参考资料:http://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/current/spring-framework-reference/htmlsingle/#mvc-features
1 Spring Web MVC框架介绍
DispatcherServlet是框架的设计核心,他负责分发请求给处理器、包括可配置的处理映射,视图表现,本地化,时区以及可上传文件式的主题。
默认的处理器基于注解@Controller和@RequestMapping,提供一个相当大幅度的灵活度处理的方法。
通过Spring 3.0,@Controller能允许你通过@PathVariable注解创建一个RESTful的web站点和应用程序。
通过Spring MVC我们可以用任何对象作为控制对象或基于表单的对象,我们不需要实现某框架的特殊接口或继承类。Spring的数据绑定具有很高的灵活性,比如它可以处理类型错误如验证错误一样,使得通过应用程序验证,而不是系统错误。
Spring MVC的页面处理也非常灵活。Controller不仅是准备一个model的含数据的map的响应,也可以选择一个视图名,并且它可以直接写出response流并且完成请求。
视图(View)名可通过文件扩展名配置或者接受头内容的类型转让,包括bean的名字,properties问卷或者通过自定义的ViewResolver接口。
模型(Model)是一个Map接口,它考虑到完全抽象的表现层技术。你可以直接将其表示成JSP,Velocity,Freemarker,或者生成XML,JSON,Atom,和许多其他内容类型。Model的Map可以简单的转换为一个合适的格式,如JSP请求或者Velocity模板。
1.1 Spring Web MVC功能
- 清晰的分工
- 强力直观的配置
- 灵活的,无强制配置,适应性强
- 可重用的业务代码
- 自定义的数据绑定和验证
- 自定义的处理器匹配和页面响应
- 灵活的模型转换
- 自定义的时区,本地化以及主题策略
- 一个简单并强大的JSP标签库,提供了支持功能
- 对象的生命周期是包括在当前的HTTP request或者 HTTP Session中的
2 The DispatcherServlet
Spring Web MVC框架像许多其他的web MVC框架一样,基于request,并设计成围绕着核心Servlet来分发请求到控制端,控制端提供功能性。
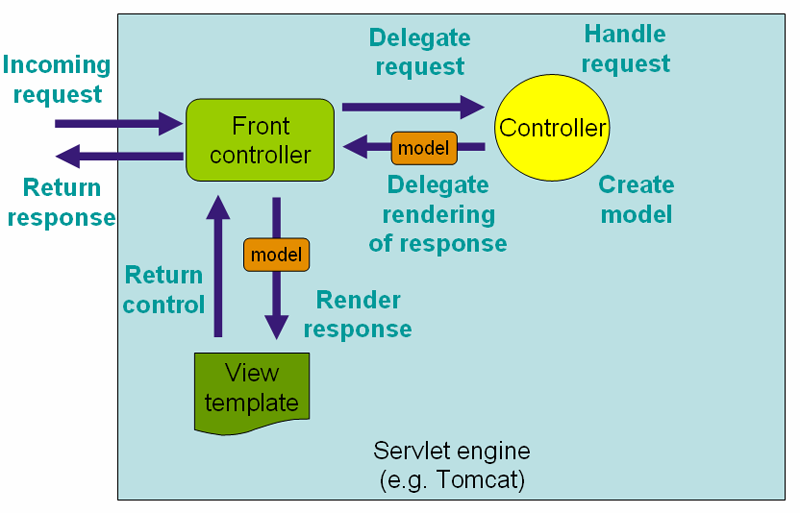
如下图,DispatcherServlet承担着Front controller的任务。
DispatcherServlet是一个Servlet,他继承自HttpServlet的基类,并且声明自web.xml。我们需要匹配请求来让DispatcherServlet处理,即<url-pattern>,
web.xml :
<web-app>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>example</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>example</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/example/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>在Servlet3.0+的环境下,也可以通过编码的手段来配置:
编码配置(等价于XML配置):
public class MyWebApplicationInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer {
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext container) {
ServletRegistration.Dynamic registration = container.addServlet("dispatcher", new DispatcherServlet());
registration.setLoadOnStartup(1);
registration.addMapping("/example/*");
}
}WebApplicationInitializer是Spring MVC提供的基类来初始化Servlet 3的容器。
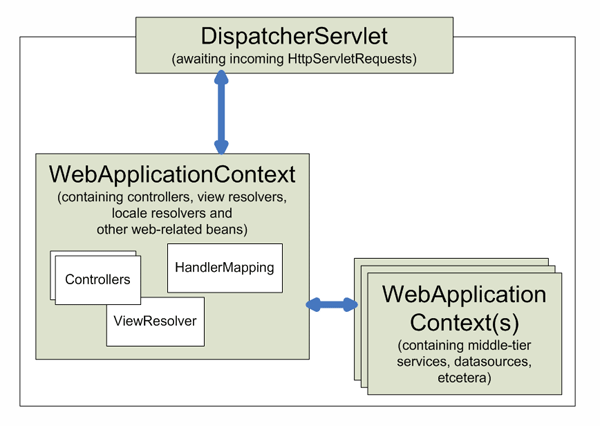
每一个DispatcherServlet都有一个自己的WebApplicationContext,而这个WebApplicationContext 继承的所有实例都定义在根WebApplicationContext中。
在初始化DispatcherServlet时,Spring MVC寻找一个[servlet-name]-servlet.xml的文件在WEB-INF下,比如example-servlet.xml。
他也可以通过配置属性contextConfigLocation来自定义配置文件目录:
<web-app>
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/root-context.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value></param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
</web-app>WebApplicationContext是ApplcationContext基于web应用功能的扩展,它不同于ApplicationContext在可以使用主题,并且可以知道哪个Servlt是被联系的。WebApplicationContext被绑定在ServletContext中,通过RequestContextUtils类中的静态方法,你可以查看WebApplicationContext。
2.1 WebApplicationContext中特殊的Bean类型
Spring的DispatcherServlet使用特殊的Bean去处理请求以及返回页面。我们可以选择单个或多个使用这些bean在WebApplicationContext中。Spring MVC准备了一个默认bean列表,所以当你没有配置时,你并不需要初始化他们。
