 二叉树
二叉树
定义:二叉树是每个结点最多有两个子树的树结构。
性质:
1)二叉树的每个结点至多只有二棵子树(不存在度大于2的结点
2)二叉树的子树有左右之分,次序不能颠倒
3)二叉树的第i层至多有2^{i-1}个结点
4)深度为k的二叉树至多有2^k-1个结点
满二叉树
定义:一棵深度为k,且有2^k-1个节点的二叉树,称为满二叉树。
性质:每一层上的节点数都是最大节点数
完全二叉树
定义:一棵二叉树中,除最后一层外,若其余层都是满的,并且最后一层或者是满的,或者是在右边缺少连续若干节点
性质:
1)具有n个节点的完全二叉树的深度为log2(n+1)
2)深度为k的完全二叉树,至少有2^(k-1)个节点,至多有2^k-1个节点
线索二叉树
定义:利用二叉链表中的空指针域,存放指向结点在某种遍历次序下的前驱和后继结点的指针(这种附加的指针称为”线索”)
哈夫曼树(最优二叉树)
定义:哈夫曼树是带权路径长度最短的树,权值较大的结点离根较近
二叉搜索树/二叉排序树/二叉查找树
定义:它或者是一棵空树,或者是具有下列性质的二叉树: 若它的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值; 若它的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值
平衡二叉树
定义:平衡二叉树又称AVL树,它是一 棵空树或它的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1
伸展树
定义:伸展树是在查询或删除时对二叉查找树进行伸展操作,并保证从空树开始任意连续M次对树的操作最多花费O(MlogN)的时间。对二叉查找树进行伸展的意义是将访问路径上的节点尽可能的推向离树根最近的地方,有益于在下次访问时用时最少。通常一个节点被访问时,很可能不久会被再次访问。
红黑树
定义:是一种自平衡二叉查找树,其性质决定了最大一条路径节点个数不会超过最小的两倍
1)性质1. 节点是红色或黑色。
2)性质2. 根节点是黑色。
3)性质3 每个叶节点(NIL节点,空节点)是黑色的。
4)性质4 每个红色节点的两个子节点都是黑色。(从每个叶子到根的所有路径上不能有两个连续的红色节点)
5)性质5. 从任一节点到其每个叶子的所有路径都包含相同数目的黑色节点。
B树
定义:二叉搜索树
性质:
1)所有非叶子结点至多拥有两个儿子(Left和Right);
2)所有结点存储一个关键字;
3)非叶子结点的左指针指向小于其关键字的子树,右指针指向大于其关键字的子树;
B-树
定义:是一种多路搜索树
B+树
定义:B+树是B-树的变体,也是一种多路搜索树,所有关键字都在叶子结点出现
B*树
定义:是B+树的变体,在B+树的非根和非叶子结点再增加指向兄弟的指针,节点分裂优先给兄弟节点
搜索二叉树
搜索二叉树一定要说明以什么标准来排序
经典的搜索二叉树,树上没有重复的用来排序的key值
如果有重复节点的需求,可以在一个节点内部增加数据项
搜索二叉树查询key(查询某个key存在还是不存在)
1)如果当前节点的value==key,返回true
2)如果当前节点的value<key,当前节点向左移动
3)如果当前节点的value>key,当前节点向右移动
4)如果当前节点变成null,返回false
搜索二叉树插入新的key
和查询过程一样,但当前节点滑到空的时候,就插入在这里
搜索二叉树删除key
0)先找到key所在的节点
1)如果该节点没有左孩子、没有右孩子,直接删除即可
2)如果该节点有左孩子、没有右孩子,直接用左孩子顶替该节点
3)如果该节点没有左孩子、有右孩子,直接用右孩子顶替该节点
4)如果该节点有左孩子、有右孩子,用该节点后继节点顶替该节点
搜索二叉树特别不讲究
1)基础的搜索二叉树,添加、删除时候不照顾平衡性
2)数据状况很差时,性能就很差
给搜索二叉树引入两个动作:左旋、右旋


AVL树、SB树、红黑树的共性:给搜索二叉树引入两个动作:左旋、右旋,调整平衡性
1)都是搜索二叉树
2)插入、删除、查询(一切查询)搜索二叉树怎么做,这些结构都这么做
3)使用调整的基本动作都只有左旋、右旋
4)插入、删除时,从最底层被影响到的节点开始,对往上路径的节点做平衡性检查
5)因为只对一条向上路径的每个节点做O(1)的检查和调整,所以可以做到O(logN)
AVL树、SB树、红黑树的不同
1)平衡性的约束不同
AVL树最严格、SB树稍宽松、红黑树最宽松
2)插入、删除和搜索二叉树一样,但是额外,做各自的平衡性调整。各自的平衡性调整所使用的动作都是左旋或者右旋
AVL树
1)最严格的平衡性,任何节点左树高度和右树高度差不超过1
2)往上沿途检查每个节点时,都去检查四种违规情况:LL、RR、LR、RL
3)不同情况虽然看起来复杂,但是核心点是:
LL(做一次右旋)、RR(做一次左旋)
LR和RL(利用旋转让底层那个上到顶部)
//定义结构
public static class AVLNode<K extends Comparable<K>, V> {
public K k;
public V v;
public AVLNode<K, V> l;
public AVLNode<K, V> r;
public int h;
public AVLNode(K key, V value) {
k = key;
v = value;
h = 1;
}
}
public static class AVLTreeMap<K extends Comparable<K>, V> {
private AVLNode<K, V> root;
private int size;
public AVLTreeMap() {
root = null;
size = 0;
}
//右旋
private AVLNode<K, V> rightRotate(AVLNode<K, V> cur) {
AVLNode<K, V> left = cur.l;
cur.l = left.r;
left.r = cur;
cur.h = Math.max((cur.l != null ? cur.l.h : 0), (cur.r != null ? cur.r.h : 0)) + 1;
left.h = Math.max((left.l != null ? left.l.h : 0), (left.r != null ? left.r.h : 0)) + 1;
return left;
}
//左旋
private AVLNode<K, V> leftRotate(AVLNode<K, V> cur) {
AVLNode<K, V> right = cur.r;
cur.r = right.l;
right.l = cur;
cur.h = Math.max((cur.l != null ? cur.l.h : 0), (cur.r != null ? cur.r.h : 0)) + 1;
