参考http://blog.csdn.net/hackbuteer1/article/details/6657109
一、 求解N皇后问题是算法中回溯法应用的一个经典案例
回溯算法也叫试探法,它是一种系统地搜索问题的解的方法。回溯算法的基本思想是:从一条路往前走,能进则进,不能进则退回来,换一条路再试。
下面是算法的高级伪码描述,这里用一个N*N的矩阵来存储棋盘:
1) 算法开始, 清空棋盘,当前行设为第一行,当前列设为第一列
2) 在当前行,当前列的位置上判断是否满足条件(即保证经过这一点的行,列与斜线上都没有两个皇后),若不满足,跳到第4步
3) 在当前位置上满足条件的情形:
在当前位置放一个皇后,若当前行是最后一行,记录一个解;
若当前行不是最后一行,当前行设为下一行, 当前列设为当前行的第一个待测位置;
若当前行是最后一行,当前列不是最后一列,当前列设为下一列;
若当前行是最后一行,当前列是最后一列,回溯,即清空当前行及以下各行的棋盘,然后,当前行设为上一行,当前列设为当前行的下一个待测位置;
以上返回到第2步
4) 在当前位置上不满足条件的情形:
若当前列不是最后一列,当前列设为下一列,返回到第2步;
若当前列是最后一列了,回溯,即,若当前行已经是第一行了,算法退出,否则,清空当前行及以下各行的棋盘,然后,当前行设为上一行,当前列设为当前行的下一个待测位置,返回到第2步;
算法的基本原理是上面这个样子,但不同的是用的数据结构不同,检查某个位置是否满足条件的方法也不同。为了提高效率,有各种优化策略,如多线程,多分配内存表示棋盘等。
(1)非递归方法
//Solution.h
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution
{
public:
Solution();
~Solution();
public:
const static int QUEENFREE = INT_MAX;
bool eightQueens(vector<int> &vi, int n);
bool islegalMove(vector<int> &vi, int row, int col);
void print(vector<int> &vi);
};
//Solution.cpp
#include "Solution.h"
Solution::Solution()
{
}
Solution::~Solution()
{
}
bool Solution::eightQueens(vector<int> &vi, int n = 8)
{
int m = 0;
vi.clear();
vi.resize(n, QUEENFREE);
int k = 0;
while (k >= 0)
{
//k代表即将需要填入皇后的行数
int i = 0;
for (; i < n; i++)//i代表在这一行填入皇后的列数
{
if (islegalMove(vi, k, i))
{
//如果vi[k]不等于QUEEFREE那么就是说明,这是从下一层返回来的k值。
//第一次进入该层就应该满足条件就填写了,但是如果是下一层返回来的话,
//就不能填写比前值更小的值了,这也是Backtracking算法的一个特征:
//是按一定循序的值循环探索适合的解。
//这里不用栈,只用k执行了差不都是栈的功能。
if (vi[k] == QUEENFREE || vi[k] < i)
{
vi[k] = i;
if (k == n - 1)
{
printf("answer %d : \n", ++m);
print(vi);
continue;
}
k++;
break;
}
}
}
if (i == n)
{
vi[k] = QUEENFREE;
k--;
}
}
return true;
}
bool Solution::islegalMove(vector<int> &vi, int row, int col)
{
for (int i = 0; i < vi.size(); i++)
{
if (i != row &&vi[i] == col)
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < vi.size(); i++)
{
if (i != row && (vi[i] - i == col - row || vi[i] + i == col + row))
return false;
}
return true;
}
void Solution::print(vector<int> &vi)
{
for (auto x : vi)
{
for (int i = 0; i < vi.size(); i++)
{
if (i == x)
cout << "Q ";
else
cout << ". ";
}
cout << endl;
}
for (auto x : vi)
cout << x << " ";
cout << endl;
cout << "------------------\n";
}
//main.cpp
#include"Solution.h"
int main()
{
vector<int> queen;
Solution solu;
solu.eightQueens(queen, 8);
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
//Solution2.h
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 8;
class Solution2
{
public:
Solution2();
~Solution2();
public:
static const int INITIAL;
static int q[N];
void init();
void print();
bool judge(int row, int col);
void search(int cur);
private:
int count;
int cur;
};
//Solution2.cpp
#include "Solution2.h"
Solution2::Solution2()
{
count = 0;
}
Solution2::~Solution2()
{
}
int Solution2::q[N];
const int Solution2::INITIAL = -10000;
void Solution2::init()
{
int *p;
for (p = q; p < q + N; ++p)
{
*p = INITIAL;
}
}
void Solution2::search(int cur)
{
if (cur == N)
{
count++;
cout << "answer " << count << " : \n";
print();
}
else
{
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
int ok = 1;
q[cur] = i;
if (judge(cur, i))
{
search(cur + 1);
}
}
}
}
bool Solution2::judge(int row, int col)
{
for (int j = 0; j < row; j++)
{
if (q[row] == q[j] || row - q[row] == j - q[j] || row + q[row] == j + q[j])
return false;
}
return true;
}
void Solution2::print() //打印输出N皇后的一组解
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < N; ++i)
{
for (j = 0; j < N; ++j)
{
if (q[i] != j) //a[i]为初始值
printf("%c ", '.');
else //a[i]表示在第i行的第a[i]列可以放置皇后
printf("%c ", '#');
}
printf("\n");
}
for (i = 0; i < N; ++i)
printf("%d ", q[i]);
printf("\n");
printf("--------------------------------\n");
