Mach-O文件简介
Mach-O是Mach Object的缩写,它是MacOS/iOS的目标文件,静态库,动态库的标准格式文件。它由Header,LoadCommands,Data(Loader Info)组成,Header保存了当前应用程序的文件类型,支持的CPU架构信息。LoadCommands指示loader如何加载二进制数据,比如main函数在什么位置,依赖了哪些动态库等。Data部分存放了可执行文件的数据,比如代码,字符串常量,类,方法等。在MachO文件的末尾,还有Loader Info信息,这里面表示可执行文件依赖的字符串表,符号表等信息。
常见的Mach-O文件类型有
#define MH_OBJECT 0x1 /* relocatable object file */
#define MH_EXECUTE 0x2 /* demand paged executable file */
#define MH_FVMLIB 0x3 /* fixed VM shared library file */
#define MH_CORE 0x4 /* core file */
#define MH_PRELOAD 0x5 /* preloaded executable file */
#define MH_DYLIB 0x6 /* dynamically bound shared library */
#define MH_DYLINKER 0x7 /* dynamic link editor */
#define MH_BUNDLE 0x8 /* dynamically bound bundle file */
#define MH_DYLIB_STUB 0x9 /* shared library stub for static
linking only, no section contents */
#define MH_DSYM 0xa /* companion file with only debug
sections */
MH_OBJECT包含了目标文件.o,静态库文件文件
MH_EXECUTE是一个可执行文件
MH_DYLIB是动态库文件,通常以.dylb结尾或者.framwork结尾
MH_DYLINKER是动态库的加载器
MH_DSYM是dSYM文件,比如iOS的crash信息仅仅包含二进制,如何找到对应的代码,需要使用dSYM文件进行解析。
Mach-O文件头文件
Mach-O Header头文件
32位MachO文件
struct mach_header {
uint32_t magic; /* mach magic number identifier */
int32_t cputype; /* cpu specifier */
int32_t cpusubtype; /* machine specifier */
uint32_t filetype; /* type of file */
uint32_t ncmds; /* number of load commands */
uint32_t sizeofcmds; /* the size of all the load commands */
uint32_t flags; /* flags */
};
64位MachO文件
struct mach_header_64 {
uint32_t magic; /* mach magic number identifier */
int32_t cputype; /* cpu specifier */
int32_t cpusubtype; /* machine specifier */
uint32_t filetype; /* type of file */
uint32_t ncmds; /* number of load commands */
uint32_t sizeofcmds; /* the size of all the load commands */
uint32_t flags; /* flags */
uint32_t reserved; /* reserved */
};
Loader Command头文件
32位Loader Command头文件
/*
* The segment load command indicates that a part of this file is to be
* mapped into the task's address space. The size of this segment in memory,
* vmsize, maybe equal to or larger than the amount to map from this file,
* filesize. The file is mapped starting at fileoff to the beginning of
* the segment in memory, vmaddr. The rest of the memory of the segment,
* if any, is allocated zero fill on demand. The segment's maximum virtual
* memory protection and initial virtual memory protection are specified
* by the maxprot and initprot fields. If the segment has sections then the
* section structures directly follow the segment command and their size is
* reflected in cmdsize.
*/
struct segment_command { /* for 32-bit architectures */
uint32_t cmd; /* LC_SEGMENT */
uint32_t cmdsize; /* includes sizeof section structs */
char segname[16]; /* segment name */
uint32_t vmaddr; /* memory address of this segment */
uint32_t vmsize; /* memory size of this segment */
uint32_t fileoff; /* file offset of this segment */
uint32_t filesize; /* amount to map from the file */
int32_t maxprot; /* maximum VM protection */
int32_t initprot; /* initial VM protection */
uint32_t nsects; /* number of sections in segment */
uint32_t flags; /* flags */
};
64位Loader Command头文件
/*
* The 64-bit segment load command indicates that a part of this file is to be
* mapped into a 64-bit task's address space. If the 64-bit segment has
* sections then section_64 structures directly follow the 64-bit segment
* command and their size is reflected in cmdsize.
