Jzzhu has a big rectangular chocolate bar that consists of n × m unit squares. He wants to cut this bar exactly k times. Each cut must meet the following requirements:
- each cut should be straight (horizontal or vertical);
- each cut should go along edges of unit squares (it is prohibited to divide any unit chocolate square with cut);
- each cut should go inside the whole chocolate bar, and all cuts must be distinct.
The picture below shows a possible way to cut a 5 × 6 chocolate for 5 times.
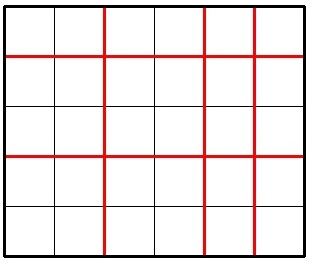
Imagine Jzzhu have made k cuts and the big chocolate is splitted into several pieces. Consider the smallest (by area) piece of the chocolate, Jzzhu wants this piece to be as large as possible. What is the maximum possible area of smallest piece he can get with exactlyk cuts? The area of a chocolate piece is the number of unit squares in it.
A single line contains three integers n, m, k (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 109; 1 ≤ k ≤ 2·109).
Output a single integer representing the answer. If it is impossible to cut the big chocolate k times, print -1.
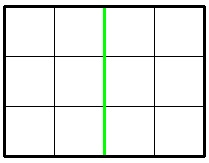
3 4 1
6
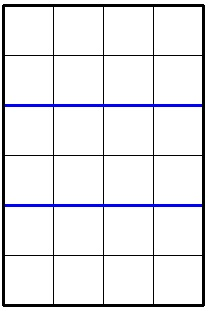
6 4 2
8
2 3 4
-1
In the first sample, Jzzhu can cut the chocolate following the picture below:
In the second sample the optimal division looks like this:
In the third sample, it's impossible to cut a 2 × 3 chocolate 4 times.
切巧克力 必须要横切或纵切 必须要沿着巧克力的边切 不能破坏巧克力的大小 求切出的 最小块最大的面积
借鉴别人的证明 我感觉挺巧妙的
不难发现如果纵向切k1刀,横向切k2刀,那么答案应该是 (n/(k1+1)) * (m/(k2+1)),除法是取整的。虽然是取整,但是不难发现其实就是要(k1+1)*(k2+1)最小,根据均值不等式,k1+k2=k(定值) k1==k2的时候(k1+1)*(k2+1)=k1*k2+k1+k2+1=k1*k2+k+1应该是取最大值,所以当k1,k2越接近两端的时候这个值才会最小,所以我们总是先把某一维的切掉,然后再考虑剩下那一维。
所以首先判断能不能在一维切完 切不完就把剩余的刀数用来切第二维 第一维 的大小已经变成1了 所以面积是用1去乘第二维产生的
代码:
<span style="font-family:KaiTi_GB2312;font-size:18px;">#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string.h>
#include <string>
#define eps 1e-8
#define op operator
#define MOD 10009
#define MAXN 100100
#define FOR(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i<=b;i++)
#define FOV(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i>=b;i--)
#define REP(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i<b;i++)
#define REV(i,a,b) for(int i=a-1;i>=b;i--)
#define MEM(a,x) memset(a,x,sizeof a)
#define ll __int64
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//freopen("ceshi.txt","r",stdin);
ll n,m,k;
while(scanf("%I64d%I64d%I64d",&n,&m,&k)!=EOF)
{
ll ans1,ans2;
if(m-1+n-1<k)
{
printf("-1\n");
continue;
}
if(k<=n-1||k<=m-1)
{
ans1=n/(k+1)*m;
ans2=m/(k+1)*n;
}
else
{
ans1=m/(k-(n-1)+1)*1;
ans2=n/(k-(m-1)+1)*1;
}
printf("%I64d\n",max(ans1,ans2));
}
return 0;
}
</span>








 探讨如何通过切巧克力的次数最大化最小块的面积,并提供一种利用均值不等式的解决方案。
探讨如何通过切巧克力的次数最大化最小块的面积,并提供一种利用均值不等式的解决方案。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








