一、BlockingQueue介绍与常用方法
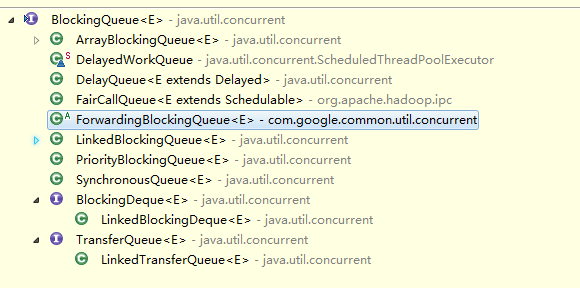
BlockingQueue是一个阻塞队列。在高并发场景是用得非常多的,在线程池中。如果运行线程数目大于核心线程数目时,也会尝试把新加入的线程放到一个BlockingQueue中去。队列的特性就是先进先出很容易理解,在java里头它的实现类主要有下图的几种,其中最常用到的是ArrayBlockingQueue、LinkedBlockingQueue及SynchronousQueue这三种,这三个也是今天主要讲的类。
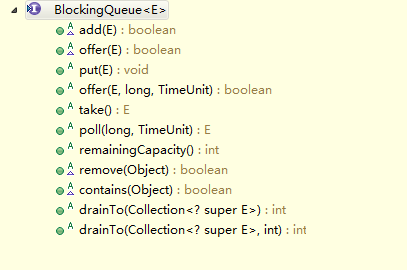
它主要的方法有
BlockingQueue的核心方法:
1、放入数据
(1) add(object)
队列没满的话,放入成功。否则抛出异常。
(2)offer(object):
表示如果可能的话,将object加到BlockingQueue里,即如果BlockingQueue可以容纳,则返回true,否则返回false.(本方法不阻塞当前执行方法的线程)
(3)offer(E o, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
可以设定等待的时间,如果在指定的时间内,还不能往队列中加入BlockingQueue,则返回失败。
(4)put(object)
把object加到BlockingQueue里,如果BlockQueue没有空间,则调用此方法的线程阻塞。直到BlockingQueue里面有空间再继续.
2、获取数据
(1)poll(time)
取走BlockingQueue里排在首位的对象,若不能立即取出,则可以等time参数规定的时间,取不到时返回null;
(2)poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
从BlockingQueue取出一个队首的对象,如果在指定时间内,队列一旦有数据可取,则立即返回队列中的数据。否则知道时间超时还没有数据可取,返回失败。
(3)take()
取走BlockingQueue里排在首位的对象,若BlockingQueue为空,阻断进入等待状态直到BlockingQueue有新的数据被加入;
(4)drainTo()
一次性从BlockingQueue获取所有可用的数据对象(还可以指定获取数据的个数),通过该方法,可以提升获取数据效率;不需要多次分批加锁或释放锁。
二、ArrayBlockingQueue
一个基本数组的阻塞队列。可以设置列队的大小。
ArrayBlockingQueue的源码是比较简单的,下面是笔者抽取了一部分源码并加以注释。它的基本原理实际还是数组,只不过存、取、删时都要做队列是否满或空的判断。然后加锁访问。
- package java.util.concurrent;
- import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
- import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
- import java.util.AbstractQueue;
- import java.util.Collection;
- import java.util.Iterator;
- import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
- import java.lang.ref.WeakReference;
- import java.util.Spliterators;
- import java.util.Spliterator;
- public class ArrayBlockingQueue<E> extends AbstractQueue<E>
- implements BlockingQueue<E>, java.io.Serializable {
- private static final long serialVersionUID = -817911632652898426L;
- /** 真正存入数据的数组*/
- final Object[] items;
- /** take, poll, peek or remove的下一个索引 */
- int takeIndex;
- /** put, offer, or add的下一个索引 */
- int putIndex;
- /**队列中元素个数*/
- int count;
- /**可重入锁 */
- final ReentrantLock lock;
- /** 队列不为空的条件 */
- private final Condition notEmpty;
- /** 队列未满的条件 */
- private final Condition notFull;
- transient Itrs itrs = null;
- /**
- *当前元素个数-1
- */
- final int dec(int i) {
- return ((i == 0) ? items.length : i) - 1;
- }
- /**
- * 返回对应索引上的元素
- */
- @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
- final E itemAt(int i) {
- return (E) items[i];
- }
- /**
- * 非空检查
- *
- * @param v the element
- */
- private static void checkNotNull(Object v) {
- if (v == null)
- throw new NullPointerException();
- }
- /**
- * 元素放入队列,注意调用这个方法时都要先加锁
- *
- */
- private void enqueue(E x) {
- final Object[] items = this.items;
- items[putIndex] = x;
- if (++putIndex == items.length)
- putIndex = 0;
- count++;//当前拥有元素个数加1
- notEmpty.signal();//有一个元素加入成功,那肯定队列不为空
- }
- /**
- * 元素出队,注意调用这个方法时都要先加锁
- *
- */
- private E dequeue() {
- final Object[] items = this.items;
- @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
- E x = (E) items[takeIndex];
- items[takeIndex] = null;
- if (++takeIndex == items.length)
- takeIndex = 0;
- count--;/当前拥有元素个数减1
- if (itrs != null)
- itrs.elementDequeued();
- notFull.signal();//有一个元素取出成功,那肯定队列不满
- return x;
- }
- /**
- * 指定删除索引上的元素
- *
- */
- void removeAt(final int removeIndex) {
- final Object[] items = this.items;
- if (removeIndex == takeIndex) {
- items[takeIndex] = null;
- if (++takeIndex == items.length)
- takeIndex = 0;
- count--;
- if (itrs != null)
- itrs.elementDequeued();
- } else {
- final int putIndex = this.putIndex;
- for (int i = removeIndex;;) {
- int next = i + 1;
- if (next == items.length)
- next = 0;
- if (next != putIndex) {
- items[i] = items[next];
- i = next;
- } else {
- items[i] = null;
- this.putIndex = i;
- break;
- }
- }
- count--;
- if (itrs != null)
- itrs.removedAt(removeIndex);
- }