*/
struct segment_command_64 { /* for 64-bit architectures */
uint32_t cmd; /* LC_SEGMENT_64 */
uint32_t cmdsize; /* includes sizeof section_64 structs */
char segname[16]; /* segment name */
uint64_t vmaddr; /* memory address of this segment */
uint64_t vmsize; /* memory size of this segment */
uint64_t fileoff; /* file offset of this segment */
uint64_t filesize; /* amount to map from the file */
int32_t maxprot; /* maximum VM protection */
int32_t initprot; /* initial VM protection */
uint32_t nsects; /* number of sections in segment */
uint32_t flags; /* flags */
};
在segment里面有Section,Section相关头文件如下
/*
* A segment is made up of zero or more sections. Non-MH_OBJECT files have
* all of their segments with the proper sections in each, and padded to the
* specified segment alignment when produced by the link editor. The first
* segment of a MH_EXECUTE and MH_FVMLIB format file contains the mach_header
* and load commands of the object file before its first section. The zero
* fill sections are always last in their segment (in all formats). This
* allows the zeroed segment padding to be mapped into memory where zero fill
* sections might be. The gigabyte zero fill sections, those with the section
* type S_GB_ZEROFILL, can only be in a segment with sections of this type.
* These segments are then placed after all other segments.
*
* The MH_OBJECT format has all of its sections in one segment for
* compactness. There is no padding to a specified segment boundary and the
* mach_header and load commands are not part of the segment.
*
* Sections with the same section name, sectname, going into the same segment,
* segname, are combined by the link editor. The resulting section is aligned
* to the maximum alignment of the combined sections and is the new section's
* alignment. The combined sections are aligned to their original alignment in
* the combined section. Any padded bytes to get the specified alignment are
* zeroed.
*
* The format of the relocation entries referenced by the reloff and nreloc
* fields of the section structure for mach object files is described in the
* header file <reloc.h>.
*/
struct section { /* for 32-bit architectures */
char sectname[16]; /* name of this section */
char segname[16]; /* segment this section goes in */
uint32_t addr; /* memory address of this section */
uint32_t size; /* size in bytes of this section */
uint32_t offset; /* file offset of this section */