| Bean Type | 说明 |
|---|---|
| HandlerMapping | Maps来自请求到处理器和一个预先和延后处理器(即拦截器),基于一些可改变的规则来自HandlerMapping实现。最常用的实现支持注解的控制器 |
| HandlerAdapter | 帮助DispatcherServlet执行一个处理器去匹配不被理会的请求。例如一个注解的controller需要处理大量的注解,因此HandlerAdpater的主要用途是隐藏DisptatcherServlet的细节 |
| HandlerExceptionResolver | 匹配错误至页面 |
| ViewResolver | 处理基于String的View名字至存在的View页面 |
| LocaleResolver&LocaleContextResolver | 用于国际化 |
| ThemeResolver | 提供能用的Web应用主题 |
| MulitipartResolver | 解析上传文件请求 |
| FlashMapManager | 保存并搜索“input”和“output”,能用于传递属性至不同的request,经常用于重定向 |
2.2 默认的DispatcherServlet配置
所有的特殊Bean都有配置,在org.springframework.web.servlet中的DispatcherServlet.properties。
2.3 DispatcherServlet的处理顺序
- 获取WebApplicationContext并被绑定为一个控制器以及其他元素可使用的属性。
- 本地的解析器被绑定到请求。
- 主题解析器被绑定。
- 如果指定了复合文件解析器,则请求将检查符合文件
- 搜索适当的处理器
- 如果返回了一个model,则提供一个view。
DispatcherServlet可初始化这几个属性:contextClass(自定义的类),contextConfigLocation(配置文件),namespace(默认为[servlet-name]-servlet)。
3 实现Controllers
@Controller
public class HelloWorldController {
@RequestMapping("/helloWorld")
public String helloWorld(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("message", "Hello World!");
return "helloWorld";
}
}@Controller和@RequestMapping这2个注解提供了灵活的方法名即签名配置。
在以上例子中方法需要接受一个Model类型的形参,并且返回一个String类型的视图名。
3.1 通过@Controller来定义controller
只需要启动扫描注解包就可以使用@Controller来定义包
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="org.springframework.samples.petclinic.web"/>
<!-- ... -->
</beans>3.2 通过@RequestMapping来匹配请求
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/appointments")
public class AppointmentsController {
private final AppointmentBook appointmentBook;
@Autowired
public AppointmentsController(AppointmentBook appointmentBook) {
this.appointmentBook = appointmentBook;
}
/* 对于/appointments的HTTP的GET请求调用这个方法 */
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
public Map<String, Appointment> get() {
return appointmentBook.getAppointmentsForToday();
}
@RequestMapping(value="/{day}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public Map<String, Appointment> getForDay(@PathVariable @DateTimeFormat(iso=ISO.DATE) Date day, Model model) {
return appointmentBook.getAppointmentsForDay(day);
}
/* 对于/appointments/new 的HTTP的GET请求调用这个方法 */
@RequestMapping(value="/new", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public AppointmentForm getNewForm() {
return new AppointmentForm();
}
/* 对于/appointments的HTTP的POST请求调用这个方法 */
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String add(@Valid AppointmentForm appointment, BindingResult result) {
if (result.hasErrors()) {
return "appointments/new";
}
appointmentBook.addAppointment(appointment);
return "redirect:/appointments";
}
}以上例子使用了很多@RequestMapping注解,第一个在类级别下的@RequestMapping(“/appointments”)说明所有的处理方法都是与appointments相关的。
