买不到的数目
小明开了一家糖果店。他别出心裁:把水果糖包成4颗一包和7颗一包的两种。糖果不能
拆包卖。
小朋友来买糖的时候,他就用这两种包装来组合。当然有些糖果数目是无法组合出来的
,比如要买 10 颗糖。
你可以用计算机测试一下,在这种包装情况下,最大不能买到的数量是17。大于17的任
何数字都可以用4和7组合出来。
本题的要求就是在已知两个包装的数量时,求最大不能组合出的数字。
* 输入描述: 两个正整数,表示每种包装中糖的颗数(都不多于1000)
* 程序输出: 一个正整数,表示最大不能买到的糖数, 不需要考虑无解的情况。
方法一:暴力破解
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @createDate:2019年3月13日 上午8:10:06
* @porjectName:lanqiao
* @author Static
* @version 1.0
* @since JDK 1.8.0_21
* @filename:买不带的数目.java @describe:
*/
public class 买不带的数目 {
static int Max = 100000;
static int arr[] = new int[Max];
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = sc.nextInt();
int b = sc.nextInt();
sc.close();
fun(a, b);
}
public static void fun(int a, int b) {
// MAX/a因为防止越界,Max/a=i反过来就是当i取到Max/a的时候,也不会超出Max的范围
for (int i = 0; i < Max / a; i++) {
// 同理Max-a*i/b 可以的出a*i+j*b不会超过MAX
for (int j = 0; j < (Max - a * i) / b; j++) {
// 把满足ax+by的数组都置位可以买到的数
arr[i * a + j * b] = 1;
}
}
int count = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] == 1) {
count++;
if (count == a) {
System.out.println(i - a);// i-count
break;
}
} else {
count = 0;
}
}
}
}方法二:公式法
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = sc.nextInt();
int b = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(a*b-(a+b));
}
}总结:方法一耗时较高,如果非编程题可用,方法二数学公式,如果有数学功底建议使用数学公式
打印十字图
小明为某机构设计了一个十字型的徽标(并非红十字会啊),如下所示(可参见p1.jpg)
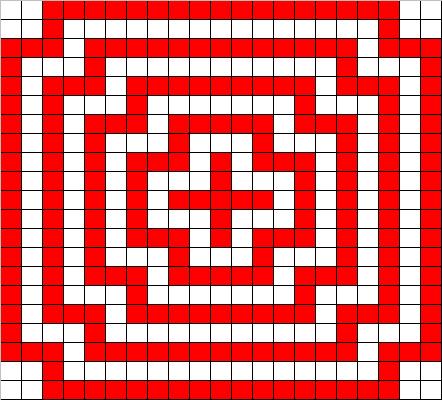
对方同时也需要在电脑dos窗口中以字符的形式输出该标志,并能任意控制层数。
为了能准确比对空白的数量,程序要求对行中的空白以句点(.)代替,红色部分用$代替。
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @createDate:2019年3月13日 上午9:22:04
* @porjectName:lanqiao
* @author Static
* @version 1.0
* @since JDK 1.8.0_21
* @filename:打印十字.java @describe:
*/
public class 打印十字 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
fun(n);
}
public static void fun(int n) {
int t = n * 4 + 5;
char arr[][] = new char[t][t];
// 初始化二维数组为.