right.h = Math.max((right.l != null ? right.l.h : 0), (right.r != null ? right.r.h : 0)) + 1;
return right;
}
//调整平衡性
private AVLNode<K, V> maintain(AVLNode<K, V> cur) {
if (cur == null) {
return null;
}
int leftHeight = cur.l != null ? cur.l.h : 0;
int rightHeight = cur.r != null ? cur.r.h : 0;
if (Math.abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) > 1) {
if (leftHeight > rightHeight) {
int leftLeftHeight = cur.l != null && cur.l.l != null ? cur.l.l.h : 0;
int leftRightHeight = cur.l != null && cur.l.r != null ? cur.l.r.h : 0;
if (leftLeftHeight >= leftRightHeight) {
cur = rightRotate(cur);
} else {
cur.l = leftRotate(cur.l);
cur = rightRotate(cur);
}
} else {
int rightLeftHeight = cur.r != null && cur.r.l != null ? cur.r.l.h : 0;
int rightRightHeight = cur.r != null && cur.r.r != null ? cur.r.r.h : 0;
if (rightRightHeight >= rightLeftHeight) {
cur = leftRotate(cur);
} else {
cur.r = rightRotate(cur.r);
cur = leftRotate(cur);
}
}
}
return cur;
}
private AVLNode<K, V> findLastIndex(K key) {
AVLNode<K, V> pre = root;
AVLNode<K, V> cur = root;
while (cur != null) {
pre = cur;
if (key.compareTo(cur.k) == 0) {
break;
} else if (key.compareTo(cur.k) < 0) {
cur = cur.l;
} else {
cur = cur.r;
}
}
return pre;
}
private AVLNode<K, V> findLastNoSmallIndex(K key) {
AVLNode<K, V> ans = null;
AVLNode<K, V> cur = root;
while (cur != null) {
if (key.compareTo(cur.k) == 0) {
ans = cur;
break;
} else if (key.compareTo(cur.k) < 0) {
ans = cur;
cur = cur.l;
} else {
cur = cur.r;
}
}
return ans;
}
private AVLNode<K, V> findLastNoBigIndex(K key) {
AVLNode<K, V> ans = null;
AVLNode<K, V> cur = root;
while (cur != null) {
if (key.compareTo(cur.k) == 0) {
ans = cur;
break;
} else if (key.compareTo(cur.k) < 0) {
cur = cur.l;
} else {
ans = cur;
cur = cur.r;
}
}
return ans;
}
//添加节点
private AVLNode<K, V> add(AVLNode<K, V> cur, K key, V value) {
if (cur == null) {
return new AVLNode<K, V>(key, value);
} else {
if (key.compareTo(cur.k) < 0) {
cur.l = add(cur.l, key, value);
} else {
cur.r = add(cur.r, key, value);
}
cur.h = Math.max(cur.l != null ? cur.l.h : 0, cur.r != null ? cur.r.h : 0) + 1;
return maintain(cur);
}
}
// 在cur这棵树上,删掉key所代表的节点
// 返回cur这棵树的新头部
private AVLNode<K, V> delete(AVLNode<K, V> cur, K key) {
if (key.compareTo(cur.k) > 0) {
cur.r = delete(cur.r, key);
} else if (key.compareTo(cur.k) < 0) {
cur.l = delete(cur.l, key);
} else {
if (cur.l == null && cur.r == null) {
cur = null;
} else if (cur.l == null && cur.r != null) {
cur = cur.r;
} else if (cur.l != null && cur.r == null) {
cur = cur.l;
} else {
AVLNode<K, V> des = cur.r;
while (des.l != null) {
des = des.l;
}
cur.r = delete(cur.r, des.k);
des.l = cur.l;
des.r = cur.r;
cur = des;
}
}
if (cur != null) {
cur.h = Math.max(cur.l != null ? cur.l.h : 0, cur.r != null ? cur.r.h : 0) + 1;
}
return maintain(cur);
}
public int size() {
return size;
}
//是否包含某个key
public boolean containsKey(K key) {
if (key == null) {
