
在云存储领域中,Amazon S3已成为存储海量数据的基石。然而,随着组织在Amazon S3中积累了数TB甚至数PB的对象,管理和从这些数据中提取价值变得越来越具有挑战性。这就是Amazon S3元数据和Amazon S3元数据表发挥作用的地方,这些强大的工具允许组织有效地组织、跟踪和查询大规模的对象元数据。
本文将探讨Amazon S3元数据和Amazon S3元数据表的功能、用例,以及如何用Model Context Protocol(MCP)构建Amazon S3数据洞察。
了解Amazon S3对象元数据
在深入探讨Amazon S3元数据表之前,了解对象元数据本身至关重要,Amazon S3支持以下两种类型的元数据。
1
系统定义的元数据
系统定义的元数据是由亚马逊云科技服务自动分配和管理的,每个对象都有:
系统控制:创建日期、大小和ETag等属性,由Amazon S3管理,无法修改。
用户控制:存储类、加密设置和网站重定向位置等属性,可以由用户在创建对象时配置。
重要的系统定义的元数据包括:
对象创建与修改时间戳。
对象大小。
ETag(实体标签)用于内容验证。
存储类(STANDARD、INTELLIGENT_TIERING等)。
加密状态和使用的密钥。
分段上传状态。
校验和算法。
2
用户定义的元数据
用户定义的元数据由您可以与Amazon S3对象关联的自定义名称——值对组成:
使用REST API时必须以x-amz-meta-前缀开头。
大小限制为2KB。
用于附加应用程序特定信息。
可通过Amazon S3元数据表搜索以增强可发现性。
不能在不复制或替换对象的情况下修改。
用户定义元数据示例如下。
x-amz-meta-location: beijingx-amz-meta-creator: zhang_weix-amz-meta-camera-model: Canon EOS R5左右滑动查看完整示意
Amazon S3元数据表:加速数据发现
Amazon S3元数据表是一项功能,通过自动捕获对象元数据并将其存储在完全托管的Apache Iceberg表中,显著提高了数据发现能力。这些表提供了一种强大而灵活的方式来查询和分析您的Amazon S3对象元数据。
Amazon S3元数据表的工作原理
1
自动元数据捕获
当对象在Amazon S3存储桶中创建、更新或删除时,Amazon S3元数据表自动捕获并存储元数据,格式为Apache Iceberg。
2
基于事件的记录
元数据表中的每一行代表存储桶中对象发生的变异事件(CREATE、UPDATE_METADATA或DELETE)。
3
丰富的模式
表包含全面的元数据列,如:
基本对象信息(存储桶、键、大小、时间戳)。
存储属性(存储类、加密状态)。
安全详情(Amazon KMS密钥ARN、请求者身份)。
自定义数据(对象标签和用户定义的元数据)。
操作详情(请求ID、源IP地址)。
4
表维护
亚马逊云科技服务自动执行优化操作(如压缩)以确保查询性能保持高水平。
Amazon S3元数据表的主要优势
1.增强的可发现性:根据元数据、标签或甚至创建者与修改者快速找到对象。
2.分析洞察:生成存储使用模式、审计安全配置和跟踪对象生命周期。
3.与分析服务集成:通过Amazon Athena、Amazon Redshift和Amazon EMR等服务无缝查询。
4.数据和元数据分离:查询元数据而无需访问实际对象。
5.事件跟踪:了解对象何时以及如何创建、更新或删除。

用例
1
内容管理和组织
媒体公司和内容创作者可以利用Amazon S3元数据组织庞大的数字资产库。
-- 查找所有在北京使用特定相机型号拍摄的图像SELECT bucket, key, user_metadataFROM aws_s3_metadata.your_metadata_tableWHERE user_metadata['location'] = 'beijing' AND user_metadata['camera-model'] = 'Canon EOS R5'左右滑动查看完整示意
2
安全和合规审计
安全团队可以监控对象加密和访问模式。
-- 查找未加密的对象或使用特定加密密钥的对象SELECT bucket, key, encryption_status, kms_key_arnFROM aws_s3_metadata.your_metadata_tableWHERE encryption_status IS NULL OR encryption_status != 'SSE-KMS'左右滑动查看完整示意
3
成本优化
财务和DevOps团队可以分析存储使用模式。
-- 按存储桶分析存储类分布SELECT bucket, storage_class, COUNT(*) as object_count, SUM(size) as total_sizeFROM aws_s3_metadata.your_metadata_tableGROUP BY bucket, storage_classORDER BY total_size DESC左右滑动查看完整示意
4
数据治理和血缘
数据治理团队可以跟踪对象生命周期和修改。
-- 跟踪随时间的对象修改SELECT key, record_type, record_timestamp, requester, source_ip_addressFROM aws_s3_metadata.your_metadata_tableWHERE key = 'important_file.pdf'ORDER BY record_timestamp左右滑动查看完整示意
结合MCP Servers
与Amazon S3元数据
MCP是一种开放协议,用于标准化应用程序向大语言模型(LLM)提供上下文的方式。您可以将MCP视为AI应用程序的USB-C端口,正如USB-C提供了一种标准化的方式,将您的设备连接到各种外设和配件,MCP提供了一种标准化的方式,将AI模型连接到不同的数据源和工具。