}
//main.cpp
#include"Solution2.h"
int main()
{
Solution2 solu;
solu.init();
solu.search(0);
return 0;
}二、使用位运算来求解N皇后的高效算法
//Solution3.h
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<ctime>
using namespace std;
const int N = 8;
class Solution3
{
public:
Solution3();
~Solution3();
private:
// sum用来记录皇后放置成功的不同布局数;upperlim用来标记所有列都已经放置好了皇后。
long sum, upperlim, count;
public:
// 试探算法从最右边的列开始。
static const int INITIAL;
static int q[N];
void init();
void test(long row, long ld, long rd);
void print();
int get_sum();
};
//Solution3.cpp
#include "Solution3.h"
Solution3::Solution3()
{
sum = 0;
upperlim = (1 << N) - 1;
count = -1;
}
Solution3::~Solution3()
{
}
int Solution3::q[N];
const int Solution3::INITIAL = -10000;
void Solution3::init()
{
int *p;
for (p = q; p < q + N; ++p)
{
*p = INITIAL;
}
}
void Solution3::test(long row, long ld, long rd)
{
count++;
if (row != upperlim)
{
// row,ld,rd进行“或”运算,求得所有可以放置皇后的列,对应位为0,
// 然后再取反后“与”上全1的数,来求得当前所有可以放置皇后的位置,对应列改为1
// 也就是求取当前哪些列可以放置皇后
long pos = upperlim & ~(row | ld | rd);
while (pos) // 0 -- 皇后没有地方可放,回溯
{
// 拷贝pos最右边为1的bit,其余bit置0
// 也就是取得可以放皇后的最右边的列
long p = pos & -pos;
for (int k = 0; k < N; k++)
{
if (p&(1 << k))
q[count] = 7 - k;
}
// 将pos最右边为1的bit清零
// 也就是为获取下一次的最右可用列使用做准备,
// 程序将来会回溯到这个位置继续试探
pos -= p;
// row + p,将当前列置1,表示记录这次皇后放置的列。
// (ld + p) << 1,标记当前皇后左边相邻的列不允许下一个皇后放置。
// (ld + p) >> 1,标记当前皇后右边相邻的列不允许下一个皇后放置。
// 此处的移位操作实际上是记录对角线上的限制,只是因为问题都化归
// 到一行网格上来解决,所以表示为列的限制就可以了。显然,随着移位
// 在每次选择列之前进行,原来N×N网格中某个已放置的皇后针对其对角线
// 上产生的限制都被记录下来了
test(row + p, (ld + p) << 1, (rd + p) >> 1);
}
}
else
{
// row的所有位都为1,即找到了一个成功的布局,回溯
sum++;
cout << "answer " << sum << " : \n";
print();
}
count--;
}
void Solution3::print()
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < N; ++i)
{
for (j = 0; j < N; ++j)
{
if (q[i] != j) //a[i]为初始值
printf("%c ", '.');
else //a[i]表示在第i行的第a[i]列可以放置皇后
printf("%c ", '#');
}
printf("\n");
}
for (i = 0; i < N; ++i)
printf("%d ", q[i]);
printf("\n");
printf("--------------------------------\n");
}
int Solution3::get_sum()
{
return sum;
}
//main.cpp
#include"Solution3.h"
int main()
{
time_t tm;
tm = time(0);
Solution3 solu;
solu.init();
solu.test(0, 0, 0);
printf("共有%ld种排列,计算时间%lf毫秒 \n", solu.get_sum(), (double)((time(0) - tm) * 1000));
return 0;
}【代码说明】
p = pos & (~pos + 1)其结果是取出最右边的那个1。这样,p就表示该行的某个可以放子的位置,把它从pos中移除并递归调用test过程。
注意递归调用时三个参数的变化,每个参数都加上了一个禁位,但两个对角线方向的禁位对下一行的影响需要平移一位。最后,如果递归到某个时候发现row=upperlim了,说明n个皇后全放进去了,找到的解的个数加一。
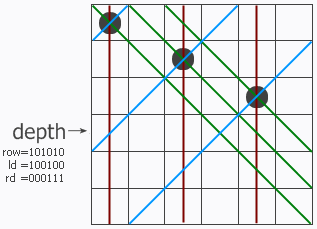
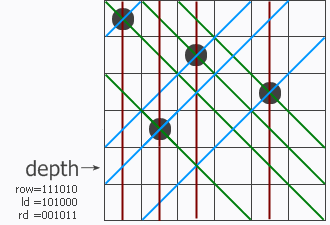
注:
upperlime:=(1 << n)-1 就生成了n个1组成的二进制数。
这个程序是从上向下搜索的。
pos & -pos 的意思就是取最右边的 1 再组成二进制数,相当于 pos &(~pos +1),因为取反以后刚好所有数都是相反的(怎么听着像废话),再加 1 ,就是改变最低位,如果低位的几个数都是1,加的这个 1 就会进上去,一直进到 0 ,在做与运算就和原数对应的 1 重合了。举例可以说明:
原数 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 原数 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1
取反 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 取反 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0
加1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 加1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1
与运算 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 and 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
其中呢,这个取反再加 1 就是补码,and 运算 与负数,就是按位和补码与运算。
(ld | p)<< 1 是因为由ld造成的占位在下一行要右移一下;
(rd | p)>> 1 是因为由rd造成的占位在下一行要左移一下。
ld rd row 还要和upperlime 与运算 一下,这样做的结果就是从最低位数起取n个数为有效位置,原因是在上一次的运算中ld发生了右移,如果不and的话,就会误把n以外的位置当做有效位。
pos 已经完成任务了还要减去p 是因为?
while 循环是因为?
在进行到某一层的搜索时,pos中存储了所有的可放位置,为了求出所有解,必须遍历所有可放的位置,而每走过一个点必须要删掉它,否则就成死循环啦!
这个是目前公认N皇后的最高效算法。






















 4884
4884











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








