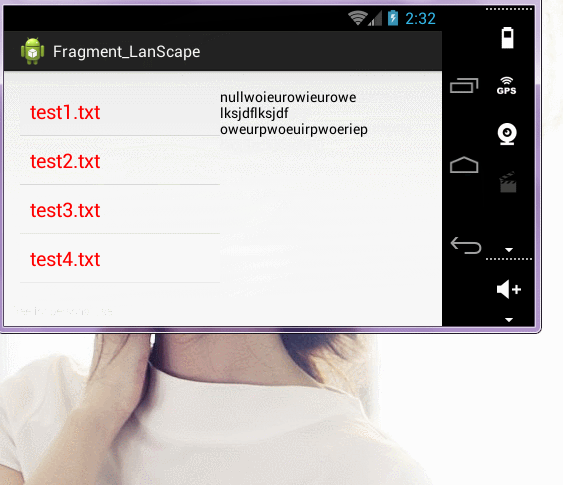
6.横屏竖屏动态变化布局
1)创建一个在横屏时加载的布局文件夹
竖屏布局:只有一个fragment
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context=".MainActivity" >
<fragment
android:id="@+id/fragment"
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent" android:name="com.beiing.fragmentlandscapefragment.FilesFragment"
/>
</RelativeLayout>横屏布局:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context=".MainActivity" >
<fragment
android:id="@+id/fragment"
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent" android:name="com.beiing.fragmentlandscapefragment.FilesFragment"
/>
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/container"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/fragment"
/>
</RelativeLayout>
2)判断横屏竖屏:根据横屏竖屏得到不同的操作
// 判断屏幕方向
if (getResources().getConfiguration().orientation == Configuration.ORIENTATION_LANDSCAPE) {
ContentFragment fragment = new ContentFragment();
fragment.setArguments(bundle);
getFragmentManager().beginTransaction()
.replace(R.id.container, fragment)
.addToBackStack(null)
.commit();
}
else
{
Intent intent = new Intent(getActivity(),ContentActivity.class);
intent.putExtras(bundle);
startActivity(intent);
}效果图:
我的总结:
1)实际开发中,fragment使用非常多,用法大都是在一个显示界面中底部放上一些按钮,中间一个fragment,这样就不用一个activity一个activity的跳了
2)引包的时候注意,一个是android.app.Fragment,还有一个向下兼容的
android.support.v4.app.Fragment;用后一个包的fragment时activity也要用这个包的FragmentActivity
3)在实现1)说的那种类似标签页时,需要注意不要每次都通过事务FragmentTransaction的replace()方法去变换界面,这样会导致该fragment重新创建,如果这个fragment里面有从网络获取数据的操作,这样,变换一次加载一次,谁受得了,解决方法是,在MainActivity中定义相应fragment的成员,然后一次加入FragmentManager中,然后想要显示哪个fragment只用调用FragmentTransaction 的show方法和hide方法。后面具体项目会遇到。


























 4万+
4万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