uint32_t align; /* section alignment (power of 2) */
uint32_t reloff; /* file offset of relocation entries */
uint32_t nreloc; /* number of relocation entries */
uint32_t flags; /* flags (section type and attributes)*/
uint32_t reserved1; /* reserved (for offset or index) */
uint32_t reserved2; /* reserved (for count or sizeof) */
};
struct section_64 { /* for 64-bit architectures */
char sectname[16]; /* name of this section */
char segname[16]; /* segment this section goes in */
uint64_t addr; /* memory address of this section */
uint64_t size; /* size in bytes of this section */
uint32_t offset; /* file offset of this section */
uint32_t align; /* section alignment (power of 2) */
uint32_t reloff; /* file offset of relocation entries */
uint32_t nreloc; /* number of relocation entries */
uint32_t flags; /* flags (section type and attributes)*/
uint32_t reserved1; /* reserved (for offset or index) */
uint32_t reserved2; /* reserved (for count or sizeof) */
uint32_t reserved3; /* reserved */
};
常见的Load Command有
#define LC_SYMTAB 0x2 /* link-edit stab symbol table info */
#define LC_DYSYMTAB 0xb /* dynamic link-edit symbol table info */
#define LC_LOAD_DYLIB 0xc /* load a dynamically linked shared library */
#define LC_LOAD_DYLINKER 0xe /* load a dynamic linker */
#define LC_SEGMENT_64 0x19 /* 64-bit segment of this file to be
mapped */
#define LC_UUID 0x1b /* the uuid */
#define LC_CODE_SIGNATURE 0x1d /* local of code signature */
#define LC_DYLD_INFO_ONLY (0x22|LC_REQ_DYLD) /* compressed dyld information only */
#define LC_LAZY_LOAD_DYLIB 0x20 /* delay load of dylib until first use *
#define LC_FUNCTION_STARTS 0x26 /* compressed table of function start addresses */
#define LC_MAIN (0x28|LC_REQ_DYLD) /* replacement for LC_UNIXTHREAD */
如何查看MachO文件
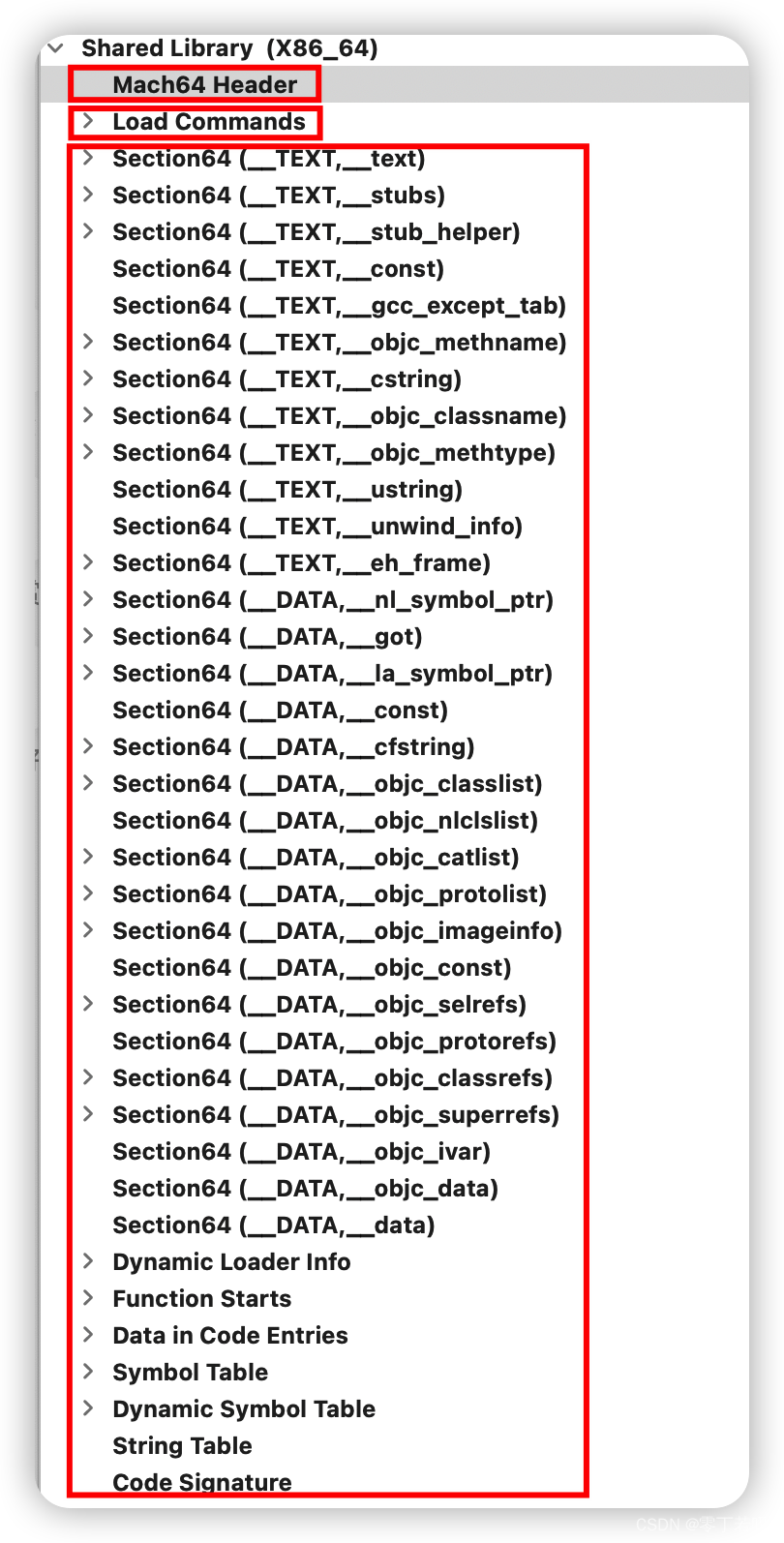
可以下载MachOView软件查看Mach-O文件,可以看到Mach-O文件分为Mach64 Header,Load Commands,Data(包含Loader Info)三个部分。
代码获取MachO信息
我们以获取MachO的filetype为例,尝试用代码获取MachO文件信息。
获取工程依赖的所有库
在主工程的ViewController里面引入头文件,并且在合适位置写入以下代码获取主工程依赖的所有库并打印库的类型。
// #import <mach-o/dyld.h>
int count = _dyld_image_count();
for(int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
const struct mach_header *machHeader = _dyld_get_image_header(i);
const char* name = _dyld_get_image_name(i);
NSLog(@"filetype is %d, name is %s", machHeader->filetype, name);
}






















 539
539











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