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length; j++) {
arr[i][j] = '.';
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < t / 2; i += 2) {
for (int j = i + 2; j < t / 2 + 1; j++) {
arr[i][j] = '$';
arr[j][i] = '$';
}
arr[i + 1][i + 2] = '$';
arr[i + 2][i + 1] = '$';
arr[i + 2][i + 2] = '$';
}
for (int x = 0; x < t / 2 + 1; x++) {
for (int i = 0, j = t - 1; j >= i; i++, j--) {
arr[x][j] = arr[x][i];
}
}
for (int x = 0; x < t; x++) {
for (int i = 0, j = t - 1; j >= i; i++, j--) {
arr[j][x] = arr[i][x];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length; j++) {
System.out.print(arr[i][j]);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
总结:先分析左上部分,在把左右镜像复制,上下镜像复制就OK了
核桃的数量
小张是软件项目经理,他带领3个开发组。工期紧,今天都在加班呢。为鼓舞士气,小张打算给
每个组发一袋核桃(据传言能补脑)。他的要求是:
1. 各组的核桃数量必须相同
2. 各组内必须能平分核桃(当然是不能打碎的)
3. 尽量提供满足1,2条件的最小数量(节约闹革命嘛)
* 输入描述:
程序从标准输入读入:
a b c
a,b,c都是正整数,表示每个组正在加班的人数,用空格分开(a,b,c<30)
* 程序输出:
程序输出:
一个正整数,表示每袋核桃的数量。
例如:
用户输入:
2 4 5
程序输出:
20
再例如:
用户输入:
3 1 1
程序输出:
3
/**
* @createDate:2019年3月13日 下午5:27:17
* @porjectName:lanqiao
* @author Static
* @version 1.0
* @since JDK 1.8.0_21
* @filename:核桃的数量s.java @describe:
*/
public class 核桃的数量s {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = sc.nextInt();
int b = sc.nextInt();
int c = sc.nextInt();
int sum = a * b * c;
for (int i = 1; i < sum; i++) {
if (i % a == 0 && i % b == 0 && i % c == 0) {
sum = i;
break;
}
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}总结:这题就是求最小公倍数,我们初步把最小公倍数定位三数相乘,因为三数相乘必定是这三个数的公倍数,然后在三数相乘的数里面找最小的公倍数,如果找到了,就把最小公倍数设为i,否则三数相乘就是最小公倍数!
逆波兰表达式
正常的表达式称为中缀表达式,运算符在中间,主要是给人阅读的,机器求解并不方便。
例如:3 + 5 * (2 + 6) - 1
而且,常常需要用括号来改变运算次序。
相反,如果使用逆波兰表达式(前缀表达式)表示,上面的算式则表示为:
- + 3 * 5 + 2 6 1
不再需要括号,机器可以用递归的方法很方便地求解。
为了简便,我们假设:
1. 只有 + - * 三种运算符
2. 每个运算数都是一个小于10的非负整数
下面的程序对一个逆波兰表示串进行求值。
其返回值为一个数组:其中第一元素表示求值结果,第二个元素表示它已解析的字符数。
static int[] evaluate(String x) {
if (x.length() == 0)
return new int[] { 0, 0 };
char c = x.charAt(0);
if (c >= '0' && c <= '9')
return new int[] { c - '0', 1 };
int[] v1 = evaluate(x.substring(1));
int[] v2 = __________________________________________; // 填空位置
int v = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
if (c == '+')
v = v1[0] + v2[0];
if (c == '*')
v = v1[0] * v2[0];
if (c == '-')
v = v1[0] - v2[0];
return new int[] { v, 1 + v1[1] + v2[1] };
}
/**
* @createDate:2019年3月13日 下午5:34:20
* @porjectName:lanqiao
* @author Static
* @version 1.0
* @since JDK 1.8.0_21
* @filename:逆波兰表达式s.java @describe:
*/
public class 逆波兰表达式s {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int t[] = evaluate("-+3*5+261");
System.out.println(t[0]);
}
static int[] evaluate(String x) {
// 3 * 5 + 2 6 1
// + 3 * 5 + 2 6 1
// - + 3 * 5 + 2 6 1
if (x.length() == 0)
return new int[] { 0, 0 };
char c = x.charAt(0);
if (c >= '0' && c <= '9')
return new int[] { c - '0', 1 };
int[] v1 = evaluate(x.substring(1));
// [3][1]
int[] v2 = evaluate(x.substring(v1[1] + 1)); // 填空位置
int v = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
