#include "iostream"
#include "algorithm"
#include "fstream"
using namespace std;
//求n的阶乘
int factorial(int n)
{
int f = 1;
for(int i=2; i<=n; i++)
f *= i;
return f;
}
/*
2 6 4 5 8 1 7 3
tot=0;
比2小的数有1个,则 tot+=1*7!;
比6小的数有4个,则 tot+=4*6!;
比4小的数有2个,则 tot+=2*5!;
比5小的数有2个,则 tot+=2*4!;
比8小的数有3个,则 tot+=3*3!;
比1小的数有0个,则 tot+=0*2!;
比7小的数有1个,则 tot+=1*1!;
比3小的数没有;
*/
//返回a[0,n-1]的字典序
int num(int a[], int n)
{
int count = 0;
int *b = new int[n];
copy(a, a+n, b);
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<i; j++)
if(b[j] < b[i])
b[i]--;
b[i]--;
count += factorial(n-i-1) * b[i];
}
return count;
}
/*
如何得到2 6 4 5 8 1 7 3的下一个排列?
1,从尾部往前找第一个P(i-1) < P(i)的位置
2 6 4 4 5 8 1 <- 7 <- 3
最终找到1是第一个变小的数字,记录下1的位置i-1
2,从尾部往前找到第一个大于1的数
2 6 4 4 5 8 1 7 3 <-
最终找到3的位置,记录位置为m
3,交换位置i-1和m的值
2 6 4 4 5 8 3 7 1
4,倒序i位置后的所有数据
2 6 4 4 5 8 3 1 7
*/
//得到a[0,n-1]的下一个排列
void nextPerm(int a[], int n)
{
int min, max;
for(int i=n-1; i>=0; i--) //1
if(a[i-1]<a[i])
{
min = i-1;
break;
}
for(i=n-1; i>=0; i--) //2
if(a[i]>a[min])
{
max = i;
break;
}
swap(a[min], a[max]); //3
reverse(a+min+1, a+n); //4
}
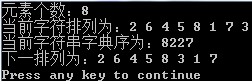
int main()
{
ifstream fin("dict.txt");
int n;
fin >> n;
cout << "元素个数:" << n;
int *a = new int[n];
cout << "\n当前字符排列为:";
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
fin >> a[i];
cout << a[i] << " ";
}
int count = num(a, n);
cout << "\n当前字符串字典序为:" << count << endl;
nextPerm(a, n);
cout << "下一排列为:";
for(i=0; i<n; i++)
cout << a[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
fin.close();
return 0;
} 排列的字典序问题
最新推荐文章于 2019-09-14 20:23:49 发布






















 1296
1296

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