- notFull.signal();//有一个元素删除成功,那肯定队列不满
- }
- /**
- *
- * 构造函数,设置队列的初始容量
- */
- public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity) {
- this(capacity, false);
- }
- /**
- * 构造函数。capacity设置数组大小 ,fair设置是否为公平锁
- * capacity and the specified access policy.
- */
- public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity, boolean fair) {
- if (capacity <= 0)
- throw new IllegalArgumentException();
- this.items = new Object[capacity];
- lock = new ReentrantLock(fair);//是否为公平锁,如果是的话,那么先到的线程先获得锁对象。
- //否则,由操作系统调度由哪个线程获得锁,一般为false,性能会比较高
- notEmpty = lock.newCondition();
- notFull = lock.newCondition();
- }
- /**
- *构造函数,带有初始内容的队列
- */
- public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity, boolean fair,
- Collection<? extends E> c) {
- this(capacity, fair);
- final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
- lock.lock(); //要给数组设置内容,先上锁
- try {
- int i = 0;
- try {
- for (E e : c) {
- checkNotNull(e);
- items[i++] = e;//依次拷贝内容
- }
- } catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
- throw new IllegalArgumentException();
- }
- count = i;
- putIndex = (i == capacity) ? 0 : i;//如果putIndex大于数组大小 ,那么从0重新开始
- } finally {
- lock.unlock();//最后一定要释放锁
- }
- }
- /**
- * 添加一个元素,其实super.add里面调用了offer方法
- */
- public boolean add(E e) {
- return super.add(e);
- }
- /**
- *加入成功返回true,否则返回false
- *
- */
- public boolean offer(E e) {
- checkNotNull(e);
- final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
- lock.lock();//上锁
- try {
- if (count == items.length) //超过数组的容量
- return false;
- else {
- enqueue(e); //放入元素
- return true;
- }
- } finally {
- lock.unlock();
- }
- }
- /**
- * 如果队列已满的话,就会等待
- */
- public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
- checkNotNull(e);
- final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
- lock.lockInterruptibly();//和lock()方法的区别是让它在阻塞时也可抛出异常跳出
- try {
- while (count == items.length)
- notFull.await(); //这里就是阻塞了,要注意。如果运行到这里,那么它会释放上面的锁,一直等到notify
- enqueue(e);
- } finally {
- lock.unlock();
- }
- }
- /**
- * 带有超时时间的插入方法,unit表示是按秒、分、时哪一种
- */
- public boolean offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
- throws InterruptedException {
- checkNotNull(e);
- long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
- final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
- lock.lockInterruptibly();
- try {
- while (count == items.length) {
- if (nanos <= 0)
- return false;
- nanos = notFull.awaitNanos(nanos);//带有超时等待的阻塞方法
- }
- enqueue(e);//入队
- return true;
- } finally {
- lock.unlock();
- }
- }
- //实现的方法,如果当前队列为空,返回null
- public E poll() {
- final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
- lock.lock();
- try {
- return (count == 0) ? null : dequeue();
- } finally {
- lock.unlock();
- }
- }
- //实现的方法,如果当前队列为空,一直阻塞
- public E take() throws InterruptedException {
- final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
- lock.lockInterruptibly();
- try {
- while (count == 0)
- notEmpty.await();//队列为空,阻塞方法
- return dequeue();
- } finally {
- lock.unlock();
- }
- }
- //带有超时时间的取元素方法,否则返回Null
- public E poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
- long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
- final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
- lock.lockInterruptibly();
- try {
- while (count == 0) {
- if (nanos <= 0)
- return null;
- nanos = notEmpty.awaitNanos(nanos);//超时等待
- }
- return dequeue();//取得元素
- } finally {
- lock.unlock();
- }
- }
- //只是看一个队列最前面的元素,取出是不删除队列中的原来元素。队列为空时返回null
- public E peek() {
- final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
- lock.lock();
- try {
- return itemAt(takeIndex); // 队列为空时返回null
- } finally {
- lock.unlock();
- }
- }
- /**
- * 返回队列当前元素个数
- *
- */
- public int size() {
- final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
- lock.lock();
- try {
- return count;