return false;
}
AVLNode<K, V> lastNode = findLastIndex(key);
return lastNode != null && key.compareTo(lastNode.k) == 0 ? true : false;
}
public void put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null) {
return;
}
AVLNode<K, V> lastNode = findLastIndex(key);
if (lastNode != null && key.compareTo(lastNode.k) == 0) {
lastNode.v = value;
} else {
size++;
root = add(root, key, value);
}
}
public void remove(K key) {
if (key == null) {
return;
}
if (containsKey(key)) {
size--;
root = delete(root, key);
}
}
public V get(K key) {
if (key == null) {
return null;
}
AVLNode<K, V> lastNode = findLastIndex(key);
if (lastNode != null && key.compareTo(lastNode.k) == 0) {
return lastNode.v;
}
return null;
}
public K firstKey() {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
AVLNode<K, V> cur = root;
while (cur.l != null) {
cur = cur.l;
}
return cur.k;
}
public K lastKey() {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
AVLNode<K, V> cur = root;
while (cur.r != null) {
cur = cur.r;
}
return cur.k;
}
public K floorKey(K key) {
if (key == null) {
return null;
}
AVLNode<K, V> lastNoBigNode = findLastNoBigIndex(key);
return lastNoBigNode == null ? null : lastNoBigNode.k;
}
public K ceilingKey(K key) {
if (key == null) {
return null;
}
AVLNode<K, V> lastNoSmallNode = findLastNoSmallIndex(key);
return lastNoSmallNode == null ? null : lastNoSmallNode.k;
}
}SB树(size-balance-tree)
1)让每一个叔叔节点为头的数,节点个数都不少于其任何一个侄子节点
2)也是从底层被影响节点开始向上做路径每个节点检查
3)与AVL树非常像,也是四种违规类型:LL、RR、LR、RL
4)与AVL树非常像,核心点是:
LL(做一次右旋)、RR(做一次左旋)
LR和RL(利用旋转让底层那个上到顶部)
5)与AVL树不同的是,每轮经过调整后,谁的孩子发生变化了,谁就再查
SB树在使用时候的改进
1)删除时候可以不用检查
2)就把平衡性的调整放在插入的时候
3)因为这种只要变就递归的特性,别的树没有
4)可以在节点上封装别的数据项,来增加功能
public static class SBTNode<K extends Comparable<K>, V> {
public K key;
public V value;
public SBTNode<K, V> l;
public SBTNode<K, V> r;
public int size; // 不同的key的数量
public SBTNode(K key, V value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
size = 1;
}
}
public static class SizeBalancedTreeMap<K extends Comparable<K>, V> {
private SBTNode<K, V> root;
private SBTNode<K, V> rightRotate(SBTNode<K, V> cur) {
SBTNode<K, V> leftNode = cur.l;
cur.l = leftNode.r;
leftNode.r = cur;
leftNode.size = cur.size;
cur.size = (cur.l != null ? cur.l.size : 0) + (cur.r != null ? cur.r.size : 0) + 1;
return leftNode;
}
private SBTNode<K, V> leftRotate(SBTNode<K, V> cur) {
SBTNode<K, V> rightNode = cur.r;
cur.r = rightNode.l;
rightNode.l = cur;
rightNode.size = cur.size;
cur.size = (cur.l != null ? cur.l.size : 0) + (cur.r != null ? cur.r.size : 0) + 1;
return rightNode;
}
private SBTNode<K, V> maintain(SBTNode<K, V> cur) {
if (cur == null) {
return null;
}
int leftSize = cur.l != null ? cur.l.size : 0;
int leftLeftSize = cur.l != null && cur.l.l != null ? cur.l.l.size : 0;
int leftRightSize = cur.l != null && cur.l.r != null ? cur.l.r.size : 0;
int rightSize = cur.r != null ? cur.r.size : 0;
int rightLeftSize = cur.r != null && cur.r.l != null ? cur.r.l.size : 0;