get表明只接受get请求。
用@RequestMapping注解来修饰类级别并不是必须的:
@Controller
public class ClinicController {
private final Clinic clinic;
@Autowired
public ClinicController(Clinic clinic) {
this.clinic = clinic;
}
@RequestMapping("/")
public void welcomeHandler() {
}
@RequestMapping("/vets")
public ModelMap vetsHandler() {
return new ModelMap(this.clinic.getVets());
}
}URL Template Patterns
URL模板可以用在@RequestMapping下的方法。
例如http://www.example.com/users/{userId} 可将fred注入到域中http://www.example.com/users/fred。
在Spring MVC中使用@PathVariable注解在形参中,可将其绑定到url模板中的属性。
详细例子:
@RequestMapping(value="/owners/{ownerId}", method=RequestMethod.GET)
public String findOwner(@PathVariable String ownerId, Model model) {
Owner owner = ownerService.findOwner(ownerId);
model.addAttribute("owner", owner);
return "displayOwner";
}或者:
@RequestMapping(value="/owners/{ownerId}", method=RequestMethod.GET)
public String findOwner(@PathVariable("ownerId") String theOwner, Model model) {
// implementation omitted
}在类级别使用url模板
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/owners/{ownerId}")
public class RelativePathUriTemplateController {
@RequestMapping("/pets/{petId}")
public void findPet(@PathVariable String ownerId, @PathVariable String petId, Model model) {
// implementation omitted
}
}当使用findPet( )方法后URL:/owners/42/pets/21.
@PathVariable的类型为基本类型。
URL模板也可以匹配正则表达式
3.3 定义@RequestMapping 处理器方法
@RequestMapping处理方法有很高的灵活性。
支持方法参数类型
- Request和Reponse对象(Servlet API),比如ServletRequest和HttpServletRequest
- Session object(Servlet API):HttpSession
- WebRequest或者NativeWebRequest
- Local,LocaleResolver/LocaleContextResolver
- TimeZone/ZoneId
- InputStream/Reader,request内容
- OutputStream/Writer,response内容
- HttpMethod,Http请求
- Principal:包含当前的认证用户
- @PathVariable:用于URL模板的变量
- @MatrixVariable:用于URL的键值配对的片段
- @RequsetParam:用于指定的Servlet request参数
- @RequestHeader:用于指定的Servlet request的HTTP头
- @RequestBody:用于指定的HTTP request的body
- @RequestPart:用于复合数据请求
- HttpEntity<?>参数用来访问Servlet request HTTP headers和contensts
- Map/Model,保存了视图所需要的模型数据
- RedirectAttributes:特定的重定向的属性
- Errors/BindingResult: 验证结果
- SessionStatus:
- UrlComponentsBuilder
如果使用Errors或者BindingResult,需要如下顺序:
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String processSubmit(@ModelAttribute("pet") Pet pet, BindingResult result, Model model) { ... }支持的返回类型
- ModelAndView类型,@ModelAttrivute描述的方法
- Model类型,@ModelAttribute描述的数据方法
- Map类型
- View类型
- String类型,对应view的名字
- void,相应自己
通过@RequestParam来绑定请求参数
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/pets")
@SessionAttributes("pet")
public class EditPetForm {
// ...
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String setupForm(@RequestParam("petId") int petId, ModelMap model) {
Pet pet = this.clinic.loadPet(petId);
model.addAttribute("pet", pet);
return "petForm";
}
// ...
