Dynamic Programming
DP 的历史渊源:
Richard E. Bellman (1920-1984)
Richard Bellman received the IEEE Medal of Honor, 1979. “Bellman . . . explained that he invented the name ‘dynamid programming’ to hide the fact that he was doing mathematical research at RAND under a Secretary of Defense who ‘had a pathological fear and hatred of the term, research’. He settled on the term ‘dynamic programming’ because it would be difficult to give a ‘pejorative meaning’ and because ‘it was something not even a
Congressman could object to’ ” [John Rust 2006]
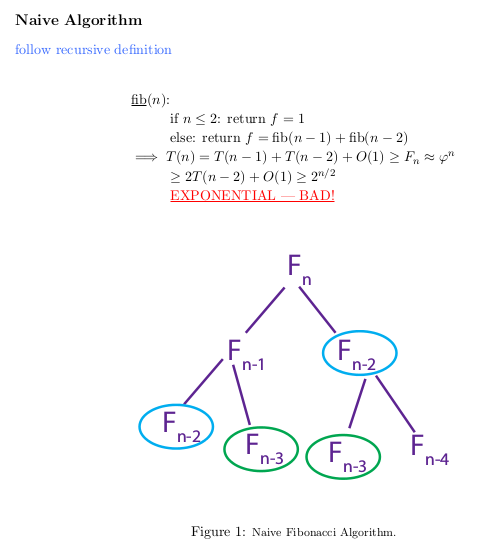
问题一:Fibonacci 数列求解问题
一般的会采用递归实现。
/****************************************************
code file : Fibonacci.c
code date : 2014.11.25
e-mail : jasonleaster@gmail.com
code description:
Here is a implementation of funciont @fib()
which will help us to compute the fibonacci array
and what we should pay attention to is that this
method is using recursion!
Reader must know that this method is convenient
way which is used to compute fibonacci array but not a
elegent way.
*****************************************************/
#include <stdio.h>
int fib(int num)
{
if(num <= 1)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return fib(num-1) + fib(num - 2);
}
}
int main()
{
int number = 0;
while(!scanf("%d",&number))
{
getchar();
printf("\nerror!input again!\n");
}
printf("The %dth fibonacci number is %d\n",number,fib(number));
return 0;
}
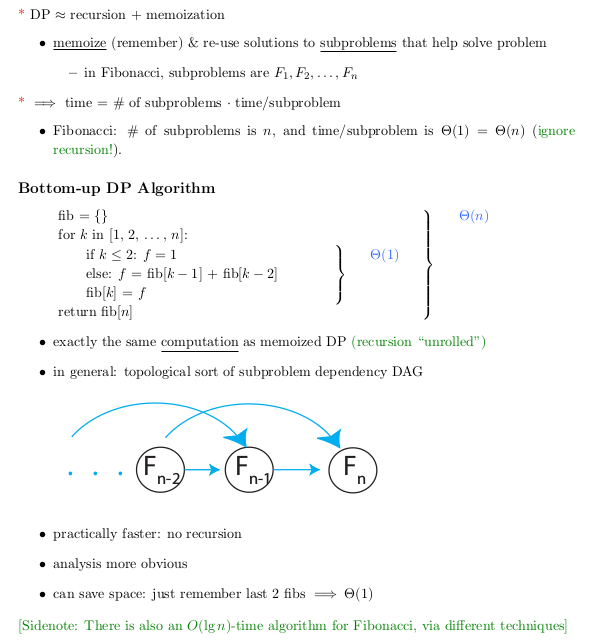
采用非递归的策略,即动态规划:
/****************************************************
code file : Fibonacci.c
code date : 2014.11.25
e-mail : jasonleaster@gmail.com
code description:
Here is a implementation of funciont @fib()
which will help us to compute the fibonacci array.
Aha! Just have glance with my code and you
will find that we didn't use recursion!YES! We do!
It's very elegent to store the last two var-
ible @prev and @prev_prev which is close to
current number.Something like this, we have a array,
1 2 3 4 5, @prev is 4 @prev_prev 3, current number is
5 :)
This method that we call it as dynamic pro-
gramming.
*****************************************************/
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int number = 0;
int prev = 1;
int prev_prev = 1;
int result = 1;
while(!scanf("%d",&number))
{
getchar();
printf("\nerror!input again!\n");
}
int temp = 0;
for(temp = 3;temp <= number;temp++)
{
result = prev + prev_prev;
prev_prev = prev;
prev = result;
}
printf("The %dth fibonacci number is %d\n",number,result);
return 0;
}
问题二: 工厂加工汽车的流水工作规划问题。
(这个是CLRS第二版上面第15章讲DP的第一个问题,但是第三章的时候被替换了)。可以从第二版上找到这个问题的详细分析。
Python 实现:
"""
Code writer : EOF
Code date : 2015.02.03
e-mail : jasonleaster@163.com
Code description :
Here is a implementation in Python as a solution
for Colonel-problem which is in <CLRS> second edition
chapter 15.
"""
def fastest_way(a, t, e, x, n) :
f1 = []
f2 = []
path = [[],[]]
# when j == 0
f1 += [ e[0] + a[0][0] ]
f2 += [ e[1] + a[1][0] ]
for j in range(1, n) :
if (f1[j-1] + a[0][j]) <= (f2[j-1] + t[1][j-1] + a[0][j]) :
f1 += [ f1[j-1] + a[0][j] ]
path[0] += [0]
else :
f1 += [ f2[j-1] + t[1][j-1] + a[0][j] ]
path[0] += [1]
if (f2[j-1] + a[1][j]) <= (f1[j-1] + t[0][j-1] + a[1][j]) :
f2 += [ f2[j-1] + a[1][j] ]
path[1] += [1]
else :
f2 += [ f1[j-1] + t[0][j-1] + a[1][j] ]
path[1] += [0]
if f1[n-1] + x[0] <= f2[n-1] + x[1] :
smallest_cost = f1[n-1] + x[0]
path[0] += [0]
path[1] += [0]
else :
smallest_cost = f2[n-1] + x[1]
path[0] += [1]
path[1] += [1]
return path
def print_stations(path) :
n = len(path[0])
i = path[0][n-1]
print "line ", i, ", station", n
for j in range(n-1, -1, -1) :
i = path[i][j]
print "line ", i, ", station", j
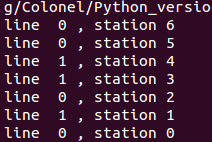
#---------------- for testing -----------------------------------------
a = [[7,9,3,4,8,4],[8,5,6,4,5,7]]
t = [[2,3,1,3,4] ,[2,1,2,2,1] ]
e = [2,4]
x = [3,2]
n = len(a[0])
path = fastest_way(a, t, e, x, n)
print_stations(path)测试结果:
问题三: 矩阵链乘法:
"""
Code writer : EOF
Code date : 2015.02.04
Code file : matrix_mult.py
e-mail : jasonleaster@163.com
Code description :
"""
def matrix_chain_order(p) :
'''
Don't forget that the size of @m and @s
is smaller than that of @p by 1.
'''
n = len(p)-1
p_inf = 2**32-1 # we assmue that the positive infinite is 2**32-1
m = [ [0 for i in range(0, n)] for i in range(0, n)]
s = [ [0 for i in range(0, n)] for i in range(0, n)]
for l in range(1, n) : # l is the chain length
for i in range(0, n-l) :
j = i + l
m[i][j] = p_inf
for k in range(i, j) :
q = m[i][k] + m[k+1][j] + p[i]*p[k+1]*p[j+1]
if q < m[i][j] :
m[i][j] = q
s[i][j] = k
return [m, s]
def print_optimal_parens(s, i, j) :
'''
Make sure that we count from zero but
but one.
row = column = len(A[0])
So the index of matrix A *can not* be
A[row][column]. Index out of range.
'''
if i is j :
print "A", i ," ",
else :
print "(",
print_optimal_parens(s, i, s[i][j])
print_optimal_parens(s, s[i][j]+1, j)
print ")",
#-----------------for testing ------------------------------------------
p = [5, 10, 3, 12, 5, 50, 6]
[m, s] = matrix_chain_order(p)
print_optimal_parens(s, 0, len(p)-2)
'''
The max index of s is len(p)-2.
Are you forget n = len(p)-1 which is
in function @matrix_chain_order ?
'''