int rightRightSize = cur.r != null && cur.r.r != null ? cur.r.r.size : 0;
if (leftLeftSize > rightSize) {
cur = rightRotate(cur);
cur.r = maintain(cur.r);
cur = maintain(cur);
} else if (leftRightSize > rightSize) {
cur.l = leftRotate(cur.l);
cur = rightRotate(cur);
cur.l = maintain(cur.l);
cur.r = maintain(cur.r);
cur = maintain(cur);
} else if (rightRightSize > leftSize) {
cur = leftRotate(cur);
cur.l = maintain(cur.l);
cur = maintain(cur);
} else if (rightLeftSize > leftSize) {
cur.r = rightRotate(cur.r);
cur = leftRotate(cur);
cur.l = maintain(cur.l);
cur.r = maintain(cur.r);
cur = maintain(cur);
}
return cur;
}
private SBTNode<K, V> findLastIndex(K key) {
SBTNode<K, V> pre = root;
SBTNode<K, V> cur = root;
while (cur != null) {
pre = cur;
if (key.compareTo(cur.key) == 0) {
break;
} else if (key.compareTo(cur.key) < 0) {
cur = cur.l;
} else {
cur = cur.r;
}
}
return pre;
}
private SBTNode<K, V> findLastNoSmallIndex(K key) {
SBTNode<K, V> ans = null;
SBTNode<K, V> cur = root;
while (cur != null) {
if (key.compareTo(cur.key) == 0) {
ans = cur;
break;
} else if (key.compareTo(cur.key) < 0) {
ans = cur;
cur = cur.l;
} else {
cur = cur.r;
}
}
return ans;
}
private SBTNode<K, V> findLastNoBigIndex(K key) {
SBTNode<K, V> ans = null;
SBTNode<K, V> cur = root;
while (cur != null) {
if (key.compareTo(cur.key) == 0) {
ans = cur;
break;
} else if (key.compareTo(cur.key) < 0) {
cur = cur.l;
} else {
ans = cur;
cur = cur.r;
}
}
return ans;
}
// 现在,以cur为头的树上,新增,加(key, value)这样的记录
// 加完之后,会对cur做检查,该调整调整
// 返回,调整完之后,整棵树的新头部
private SBTNode<K, V> add(SBTNode<K, V> cur, K key, V value) {
if (cur == null) {
return new SBTNode<K, V>(key, value);
} else {
cur.size++;
if (key.compareTo(cur.key) < 0) {
cur.l = add(cur.l, key, value);
} else {
cur.r = add(cur.r, key, value);
}
return maintain(cur);
}
}
// 在cur这棵树上,删掉key所代表的节点
// 返回cur这棵树的新头部
private SBTNode<K, V> delete(SBTNode<K, V> cur, K key) {
cur.size--;
if (key.compareTo(cur.key) > 0) {
cur.r = delete(cur.r, key);
} else if (key.compareTo(cur.key) < 0) {
cur.l = delete(cur.l, key);
} else { // 当前要删掉cur
if (cur.l == null && cur.r == null) {
// free cur memory -> C++
cur = null;
} else if (cur.l == null && cur.r != null) {
// free cur memory -> C++
cur = cur.r;
} else if (cur.l != null && cur.r == null) {
// free cur memory -> C++
cur = cur.l;
} else { // 有左有右
SBTNode<K, V> pre = null;
SBTNode<K, V> des = cur.r;
des.size--;
while (des.l != null) {
pre = des;
des = des.l;
des.size--;
}
if (pre != null) {
pre.l = des.r;
des.r = cur.r;
}
des.l = cur.l;
des.size = des.l.size + (des.r == null ? 0 : des.r.size) + 1;
// free cur memory -> C++
cur = des;
}
}
// cur = maintain(cur);
return cur;
}
private SBTNode<K, V> getIndex(SBTNode<K, V> cur, int kth) {
if (kth == (cur.l != null ? cur.l.size : 0) + 1) {
return cur;
} else if (kth <= (cur.l != null ? cur.l.size : 0)) {
return getIndex(cur.l, kth);
} else {
return getIndex(cur.r, kth - (cur.l != null ? cur.l.size : 0) - 1);
}
}