- } finally {
- lock.unlock();
- }
- }
- /**
- * 返回当前队列再放入多少个元素就满队
- */
- public int remainingCapacity() {
- final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
- lock.lock();
- try {
- return items.length - count;
- } finally {
- lock.unlock();
- }
- }
- /**
- * 从队列中删除一个元素的方法。删除成功返回true,否则返回false
- */
- public boolean remove(Object o) {
- if (o == null) return false;
- final Object[] items = this.items;
- final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
- lock.lock();
- try {
- if (count > 0) {
- final int putIndex = this.putIndex;
- int i = takeIndex;
- do {
- if (o.equals(items[i])) {
- removeAt(i); //真正删除的方法
- return true;
- }
- if (++i == items.length)
- i = 0;
- } while (i != putIndex);//一直不断的循环取出来做判断
- }
- return false;
- } finally {
- lock.unlock();
- }
- }
- /**
- * 是否包含一个元素
- */
- public boolean contains(Object o) {
- if (o == null) return false;
- final Object[] items = this.items;
- final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
- lock.lock();
- try {
- if (count > 0) {
- final int putIndex = this.putIndex;
- int i = takeIndex;
- do {
- if (o.equals(items[i]))
- return true;
- if (++i == items.length)
- i = 0;
- } while (i != putIndex);
- }
- return false;
- } finally {
- lock.unlock();
- }
- }
- /**
- * 清空队列
- *
- */
- public void clear() {
- final Object[] items = this.items;
- final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
- lock.lock();
- try {
- int k = count;
- if (k > 0) {
- final int putIndex = this.putIndex;
- int i = takeIndex;
- do {
- items[i] = null;
- if (++i == items.length)
- i = 0;
- } while (i != putIndex);
- takeIndex = putIndex;
- count = 0;
- if (itrs != null)
- itrs.queueIsEmpty();
- for (; k > 0 && lock.hasWaiters(notFull); k--)
- notFull.signal();
- }
- } finally {
- lock.unlock();
- }
- }
- /**
- * 取出所有元素到集合
- */
- public int drainTo(Collection<? super E> c) {
- return drainTo(c, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
- }
- /**
- * 取出所有元素到集合
- */
- public int drainTo(Collection<? super E> c, int maxElements) {
- checkNotNull(c);
- if (c == this)
- throw new IllegalArgumentException();
- if (maxElements <= 0)
- return 0;
- final Object[] items = this.items;
- final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
- lock.lock();
- try {
- int n = Math.min(maxElements, count);
- int take = takeIndex;
- int i = 0;
- try {
- while (i < n) {
- @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
- E x = (E) items[take];
- c.add(x);
- items[take] = null;
- if (++take == items.length)
- take = 0;
- i++;
- }
- return n;
- } finally {
- // Restore invariants even if c.add() threw
- if (i > 0) {
- count -= i;
- takeIndex = take;
- if (itrs != null) {
- if (count == 0)
- itrs.queueIsEmpty();
- else if (i > take)
- itrs.takeIndexWrapped();
- }
- for (; i > 0 && lock.hasWaiters(notFull); i--)
- notFull.signal();
- }
- }
- } finally {
- lock.unlock();
- }
- }
- }
三、LinkedBlockingQueue
接下来看看LinkedBlockingQueue的部分源码。
- package java.util.concurrent;
- import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
- import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
- import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
- import java.util.AbstractQueue;
- import java.util.Collection;
- import java.util.Iterator;
- import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
- import java.util.Spliterator;
- import java.util.Spliterators;
- import java.util.function.Consumer;
- public class LinkedBlockingQueue<E> extends AbstractQueue<E>
- implements BlockingQueue<E>, java.io.Serializable {
- private static final long serialVersionUID = -6903933977591709194L;
- /**
- * 链表节点类
- */
- static class Node<E> {
- E item;
- Node<E> next;//下一节点
- Node(E x) { item = x; }
- }
- /** 链表大小 ,默认大小 是Integer.MAX_VALUE */
- private final int capacity;
- /**当前队列中存放的元素个数,注意是原子类*/