选择MCP可以帮助您更高效地构建和管理基于LLM的应用程序和工作流程。通过利用预构建的集成、享受提供商切换的灵活性,以及遵循数据保护的最佳实践,您可以更轻松地实现您的AI项目目标。

1
定义MCP Servers工具
Amazon S3元数据表查询与分析
使用MCP Servers的Amazon S3 Tables查询模块,您可以创建提供Amazon S3活动即时洞察的API。
初始化Server。
from datetime import datetimefrom typing import Any, Dict, List, Optionalimport osimport timeimport boto3import httpxfrom mcp.server.fastmcp import FastMCP# Initialize FastMCP servermcp = FastMCP("aws_s3table_query")# Global Athena configuration# 从环境变量读取配置athena_config = { "catalog": os.getenv("ATHENA_CATALOG"), "database": os.getenv("ATHENA_DATABASE"), "table": os.getenv("ATHENA_TABLE"), "output_location": os.getenv("ATHENA_OUTPUT_LOCATION")}aws_config = { "region": os.getenv("AWS_REGION", "us-east-1")}athena_client = Nonedef initialize(): global athena_config, aws_config, athena_client # Validate required environment variables required_vars = [ ("ATHENA_DATABASE", athena_config["database"]), ("ATHENA_TABLE", athena_config["table"]), ("ATHENA_OUTPUT_LOCATION", athena_config["output_location"]) ] missing_vars = [var_name for var_name, var_value in required_vars if var_value is None] if missing_vars: raise ValueError(f"Missing required environment variables: {', '.join(missing_vars)}") # Initialize Athena client athena_client = boto3.client('athena', region_name=aws_config['region'])
# 从环境变量初始化athena连接initialize()左右滑动查看完整示意
定义工具类。
def wait_for_query_completion(query_execution_id: str) -> bool: """Wait for an Athena query to complete, returning True if successful.""" while True: response = athena_client.get_query_execution(QueryExecutionId=query_execution_id) state = response['QueryExecution']['Status']['State'] if state == 'SUCCEEDED': return True elif state in ['FAILED', 'CANCELLED']: raise Exception(f"Query {query_execution_id} failed with state {state}") time.sleep(1) # Wait before checking again
def get_query_results(query_execution_id: str) -> List[Dict[str, Any]]: """Fetch and process query results from Athena.""" results = [] paginator = athena_client.get_paginator('get_query_results') try: for page in paginator.paginate(QueryExecutionId=query_execution_id): ifnot results: # First page, get column info columns = [col['Name'] for col in page['ResultSet']['ResultSetMetadata']['ColumnInfo']] # Process each row (skip header row in first page) start_idx = 1ifnot results else0 for row in page['ResultSet']['Rows'][start_idx:]: values = [field.get('VarCharValue', None) for field in row['Data']] results.append(dict(zip(columns, values))) except Exception as e: raise Exception(f"Error fetching query results: {str(e)}") return results