问题四 最长子序列 LCS :
"""
Code writer : EOF
Code date : 2015.02.05
Code file : lcs.py
e-mail : jasonleaster@163.com
Code description :
Here is a implementation for a famous DP problem
that LCS -- longest common sub-member
"""
def lcs_length(X, Y) :
m = len(X)
n = len(Y)
c = [[0 for i in range(0, n+1)] for j in range(0, m+1)]
b = [[0 for i in range(0, n+1)] for j in range(0, m+1)]
for j in range(0, n+1) :
c[0][j] = 0
for i in range(0, m+1) :
c[i][0] = 0
for i in range(1, m+1) :
for j in range(1, n+1) :
if X[i-1] is Y[j-1] :
c[i][j] = c[i-1][j-1] + 1
b[i][j] = "+"
elif c[i-1][j] >= c[i][j-1] :
c[i][j] = c[i-1][j]
b[i][j] = "|"
else :
c[i][j] = c[i][j-1]
b[i][j] = "-"
return b
def show(c, m ,n) :
for i in range(0, m+1) :
for j in range(0, n+1) :
print c[i][j],
print
def print_lcs(b, X, i, j) :
if i is 0 or j is 0 :
return
if b[i][j] is "+" :
print_lcs(b, X, i-1, j-1)
print X[i-1],
elif b[i][j] is "|" :
print_lcs(b, X, i-1, j)
else :
print_lcs(b, X, i, j-1)
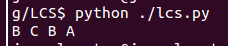
#---------------- for testing --------------------------------
X = ["A", "B", "C", "B", "D", "A", "B"]
Y = ["B", "D", "C", "A", "B", "A"]
b = lcs_length(X, Y)
print_lcs(b, X, len(X), len(Y))
注意, DP问题是求解目标问题的某一个可行解, 但是!! 目标问题不一定只有一个解!! 切记. 自己傻缺, 这里还以为是程序bug, 折腾好久.
Tencent 的AD被屏蔽之后也是蛮逗的。。。


























 371
371











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