- private final AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger();
- /**
- * 链表队列头节点
- */
- transient Node<E> head;
- /**
- * 链表队列尾节点
- */
- private transient Node<E> last;
- /** 取元素时的可重入锁 */
- private final ReentrantLock takeLock = new ReentrantLock();
- /**不为空条件*/
- private final Condition notEmpty = takeLock.newCondition();
- /**放元素是时的重入锁 */
- private final ReentrantLock putLock = new ReentrantLock();
- /** 不为满的条件 */
- private final Condition notFull = putLock.newCondition();
- /**
- * 不为空通知方法
- */
- private void signalNotEmpty() {
- final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;
- takeLock.lock();
- try {
- notEmpty.signal();
- } finally {
- takeLock.unlock();
- }
- }
- /**
- * 不为满通知方法
- */
- private void signalNotFull() {
- final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;
- putLock.lock();
- try {
- notFull.signal();
- } finally {
- putLock.unlock();
- }
- }
- /**
- * 进队
- *
- * @param node the node
- */
- private void enqueue(Node<E> node) {
- last = last.next = node;
- }
- /**
- * 出队
- */
- private E dequeue() {
- Node<E> h = head;
- Node<E> first = h.next;
- h.next = h; // help GC
- head = first;
- E x = first.item;
- first.item = null;
- return x;
- }
- /**
- * 取和入都上锁,此时无法取和放
- */
- void fullyLock() {
- putLock.lock();
- takeLock.lock();
- }
- /**
- * 释放锁
- */
- void fullyUnlock() {
- takeLock.unlock();
- putLock.unlock();
- }
- /**
- * 构造函数
- */
- public LinkedBlockingQueue() {
- this(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
- }
- /**
- * 构造函数
- *
- */
- public LinkedBlockingQueue(int capacity) {
- if (capacity <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
- this.capacity = capacity;
- last = head = new Node<E>(null);
- }
- /**
- * 构造函数
- */
- public LinkedBlockingQueue(Collection<? extends E> c) {
- this(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
- final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;
- putLock.lock(); //取得放入锁
- try {
- int n = 0;
- for (E e : c) {
- if (e == null)
- throw new NullPointerException();
- if (n == capacity)
- throw new IllegalStateException("Queue full");
- enqueue(new Node<E>(e));
- ++n;
- }
- count.set(n);
- } finally {
- putLock.unlock();
- }
- }
- //阻塞等待放入
- public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
- if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();
- int c = -1;
- Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e);
- final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;
- final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
- putLock.lockInterruptibly(); //取得放入锁
- try {
- while (count.get() == capacity) {//队列已满
- notFull.await();
- }
- enqueue(node);//入队
- c = count.getAndIncrement();//当前队列中元素个数加1
- if (c + 1 < capacity)
- notFull.signal();
- } finally {
- putLock.unlock();
- }
- if (c == 0)
- signalNotEmpty();
- }
- /**
- *带超时时间的阻塞等待放入,队列不满。放入成功返回true,否则返回fasle
- */
- public boolean offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
- throws InterruptedException {
- if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();
- long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
- int c = -1;
- final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;
- final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
- putLock.lockInterruptibly();
- try {
- while (count.get() == capacity) {
- if (nanos <= 0)
- return false;
- nanos = notFull.awaitNanos(nanos);
- }
- enqueue(new Node<E>(e));
- c = count.getAndIncrement();
- if (c + 1 < capacity)
- notFull.signal();
- } finally {
- putLock.unlock();
- }
- if (c == 0)
- signalNotEmpty();
- return true;
- }
- /**
- * 非阻塞放入。队列不满放入成功返回true,否则返回fasle
- */
- public boolean offer(E e) {
- if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();
- final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
- if (count.get() == capacity)
- return false;