}3.4 异步请求处理
4 处理匹配
我们通过@RequestMapping注解来处理匹配,然而,知道所有的HandlerMapping类都是继承自AbstractHandlerMapping可以自定义他们的行为:
- interceptors:拦截器
- defaultHandler:默认的处理器
- order:基于order属性
- alwaysUseFullPath。
- urlDecode,默认为true
<beans>
<bean id="handlerMapping" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping">
<property name="interceptors">
<bean class="example.MyInterceptor"/>
</property>
</bean>
<beans>4.1 通过HandlerInterceptor来过滤请求
<beans>
<bean id="handlerMapping" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping">
<property name="interceptors">
<list>
<ref bean="officeHoursInterceptor"/>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="officeHoursInterceptor"
class="samples.TimeBasedAccessInterceptor">
<property name="openingTime" value="9"/>
<property name="closingTime" value="18"/>
</bean>
<beans>package samples;
public class TimeBasedAccessInterceptor extends HandlerInterceptorAdapter {
private int openingTime;
private int closingTime;
public void setOpeningTime(int openingTime) {
this.openingTime = openingTime;
}
public void setClosingTime(int closingTime) {
this.closingTime = closingTime;
}
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
Object handler) throws Exception {
Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance();
int hour = cal.get(HOUR_OF_DAY);
if (openingTime <= hour && hour < closingTime) {
return true;
}
response.sendRedirect("http://host.com/outsideOfficeHours.html");
return false;
}
}5 处理页面
对于Spring处理视图,ViewResolver和View很重要,ViewResolver提供一个匹配在视图名和视图文件,view接口记录了request的准备已经处理request到视图。
5.1 通过ViewResolver接口处理views
ViewResolver:
| ViewResolver | Description |
|---|---|
| AbstractCachingViewResolver | 处理器缓存了一些视图,通常这些视图需要在使用前预处理 |
| XMLViewResolver | 实现ViewResolver能接受配置文件写在XML,默认的配置文件在/WEB-INF/views.xml |
| ResourceBundleViewResolver | 使用属性文件实现ViewResolver,默认为views.properties |
| UrlBasedViewResolver | 直接将结果映射到URL |
| InternalResourceViewResolver | UrlBasedViewResolver的次级类 |
| VelocityViewResolver | 支持VelocityView |
| ContentNegotiationgViewResolver | 实现ViewResolver接口,通过request的文件名或者accept头来生成视图 |
URLBasedViewResolver
<bean id="viewResolver"
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.UrlBasedViewResolver">
<property name="viewClass" value="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.JstlView"/>
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/"/>
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/>
</bean>ResourceBundleViewResolver
<bean id="viewResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.ResourceBundleViewResolver">
<property name="basename" value="views"/>
<property name="defaultParentView" value="parentView"/>
</bean>5.2 ViewResolver链
<bean id="jspViewResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="viewClass" value="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.JstlView"/>
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/"/>
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/>
</bean>
<bean id="excelViewResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.XmlViewResolver">
<property name="order" value="1"/>
<property name="location" value="/WEB-INF/views.xml"/>
</bean>
<!-- in views.xml -->
<beans>
<bean name="report" class="org.springframework.example.ReportExcelView"/>
</beans>5.3 重定向views
RedirectView
@RequestMapping(value = "/files/{path}", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String upload(...) {
// ...
return "redirect:files/{path}";
}The redirect: prefix
redirect:http://myhost.com/some/arbitrary/path
The forward: prefix
5.4 ContentNegotiatingViewResolver
ContentNegotiatingViewResolver 并不自己处理视图,而是委托给其他的视图处理器。
example:
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.ContentNegotiatingViewResolver">
<property name="mediaTypes">
<map>
<entry key="atom" value="application/atom+xml"/>
<entry key="html" value="text/html"/>
<entry key="json" value="application/json"/>
</map>
</property>
<property name="viewResolvers">
<list>
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.BeanNameViewResolver"/>
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/"/>
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/>
</bean>
</list>
</property>
<property name="defaultViews">
<list>
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.json.MappingJackson2JsonView" />
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="content" class="com.foo.samples.rest.SampleContentAtomView"/>6 使用闪存属性
闪存属性可以提供一个方法给请求去保存。
Spring MVC有两种主要的方式来支持闪存属性,FlashMap用来保存闪存属性当FlashMapManager用来保存,检索以及管理FlashMap的属性。
7 搭建URL
Spring MVC提供了一个机制去搭建编写URL - UrlComponentsBuilder和UriComponents
扩展并加密URL的例子:
UriComponents uriComponents = UriComponentsBuilder.fromUriString(
"http://example.com/hotels/{hotel}/bookings/{booking}").build();
URI uri = uriComponents.expand("42", "21").encode().toUri();UriComponents是不可变的,并且expand( )和encode( )执行将返回一个新的实例。
UriComponents uriComponents = UriComponentsBuilder.newInstance()
.scheme("http").host("example.com").path("/hotels/{hotel}/bookings/{booking}").build()
.expand("42", "21")
.encode();8 本地化
9 使用主题
10 Spring的文件上传
11 处理错误
12 web安全
13 约定优先配置原则
13.1 控制器的匹配
- WelcomeController 匹配 /welcome*
- HomeController 匹配 /home*
- IndexController 匹配 /index *
RegisterController 匹配 /register*
AdminController匹配/admin/*
- CatalogController匹配/catalog/*
13.2 模型的ModelMap
- x.y.User实例生成user
- x.y.Registration生成registration
- java.util.HashMap的实例生成hashMap,我们需要明确这个名字,因为hashMap是违背直觉
null作为result会跑出一个IllegalArgumentException异常
An x.y.User[] array with zero or more x.y.User elements added will have the name userList generated.