if (c == '+')
v = v1[0] + v2[0];
if (c == '*')
v = v1[0] * v2[0];
if (c == '-')
v = v1[0] - v2[0];
return new int[] { v, 1 + v1[1] + v2[1] };
}
}有理数类
有理数就是可以表示为两个整数的比值的数字。一般情况下,我们用近似的小数表示。但有些
时候,不允许出现误差,必须用两个整数来表示一个有理数。
这时,我们可以建立一个“有理数类”,下面的代码初步实现了这个目标。为了简明,它只提
供了加法和乘法运算。
class Rational {
private long ra;
private long rb;
private long gcd(long a, long b) {
if (b == 0)
return a;
return gcd(b, a % b);
}
public Rational(long a, long b) {
ra = a;
rb = b;
long k = gcd(ra, rb);
if (k > 1) { // 需要约分
ra /= k;
rb /= k;
}
}
// 加法
public Rational add(Rational x) {
return ________________________________________; // 填空位置
}
// 乘法
public Rational mul(Rational x) {
return new Rational(ra * x.ra, rb * x.rb);
}
public String toString() {
if (rb == 1)
return "" + ra;
return ra + "/" + rb;
}
}
使用该类的示例:
Rational a = new Rational(1,3);
Rational b = new Rational(1,6);
Rational c = a.add(b);
System.out.println(a + "+" + b + "=" + c);
/**
* @createDate:2019年3月13日 下午9:04:27
* @porjectName:lanqiao
* @author Static
* @version 1.0
* @since JDK 1.8.0_21
* @filename:有理数类.java @describe:
*/
public class 有理数类 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Rational a = new Rational(1, 3);
Rational b = new Rational(1, 6);
Rational c = a.add(b);
System.out.println(a + "+" + b + "=" + c);
}
}
class Rational {
private long ra;
private long rb;
private long gcd(long a, long b) {
if (b == 0)
return a;
return gcd(b, a % b);
}
public Rational(long a, long b) {
ra = a;
rb = b;
long k = gcd(ra, rb);
if (k > 1) { // 需要约分
ra /= k;
rb /= k;
}
}
// 加法
public Rational add(Rational x) {
return new Rational(x.ra * rb + ra * x.rb, x.rb * rb); // 填空位置
}
// 乘法
public Rational mul(Rational x) {
return new Rational(ra * x.ra, rb * x.rb);
}
public String toString() {
if (rb == 1)
return "" + ra;
return ra + "/" + rb;
}
}第39级台阶-记忆搜索
小明刚刚看完电影《第39级台阶》,离开电影院的时候,他数了数礼堂前的台阶数,
恰好是39级!
站在台阶前,他突然又想着一个问题:
如果我每一步只能迈上1个或2个台阶。先迈左脚,然后左右交替,最后一步是迈右脚,
也就是说一共要走偶数步。那么,上完39级台阶,有多少种不同的上法呢?
请你利用计算机的优势,帮助小明寻找答案。
/**
* @createDate:2019年3月13日 下午10:59:35
* @porjectName:lanqiao
* @author Static
* @version 1.0
* @since JDK 1.8.0_21
* @filename:第39级台阶.java @describe:
*/
public class 第39级台阶 {
static int arr[][] = new int[40][2];
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 获取开始时间
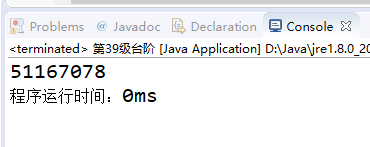
System.out.println(fun(39, 0));
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 获取结束时间
System.out.println("程序运行时间:" + (endTime - startTime) + "ms"); // 输出程序运行时间
}
public static int fun(int n, int tep) {
if (n < 0)
return 0;
if (arr[n][tep] != 0)
return arr[n][tep];
if (n == 0 && tep == 0) {
arr[n][tep] = 1;
return 1;
}
return arr[n][tep] = fun(n - 1, (tep + 1) % 2) + fun(n - 2, (tep + 1) % 2);
}
}
马虎的算式
小明是个急性子,上小学的时候经常把老师写在黑板上的题目抄错了。
有一次,老师出的题目是:36 x 495 = ?
他却给抄成了:396 x 45 = ?
但结果却很戏剧性,他的答案竟然是对的!!
因为 36 * 495 = 396 * 45 = 17820
类似这样的巧合情况可能还有很多,比如:27 * 594 = 297 * 54
假设 a b c d e 代表1~9不同的5个数字(注意是各不相同的数字,且不含0)
能满足形如: ab * cde = adb * ce 这样的算式一共有多少种呢?
