功能简介
Linux内核等待队列是内核的一套事件唤醒机制,一般用于内核中断与线程的唤醒休眠,内核线程之间的唤醒休眠。常用接口是唤醒:wake_up_interruptible,等待休眠:wait_event_interruptible。
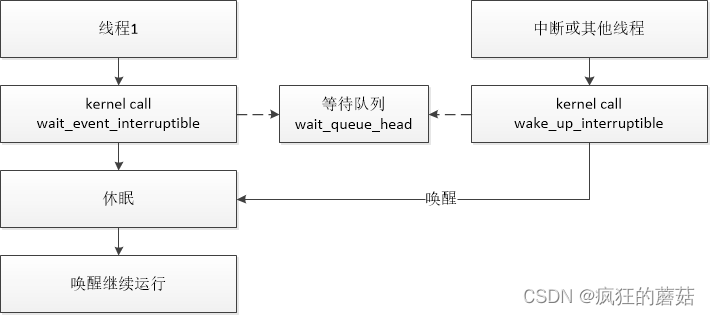
图1:等待队列常见使用流程
图1所示为等待队列常见使用流程,例如图中线程1通过系统调用进入内核,后调用wake_up_interruptible等待唤醒事件,当事件不满足条件时,线程1进入休眠状态。中断或其他线程任务事件满足条件时,调用wait_event_interruptible,唤醒等待在wait_queue_head上的线程1。其中等待队列wait_queue_head是内核中的一个struct,需要在使用时进行初始化。
内核中使用步骤
初始化
声明一个struct wait_queue_head变量test,并初始化:
DECLARE_WAIT_QUEUE_HEAD test;
再声明一个条件变量int condition = 0;
DECLARE_WAIT_QUEUE_HEAD的宏定义在include/linux/wait.h中
线程等待事件
线程的内核态调用
wait_event_interruptible(test,condition);
当condition为非0时,立马返回,不会休眠,当condition为0时,线程加入等待队列链表中,然后线程进入休眠状态。
事件产生,唤醒等待线程
当某一个事件状态满足要求,如某一个中断触发时,内核代码执行:
wake_up_interruptible(&test);
唤醒之前休眠等待在test等待队列中的线程。
内核中数据结构
在include/linux/wait.h中,有struct wait_queue_entry和struct wait_queue_entry。
/*
* A single wait-queue entry structure:
*/
struct wait_queue_entry {
unsigned int flags;
void *private;
wait_queue_func_t func;
struct list_head entry;
};
struct wait_queue_head {
spinlock_t lock;
struct list_head head;
};
t




 本文详细介绍了Linux内核中的等待队列机制,包括其基本概念、使用流程及核心数据结构。阐述了如何初始化等待队列、线程如何加入等待队列以及如何通过唤醒函数唤醒等待中的线程。
本文详细介绍了Linux内核中的等待队列机制,包括其基本概念、使用流程及核心数据结构。阐述了如何初始化等待队列、线程如何加入等待队列以及如何通过唤醒函数唤醒等待中的线程。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
















 1141
1141

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