public int size() {
return root == null ? 0 : root.size;
}
public boolean containsKey(K key) {
if (key == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("invalid parameter.");
}
SBTNode<K, V> lastNode = findLastIndex(key);
return lastNode != null && key.compareTo(lastNode.key) == 0 ? true : false;
}
// (key,value) put -> 有序表 新增、改value
public void put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("invalid parameter.");
}
SBTNode<K, V> lastNode = findLastIndex(key);
if (lastNode != null && key.compareTo(lastNode.key) == 0) {
lastNode.value = value;
} else {
root = add(root, key, value);
}
}
public void remove(K key) {
if (key == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("invalid parameter.");
}
if (containsKey(key)) {
root = delete(root, key);
}
}
public K getIndexKey(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= this.size()) {
throw new RuntimeException("invalid parameter.");
}
return getIndex(root, index + 1).key;
}
public V getIndexValue(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= this.size()) {
throw new RuntimeException("invalid parameter.");
}
return getIndex(root, index + 1).value;
}
public V get(K key) {
if (key == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("invalid parameter.");
}
SBTNode<K, V> lastNode = findLastIndex(key);
if (lastNode != null && key.compareTo(lastNode.key) == 0) {
return lastNode.value;
} else {
return null;
}
}
public K firstKey() {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
SBTNode<K, V> cur = root;
while (cur.l != null) {
cur = cur.l;
}
return cur.key;
}
public K lastKey() {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
SBTNode<K, V> cur = root;
while (cur.r != null) {
cur = cur.r;
}
return cur.key;
}
public K floorKey(K key) {
if (key == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("invalid parameter.");
}
SBTNode<K, V> lastNoBigNode = findLastNoBigIndex(key);
return lastNoBigNode == null ? null : lastNoBigNode.key;
}
public K ceilingKey(K key) {
if (key == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("invalid parameter.");
}
SBTNode<K, V> lastNoSmallNode = findLastNoSmallIndex(key);
return lastNoSmallNode == null ? null : lastNoSmallNode.key;
}
}聊聊红黑树
1)平衡性规定非常诡异
2)平衡性调整最为复杂
3)优点在于每次插入删除扰动较好,但是在今天看来这个优势也极其微弱了
原因:贪图扰动小的话,B+树、2-3-4树可能更好,还是那句话,到底图什么
4)除此之外,红黑树并不比AVL树、SB树、跳表更加优秀
5)面试上遇到,说清楚道理,不行就举报。。。
跳表(skiplist)
1)结构上根本和搜索二叉树无关
2)利用随机概率分布来使得高层索引可以无视数据规律,做到整体性能优良
3)思想是所有有序表中最先进的
4)结构简单就是多级单链表
// 跳表的节点定义
public static class SkipListNode<K extends Comparable<K>, V> {
public K key;
public V val;
public ArrayList<SkipListNode<K, V>> nextNodes;
public SkipListNode(K k, V v) {
key = k;
val = v;
nextNodes = new ArrayList<SkipListNode<K, V>>();
}
// 遍历的时候,如果是往右遍历到的null(next == null), 遍历结束
// 头(null), 头节点的null,认为最小
// node -> 头,node(null, "") node.isKeyLess(!null) true
// node里面的key是否比otherKey小,true,不是false
public boolean isKeyLess(K otherKey) {
// otherKey == null -> false