/**
* @createDate:2019年3月13日 下午11:08:27
* @porjectName:lanqiao
* @author Static
* @version 1.0
* @since JDK 1.8.0_21
* @filename:马虎的算式.java @describe:
*/
public class 马虎的算式 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int cnt = 0;
for (int a = 1; a <= 9; a++) {
for (int b = 1; b <= 9; b++) {
if (b != a)
for (int c = 1; c <= 9; c++) {
if (c != b && c != a)
for (int d = 1; d <= 9; d++) {
if (d != c && d != b && d != a)
for (int e = 1; e <= 9; e++) {
if (e != a && e != b && e != c && e != d)
if ((a * 10 + b) * (c * 100 + d * 10 + e) == (a * 100 + d * 10 + b)
* (c * 10 + e))
cnt++;
}
}
}
}
}
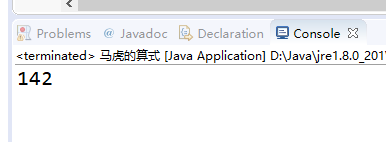
System.out.println(cnt);
}
}
组素数
素数就是不能再进行等分的数。比如:2 3 5 7 11 等。
9 = 3 * 3 说明它可以3等分,因而不是素数。
我们国家在1949年建国。如果只给你 1 9 4 9 这4个数字卡片,
可以随意摆放它们的先后顺序(但卡片不能倒着摆放啊,我们不是在脑筋急转弯!),
那么,你能组成多少个4位的素数呢?
全排列算法
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
/**
* @createDate:2019年3月13日 下午11:53:55
* @porjectName:lanqiao
* @author Static
* @version 1.0
* @since JDK 1.8.0_21
* @filename:组素数.java @describe:
*/
public class 组素数 {
static HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int arr[] = { 1, 4, 9, 9 };
fun(arr, 0, arr.length);
Iterator<Integer> iter = set.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
int temp = iter.next();
if (GetNum(temp)) {
System.out.println(temp);
}
}
}
public static void fun(int arr[], int sta, int end) {
if (sta == end) {
set.add(arr[0] * 1000 + arr[1] * 100 + arr[2] * 10 + arr[3]);
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < end; i++) {
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[sta];
arr[sta] = temp;
fun(arr, sta + 1, end);
temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[sta];
arr[sta] = temp;
}
}
}
public static boolean GetNum(int n) {
for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) {
if (n % i == 0)
return false;
}
return true;
}
}更容易理解的方法(利用循环全排列)
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
/**
* @createDate:2019年3月14日 上午12:37:31
* @porjectName:lanqiao
* @author Static
* @version 1.0
* @since JDK 1.8.0_21
* @filename:组素数s.java @describe:
*/
public class 组素数s {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>();
int temp;
for (int i = 1499; i <= 9941; i++) {
String str = String.valueOf(i);
char[] c = str.toCharArray();
Arrays.sort(c);
str = String.valueOf(c);
if (str.equals("1499")) {
set.add(i);
}
}
Iterator<Integer> iter = set.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
temp = iter.next();
if (GetNum(temp)) {
System.out.println(temp);
}
}
}
public static boolean GetNum(int n) {
for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) {
if (n % i == 0)
return false;
}
return true;
}
}全排列不懂的可以参考https://blog.csdn.net/MsStrbig/article/details/79823555,全排列算法
猜年龄
美国数学家维纳(N.Wiener)智力早熟,11岁就上了大学。他曾在1935~1936年应邀来中国清
华大学讲学。
一次,他参加某个重要会议,年轻的脸孔引人注目。于是有人询问他的年龄,他回答说:
“我年龄的立方是个4位数。我年龄的4次方是个6位数。这10个数字正好包含了从0到9这10
个数字,每个都恰好出现1次。”
请你推算一下,他当时到底有多年轻。
/**
* @createDate:2019年3月13日 下午11:41:38
* @porjectName:lanqiao
* @author Static
* @version 1.0
* @since JDK 1.8.0_21 @filename:s4_猜年龄.java @describe:
*/
public class s4_猜年龄 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
for (int i = 5; i < 40; i++) {
int a = i * i * i;
int b = i * i * i * i;
if (String.valueOf(a).length() == 4 && String.valueOf(b).length() == 6) {
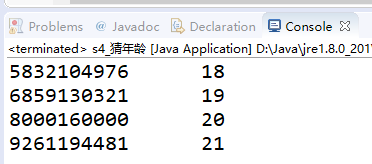
System.out.print(a + "" + b + "\t");
System.out.print(i);
System.out.println();
}
}
}
}

























 1364
1364











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








