一. 链表
链表和数组对比各有各的特点,链表插入删除快,而数组查找快。插入和删除的时间复杂度都是O(n).注意到下面链表的定义是一种recursive type 递归定义. 很多数据结构都是这样定义的.
struct list
{
elment data;
struct list* next;
};
typedef struct list* list;
二. 队列
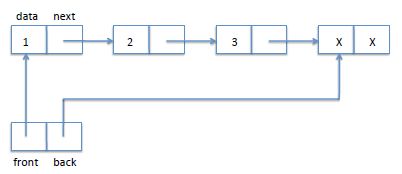
队列是先进来的元素先删除,FIFO(first in first out).队列是由一个链表外加一个指向队列首部和队列尾部的结构组成
struct queue
{
list front;//使用list类型是因为需要指向链表
list back;
};
typedef struct queue* queue;2.1 创建
只需要使用malloc为队列初始化一块内存,以及front,back指针
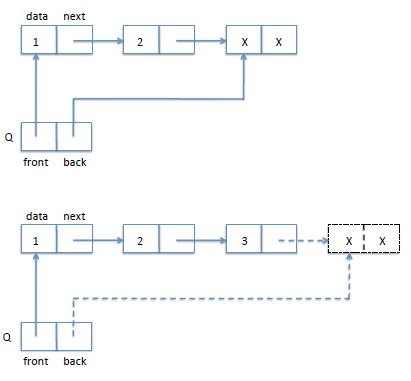
queue q_new()
{
//这个结点只需要创建一次用来存放front,back指针
queue q = (queue)malloc(sizeof(struct queue));
//这个是初始化的空结点,把它的next域置为空值NULL
list l = (list)malloc(sizeof(struct list));
q->front = l;
q->back = l;
q->back->next = NULL;//用来说明是尾结点
return q;
}2.2 插入
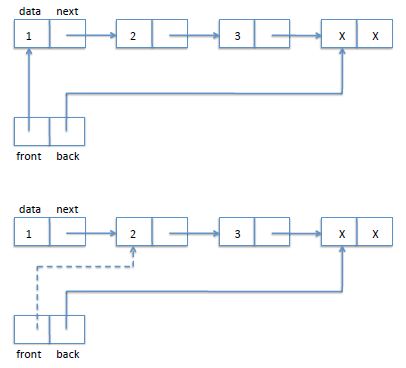
注意队列只能从尾部插入,所以只需要动一动尾部指针
这里生成的结点就是xx结点,而不是插入3结点,我没有使用额外的结点来表示队列尾部,而是没插入一个结点就把它的next域置为NULL表示队尾,每插入新的元素next域就会更新
void enq(elment data,queue q)
{
list l = (l)malloc(sizeof(struct list));
q->back->data = data;//这里是插入
q->back->next = l;
q->back = l;
q->back->next = NULL;
}
2.3 删除
队列只能删除头结点
void deq(queue q)
{
q->front = q->front->next;
}2.4 实现
#include<stdio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#include<string.h>
typedef struct list* list;
typedef struct queue* queue;
struct list
{
char * data;
struct list *next;
};
struct queue
{
list front;
list back;
};
queue q_new()//创建一个队列
{
queue q = (queue)malloc(sizeof(struct queue));
list l = (list)malloc(sizeof(struct list));
q->front = l;
q->back = l;
q->back->next = NULL;
return q;
}
void enq(queue q,char* s)//插入一个数,注意插入的第一个数是插到初始化队列里面
{
list l = (list)malloc(sizeof(struct list));
q->back->data = s;
q->back->next = l;
q->back = l;
q->back->next = NULL;
}
int is_empty(queue q)//判断队列是否为空
{
return q->back == q->front;
}
void deq(queue q)//从队列里面删除一个元素
{
if(is_empty(q) == 1)
{
printf("can not deq");
exit(-1);
}
q->front = q->front->next;
}
void printq(list l,queue q)//打印队列里面的元素
{
l = q->front;
for(l = q->front ; l->next != NULL ;l = l->next)
{
printf("%s\n",l->data);
}
}
int main()
{
list l;
queue q = q_new();
enq(q,"fantasy");
enq(q,"ming");
printq(l,q);
deq(q);
printf("删除后\n");
printq(l,q);
return 0;
}三. 栈
3.1 结构
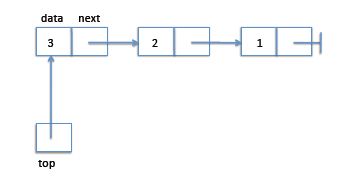
栈遵循先进后出.
栈只需要一个栈顶指针指向栈顶就行,插入删除复杂度为O(n).
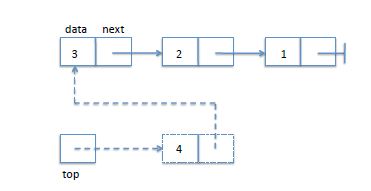
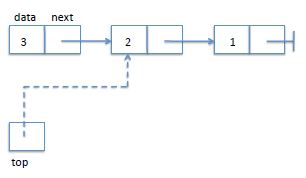
图中1表示最先进入的元素,3是最后入栈的top标识是栈顶
struct stack
{
list stack;
};
typedef struct stack* stack;3.2 创建
stack s_new()
{
stack s = (s)malloc(sizeof(struct stack));
s->top = NULL;
return s;
}3.3 插入
void push(elment data, stack s)
{
list l = (l)malloc(sizeof(struct list));
l->data = data;
l->next = s->top;
s->top = l;
}
3.4 删除
element pop(stack s)
{
if(s->top != NULL)
{
element data = s->top->data;
s->top = s->top->next;
return data;
}
else
exit(-1);
}3.5 实现
#include<stdio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
typedef struct stack* stack;
typedef struct list* list;
struct list
{
int data;
struct list *next;
};
struct stack
{
list top;
};
stack s_new()
{
stack s = (stack)malloc(sizeof(struct stack));
s->top = NULL;
return s;
}
void push(int data,stack s)
{
list l = (list)malloc(sizeof(struct list));
l->data = data;
l->next = s->top;
s->top = l;
}
void pop(stack s)
{
if(s->top != NULL)
s->top = s->top->next;
}
void print(stack s)
{
list l;
for(l = s->top;s->top!=NULL;l = s->top->next)
{
printf("%d\n",l->data);
}
}
int main()
{
stack s = s_new();
push(30,s);
push(50,s);
push(80,s);
print(s);
return 0;
}

























 4730
4730

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