return otherKey != null && (key == null || key.compareTo(otherKey) < 0);
}
public boolean isKeyEqual(K otherKey) {
return (key == null && otherKey == null)
|| (key != null && otherKey != null && key.compareTo(otherKey) == 0);
}
}
public static class SkipListMap<K extends Comparable<K>, V> {
private static final double PROBABILITY = 0.5; // < 0.5 继续做,>=0.5 停
private SkipListNode<K, V> head;
private int size;
private int maxLevel;
public SkipListMap() {
head = new SkipListNode<K, V>(null, null);
head.nextNodes.add(null); // 0
size = 0;
maxLevel = 0;
}
// 从最高层开始,一路找下去,
// 最终,找到第0层的<key的最右的节点
private SkipListNode<K, V> mostRightLessNodeInTree(K key) {
if (key == null) {
return null;
}
int level = maxLevel;
SkipListNode<K, V> cur = head;
while (level >= 0) { // 从上层跳下层
// cur level -> level-1
cur = mostRightLessNodeInLevel(key, cur, level--);
}
return cur;
}
// 在level层里,如何往右移动
// 现在来到的节点是cur,来到了cur的level层,在level层上,找到<key最后一个节点并返回
private SkipListNode<K, V> mostRightLessNodeInLevel(K key,
SkipListNode<K, V> cur,
int level) {
SkipListNode<K, V> next = cur.nextNodes.get(level);
while (next != null && next.isKeyLess(key)) {
cur = next;
next = cur.nextNodes.get(level);
}
return cur;
}
public boolean containsKey(K key) {
if (key == null) {
return false;
}
SkipListNode<K, V> less = mostRightLessNodeInTree(key);
SkipListNode<K, V> next = less.nextNodes.get(0);
return next != null && next.isKeyEqual(key);
}
// 新增、改value
public void put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null) {
return;
}
// 0层上,最右一个,< key 的Node -> >key
SkipListNode<K, V> less = mostRightLessNodeInTree(key);
SkipListNode<K, V> find = less.nextNodes.get(0);
if (find != null && find.isKeyEqual(key)) {
find.val = value;
} else { // find == null 8 7 9
size++;
int newNodeLevel = 0;
while (Math.random() < PROBABILITY) {
newNodeLevel++;
}
// newNodeLevel
while (newNodeLevel > maxLevel) {
head.nextNodes.add(null);
maxLevel++;
}
SkipListNode<K, V> newNode = new SkipListNode<K, V>(key, value);
for (int i = 0; i <= newNodeLevel; i++) {
newNode.nextNodes.add(null);
}
int level = maxLevel;
SkipListNode<K, V> pre = head;
while (level >= 0) {
// level 层中,找到最右的 < key 的节点
pre = mostRightLessNodeInLevel(key, pre, level);
if (level <= newNodeLevel) {
newNode.nextNodes.set(level, pre.nextNodes.get(level));
pre.nextNodes.set(level, newNode);
}
level--;
}
}
}
public V get(K key) {
if (key == null) {
return null;
}
SkipListNode<K, V> less = mostRightLessNodeInTree(key);
SkipListNode<K, V> next = less.nextNodes.get(0);
return next != null && next.isKeyEqual(key) ? next.val : null;
}
public void remove(K key) {
if (containsKey(key)) {
size--;
int level = maxLevel;
SkipListNode<K, V> pre = head;
while (level >= 0) {
pre = mostRightLessNodeInLevel(key, pre, level);
SkipListNode<K, V> next = pre.nextNodes.get(level);
// 1)在这一层中,pre下一个就是key
// 2)在这一层中,pre的下一个key是>要删除key
if (next != null && next.isKeyEqual(key)) {
// free delete node memory -> C++
// level : pre -> next(key) -> ...