def execute_query(query: str) -> List[Dict[str, Any]]: """Execute an Athena query and return the results.""" try: # Start query execution response = athena_client.start_query_execution( QueryString=query, QueryExecutionContext={ 'Database': athena_config['database'], 'Catalog': athena_config['catalog'] if athena_config['catalog'] else'AwsDataCatalog' }, ResultConfiguration={ 'OutputLocation': athena_config['output_location'] } ) query_execution_id = response['QueryExecutionId'] # Wait for query completion if wait_for_query_completion(query_execution_id): return get_query_results(query_execution_id) return [] except Exception as e: raise Exception(f"Error executing query: {str(e)}")
def build_where_clause( start_time: Optional[str] = None, end_time: Optional[str] = None, bucket: Optional[str] = None, record_type: Optional[str] = None, storage_class: Optional[str] = None, source_ip_address: Optional[str] = None) -> str: conditions = [] if start_time: conditions.append(f"record_timestamp >= '{start_time}'") if end_time: conditions.append(f"record_timestamp <= '{end_time}'") if bucket: conditions.append(f"bucket = '{bucket}'") if record_type: conditions.append(f"record_type = '{record_type}'") if storage_class: conditions.append(f"storage_class = '{storage_class}'") if source_ip_address: conditions.append(f"source_ip_address = '{source_ip_address}'") if conditions: return"WHERE " + " AND ".join(conditions) return""左右滑动查看完整示意
记录查询工具。
@mcp.tool()async def query_record( start_time: Optional[str] = None, end_time: Optional[str] = None, bucket: Optional[str] = None, record_type: Optional[str] = None, storage_class: Optional[str] = None, source_ip_address: Optional[str] = None) -> List[Dict[str, Any]]: """ Query S3 object records based on specified conditions. Args: start_time: Start time for record_timestamp range(ISO format) end_time: End time for record_timestamp range(ISO format) bucket: S3 bucket name record_type: Type of record storage_class: S3 storage class source_ip_address: Source IP address Returns: List of matching records """ where_clause = build_where_clause( start_time, end_time, bucket, record_type, storage_class, source_ip_address ) query = f""" SELECT bucket, key, sequence_number, record_type, record_timestamp, size, last_modified_date, e_tag, storage_class, is_multipart, encryption_status, is_bucket_key_enabled, kms_key_arn, checksum_algorithm, object_tags, user_metadata, requester, source_ip_address, request_id FROM {athena_config['database']}.{athena_config['table']} {where_clause} """ print(query) return execute_query(query)左右滑动查看完整示意
统计分析工具。