- int c = -1;
- Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e);
- final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;
- putLock.lock();
- try {
- if (count.get() < capacity) {
- enqueue(node);
- c = count.getAndIncrement();
- if (c + 1 < capacity)
- notFull.signal();
- }
- } finally {
- putLock.unlock();
- }
- if (c == 0)
- signalNotEmpty();
- return c >= 0;
- }
- //阻塞等待取出元素
- public E take() throws InterruptedException {
- E x;
- int c = -1;
- final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
- final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;
- takeLock.lockInterruptibly();
- try {
- while (count.get() == 0) {
- notEmpty.await();
- }
- x = dequeue();
- c = count.getAndDecrement();
- if (c > 1)
- notEmpty.signal();
- } finally {
- takeLock.unlock();
- }
- if (c == capacity)
- signalNotFull();
- return x;
- }
- //带有超时时间等待的取出元素
- public E poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
- E x = null;
- int c = -1;
- long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
- final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
- final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;
- takeLock.lockInterruptibly();//等待时可抛出异常跳出
- try {
- while (count.get() == 0) {
- if (nanos <= 0)
- return null;
- nanos = notEmpty.awaitNanos(nanos);//超时等待
- }
- x = dequeue();
- c = count.getAndDecrement();
- if (c > 1)
- notEmpty.signal();//不这空条件成立
- } finally {
- takeLock.unlock();
- }
- if (c == capacity)
- signalNotFull();
- return x;
- }
- //取队头元素。没有的话返回null,有的话返回元素,并将队列中删除此元素
- public E poll() {
- final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
- if (count.get() == 0)
- return null;
- E x = null;
- int c = -1;
- final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;
- takeLock.lock();//获得取得锁
- try {
- if (count.get() > 0) {
- x = dequeue();//出队
- c = count.getAndDecrement();//当前队列中元素个数减去1
- if (c > 1)
- notEmpty.signal();//不为空条件成功
- }
- } finally {
- takeLock.unlock();
- }
- if (c == capacity)
- signalNotFull();
- return x;
- }
- //取队头元素,但不从队列中删除 ,没有的话返回null,不阻塞
- public E peek() {
- if (count.get() == 0)
- return null;
- final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;
- takeLock.lock();//获得取得锁
- try {
- Node<E> first = head.next;
- if (first == null)
- return null;
- else
- return first.item;
- } finally {
- takeLock.unlock();
- }
- }
- /**
- * 删除时要同时取得放入锁和取得锁
- */
- public boolean remove(Object o) {
- if (o == null) return false;
- fullyLock();//同时取得放入锁和取得锁
- try {
- for (Node<E> trail = head, p = trail.next;
- p != null;
- trail = p, p = p.next) {
- if (o.equals(p.item)) {
- unlink(p, trail);
- return true;
- }
- }
- return false;
- } finally {
- fullyUnlock();
- }
- }
- /**
- * 是否包含
- */
- public boolean contains(Object o) {
- if (o == null) return false;
- fullyLock();//同时取得放入锁和取得锁
- try {
- for (Node<E> p = head.next; p != null; p = p.next)
- if (o.equals(p.item))
- return true;
- return false;
- } finally {
- fullyUnlock();
- }
- }
- }
从LinkedBlockingQueue的源码中,我们可以看出他和ArrayBlockingQueue主要有以下两点区别:
1、ArrayBlockingQueue数据是放在一个数组中。LinkedBlockingQueue是放在一个Node节点中,构成一个链接。
2、ArrayBlockingQueue取元素和放元素都是同一个锁,而LinkedBlockingQueue有两个锁,一个放入锁,一个取得锁。分别对应放入元素和取得元素时的操作。这是由链表的结构所确定的。但是删除一个元素时,要同时获得放入锁和取得锁。
四、SynchronousQueue
SynchronousQueue 这个队列实现了 BlockingQueue接口。该队列的特点
1.容量为0,无论何时 size方法总是返回0
2. put操作阻塞, 直到另外一个线程取走队列的元素。
3.take操作阻塞,直到另外的线程put某个元素到队列中。
4. 任何线程只能取得其他线程put进去的元素,而不会取到自己put进去的元素
- public SynchronousQueue(boolean fair) {
- transferer = fair ? new TransferQueue() : new TransferStack();
- }








 本文详细介绍了阻塞队列的概念及其在Java中的实现,包括ArrayBlockingQueue、LinkedBlockingQueue及SynchronousQueue三个常用队列的具体工作原理和源码分析。
本文详细介绍了阻塞队列的概念及其在Java中的实现,包括ArrayBlockingQueue、LinkedBlockingQueue及SynchronousQueue三个常用队列的具体工作原理和源码分析。














 4020
4020

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