pre.nextNodes.set(level, next.nextNodes.get(level));
}
// 在level层只有一个节点了,就是默认节点head
if (level != 0 && pre == head && pre.nextNodes.get(level) == null) {
head.nextNodes.remove(level);
maxLevel--;
}
level--;
}
}
}
public K firstKey() {
return head.nextNodes.get(0) != null ? head.nextNodes.get(0).key : null;
}
public K lastKey() {
int level = maxLevel;
SkipListNode<K, V> cur = head;
while (level >= 0) {
SkipListNode<K, V> next = cur.nextNodes.get(level);
while (next != null) {
cur = next;
next = cur.nextNodes.get(level);
}
level--;
}
return cur.key;
}
public K ceilingKey(K key) {
if (key == null) {
return null;
}
SkipListNode<K, V> less = mostRightLessNodeInTree(key);
SkipListNode<K, V> next = less.nextNodes.get(0);
return next != null ? next.key : null;
}
public K floorKey(K key) {
if (key == null) {
return null;
}
SkipListNode<K, V> less = mostRightLessNodeInTree(key);
SkipListNode<K, V> next = less.nextNodes.get(0);
return next != null && next.isKeyEqual(key) ? next.key : less.key;
}
public int size() {
return size;
}
}有序表题目
题目一
给定一个数组arr,和两个整数a和b(a<=b)
求arr中有多少个子数组,累加和在[a,b]这个范围上
返回达标的子数组数量
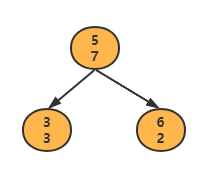
使用这种方式构建有序表:每一个节点第一个数字代表value,排序就根据这个value进行。第二个数字表示,自己+左孩子+右孩子value个数。如图代表3有3个,6有两个,5有2个
这种结构,即可以接收重复值,还可以很快的算出,大于或者小于某个值的个数。
题目二
有一个滑动窗口(讲过的):
1)L是滑动窗口最左位置、R是滑动窗口最右位置,一开始LR都在数组左侧
2)任何一步都可能R往右动,表示某个数进了窗口
3)任何一步都可能L往右动,表示某个数出了窗口
想知道每一个窗口状态的中位数
与题目一相同的存储结构,剩下的就是R往右移,就往结构中加数据,L往右移就从结构总移出数据
题目三
设计一个结构包含如下两个方法:
void add(int index, int num):把num加入到index位置
int get(int index) :取出index位置的值
void remove(int index) :把index位置上的值删除
要求三个方法时间复杂度O(logN)
设计一种数据结构,按照自然序排序:第一个数据为节点的value,第二个数字,表示该节点下有几个节点。
如图,节点按自然序排序,所以图中记录的数据原始数据为:3 3 7 5 6
改写有序表的题目核心点
1)分析增加什么数据项可以支持题目
2)有序表一定要保持内部参与排序的key不重复
3)增加这个数据项了,在平衡性调整时,保证这个数据项也能更新正确
4)做到上面3点,剩下就是搜索二叉树怎么实现你想要的接口的问题了























 310
310











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