@mcp.tool()async def query_statistics( group_by: List[str], start_time: Optional[str] = None, end_time: Optional[str] = None, bucket: Optional[str] = None, record_type: Optional[str] = None, storage_class: Optional[str] = None, source_ip_address: Optional[str] = None) -> List[Dict[str, Any]]: """ Generate statistics based on query conditions with grouping. Args: group_by: List of fields to group by(supported: bucket, source_ip_address) start_time: Start time for record_timestamp range(ISO format) end_time: End time for record_timestamp range(ISO format) bucket: S3 bucket name record_type: Type of record storage_class: S3 storage class source_ip_address: Source IP address Returns: List of statistics grouped by specified fields """ valid_group_fields = {"bucket", "source_ip_address"} group_fields = [field for field in group_by if field in valid_group_fields] ifnot group_fields: raise ValueError("Must specify at least one valid group_by field (bucket or source_ip_address)") where_clause = build_where_clause( start_time, end_time, bucket, record_type, storage_class, source_ip_address ) group_by_clause = ", ".join(group_fields) query = f""" SELECT {group_by_clause}, COUNT(*) as total_objects, SUM(size) as total_size, COUNT(DISTINCT record_type) as unique_record_types, COUNT(DISTINCT storage_class) as unique_storage_classes FROM {athena_config['database']}.{athena_config['table']} {where_clause} GROUP BY {group_by_clause} """ return execute_query(query)左右滑动查看完整示意
程序执行入口。
def main(): """Entry point for the MCP server.""" # Initialize and run the server mcp.run(transport='stdio')
if __name__ == "__main__": main()左右滑动查看完整示意
2
通过MCP Client查询
前置条件如下:
配置元数据表。
配置并使用Amazon Athena查询Amazon S3元数据表。
配置Amazon Web Services CLI。
配置元数据表:
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonS3/latest/userguide/metadata-tables-configuring.html
配置并使用Amazon Athena查询Amazon S3元数据表:
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonS3/latest/userguide/s3-tables-integrating-athena.html
配置Amazon Web Services CLI:
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/zh_cn/cli/v1/userguide/cli-chap-configure.html
*请确保给您本地的MCP Client的Amazon IAM User/Role配置拥有Amazon Athena的查询权限及Amazon Bedrock上的Claude模型权限。
以Claude Code作为MCP Client,示例如下。
# install Claude codenpm install -g @anthropic-ai/claude-codeexport CLAUDE_CODE_USE_BEDROCK=1export ANTHROPIC_MODEL='us.anthropic.claude-3-7-sonnet-20250219-v1:0'claude左右滑动查看完整示意
添加您的MCP Server。
claude mcp add-json s3table-mcp-server '{ "type": "stdio", "command": "uv", "args": [ "--directory", "/Users/xxx/mcp-server-python/aws_s3table_query", "run", "server.py" ], "env": { "ATHENA_CATALOG": "s3tablescatalog", "ATHENA_DATABASE": "aws_s3_metadata", "ATHENA_TABLE": "s3metadata_imagebucket_us_east_1", "ATHENA_OUTPUT_LOCATION": "s3://aws-athena-xxx-us-east-1/" }}'左右滑动查看完整示意