- An x.y.Foo[] array with zero or more x.y.User elements added will have the name fooList generated.
- A java.util.ArrayList with one or more x.y.User elements added will have the name userList generated.
- A java.util.HashSet with one or more x.y.Foo elements added will have the name fooList generated.
- An empty java.util.ArrayList will not be added at all (in effect, the addObject(..) call will essentially be a no-op).
14 ETag支持
15 基于代码的servlet容器配置
16 SpringMVC的配置
16.1 启动MVC的JAVA配置或XML命名空间
基于@Configuration的配置
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
public class WebConfig {
}<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd">
<mvc:annotation-driven />
</beans>16.2 自定义提供的配置
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
public class WebConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void addFormatters(FormatterRegistry registry) {
// Add formatters and/or converters
}
@Override
public void configureMessageConverters(List<HttpMessageConverter<?>> converters) {
// Configure the list of HttpMessageConverters to use
}
}16.3 拦截器配置
通过java配置:
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
public class WebConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(new LocaleInterceptor());
registry.addInterceptor(new ThemeInterceptor()).addPathPatterns("/**").excludePathPatterns("/admin/**");
registry.addInterceptor(new SecurityInterceptor()).addPathPatterns("/secure/*");
}
}<mvc:interceptors>
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.LocaleChangeInterceptor" />
<mvc:interceptor>
<mvc:mapping path="/**"/>
<mvc:exclude-mapping path="/admin/**"/>
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.theme.ThemeChangeInterceptor" />
</mvc:interceptor>
<mvc:interceptor>
<mvc:mapping path="/secure/*"/>
<bean class="org.example.SecurityInterceptor" />
</mvc:interceptor>
</mvc:interceptors>16.4 内容导航
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
public class WebConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public void configureContentNegotiation(ContentNegotiationConfigurer configurer) {
configurer.favorPathExtension(false).favorParameter(true);
}
}<mvc:annotation-driven content-negotiation-manager="contentNegotiationManager" />
<bean id="contentNegotiationManager" class="org.springframework.web.accept.ContentNegotiationManagerFactoryBean">
<property name="favorPathExtension" value="false" />
<property name="favorParameter" value="true" />
<property name="mediaTypes" >
<value>
json=application/json
xml=application/xml
</value>
</property>
</bean>16.5 View Controllers
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
public class WebConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
registry.addViewController("/").setViewName("home");
}
}<mvc:view-controller path="/" view-name="home"/>16.6 View Resolvers
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
public class WebConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public void configureViewResolvers(ViewResolverRegistry registry) {
registry.enableContentNegotiation(new MappingJackson2JsonView());
registry.jsp();
}
}<mvc:view-resolvers>
<mvc:content-negotiation>
<mvc:default-views>
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.json.MappingJackson2JsonView" />
</mvc:default-views>
</mvc:content-negotiation>
<mvc:jsp />
</mvc:view-resolvers><mvc:view-resolvers>
<mvc:content-negotiation>
<mvc:default-views>
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.json.MappingJackson2JsonView" />
</mvc:default-views>
</mvc:content-negotiation>
<mvc:freemarker cache="false" />
</mvc:view-resolvers>
<mvc:freemarker-configurer>
<mvc:template-loader-path location="/freemarker" />
</mvc:freemarker-configurer>16.7 静态资源服务
<mvc:resources mapping="/resources/**" location="/public-resources/"/><mvc:resources mapping="/resources/**" location="/public-resources/">
<mvc:resource-chain>
<mvc:resource-cache />
<mvc:resolvers>
<mvc:version-resolver>
<mvc:content-version-strategy patterns="/**"/>
</mvc:version-resolver>
</mvc:resolvers>
</mvc:resource-chain>
</mvc:resources>16.8 默认的servlet
<mvc:default-servlet-handler/><mvc:default-servlet-handler default-servlet-name="myCustomDefaultServlet"/>16.9 路径匹配
<mvc:annotation-driven>
<mvc:path-matching
suffix-pattern="true"
trailing-slash="false"
registered-suffixes-only="true"
path-helper="pathHelper"
path-matcher="pathMatcher" />
</mvc:annotation-driven>
<bean id="pathHelper" class="org.example.app.MyPathHelper" />
<bean id="pathMatcher" class="org.example.app.MyPathMatcher" />





















 1039
1039











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