用户需要替代的部分如下:
1.s3table-mcp-server:您的MCP Server配置名称,可根据您的应用场景自定义。
2./Users/xxx/mcp-server-python/aws_s3table_query:您本地MCP Server代码的目录路径。
3.环境变量:
ATHENA_CATALOG:您的Amazon Athena目录名称。
ATHENA_DATABASE:您的Amazon Athena数据库名称。
ATHENA_TABLE:您要查询的表名。
ATHENA_OUTPUT_LOCATION:Amazon Athena查询结果的Amazon S3输出位置,确保以斜杠结尾。
验证是否添加成功。
claude mcp list最后能够看到下图中的红色框则表示添加成功。

测试MCP Server
本文先演示简单的用例。
1.Amazon S3元数据查询。
2.Amazon S3元数据统计。
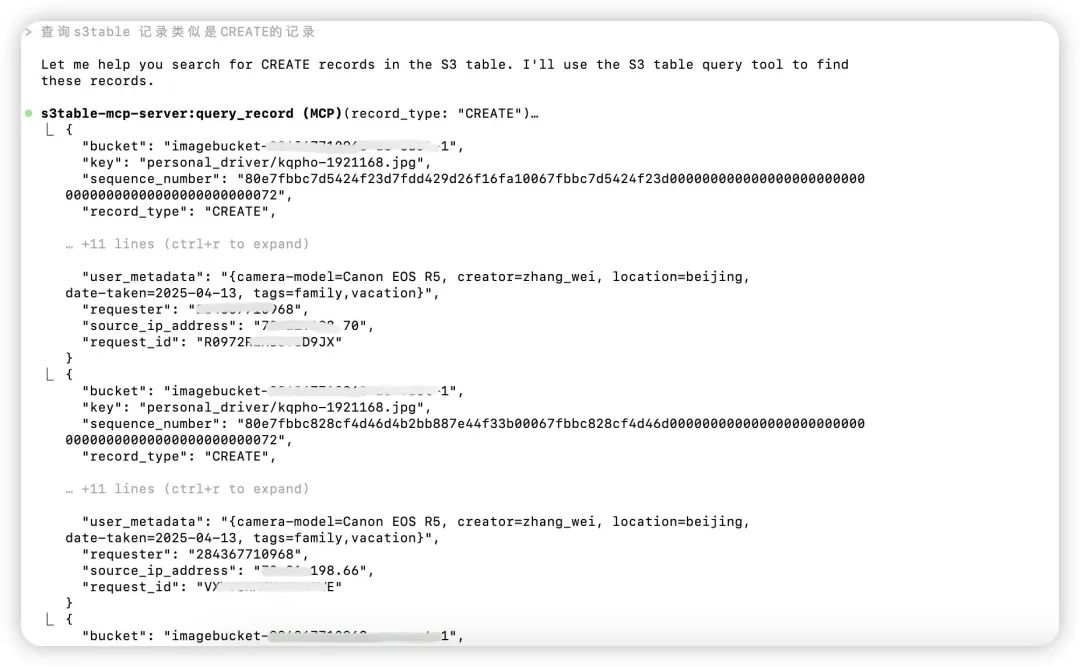
#命令行执行claude,并输入claude> 查询s3table记录类型是CREATE的记录左右滑动查看完整示意
>按照bucket分组帮我统计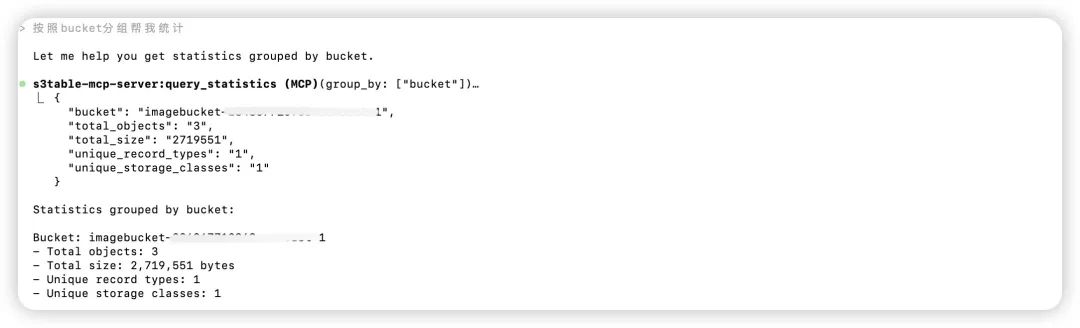
您还可以去添加新的工具,例如允许应用程序根据自定义的元数据条件发现Amazon S3内容。
@mcp.tool()async def find_objects_by_metadata(metadata_criteria: Dict[str, str]): """查找匹配特定元数据条件的 S3 对象""" # 这将需要基于 metadata_criteria 构建自定义 SQL # 例如:user_metadata['location'] = 'beijing' # 示例实现处理基本情况 where_clauses = [] for key, value in metadata_criteria.items(): where_clauses.append(f"user_metadata[}'] ='") where_clause = " AND ".join(where_clauses) # 通过 Athena 执行自定义查询 # ... return results左右滑动查看完整示意
查询及监控Amazon S3对象是否合规存储。
@mcp.tool()async def check_compliance_status(): """检查所有对象是否满足合规要求""" compliance_issues = [] # 检查未加密的对象 unencrypted = await query_record(encryption_status=None) if unencrypted: compliance_issues.append "issue": "unencrypted_objects", "count": len(unencrypted), "objects": [f" for obj in unencrypted[:5]] 不当的存储类 improper_storage = await query_record(storage_class="REDUCED_REDUNDANCY") if improper_storage: compliance_issues.append "improper_storage_class", "count": len(improper_storage), "objects": [f"]}/{obj['key' "compliant": len(compliance_issues) == 0, "issues": compliance_issues左右滑动查看完整示意
最佳实践建议
1
一致的元数据策略
制定标准化的元数据命名约定,并确保在整个组织中一致应用。
2
查询优化
在查询元数据表时:
尽早过滤以减少扫描的数据。
使用分区修剪进行基于日期的查询。
限制列选择仅为您需要的内容。
3
成本管理
元数据表增加的存储成本最小,但查询成本取决于使用的分析服务。
考虑表维护以最小化存储成本。
删除不再需要的元数据表。
4
安全规划
记住元数据表包含有关对象的敏感信息。
对元数据表应用适当的访问控制。
考虑哪些元数据可能是敏感的(如自定义标签或用户身份)。
结论
MCP Servers代表了在生成式AI Agent与企业数据服务集成方面的重要探索。通过标准化的协议,开发者能够让AI模型与各种数据源(如Amazon S3元数据)无缝连接,从而打开智能应用的新可能性。
对于希望更全面理解和可视化这些数据的组织,Amazon QuickSight等专业BI服务提供了强大的补充工具。特别令人兴奋的是,Amazon Q in QuickSight的引入将自然语言查询能力带入分析流程,使非技术用户也能通过对话方式获取洞察。
通过这种方式,组织不仅可以将Amazon S3存储转变为智能、可搜索的数据服务,还能利用生成式AI的力量实现更直观的数据交互和决策制定。无论您是管理庞大的内容库、确保合规性,还是优化云存储成本,Amazon S3元数据、MCP Servers和智能BI工具的结合,为现代云原生环境中的创新提供了坚实基础。
本篇作者

庄颖勤
亚马逊云科技解决方案架构师,负责基于亚马逊云科技的云计算方案架构设计、咨询、实施等工作。在DevOps、CI/CD和容器等领域拥有丰富的技术和支持经验,致力于帮助客户实现技术创新和业务发展。


星标不迷路,开发更极速!
关注后记得星标「亚马逊云开发者」
听说,点完下面4个按钮
就不会碰到bug了!
点击阅读原文查看博客!获得更详细内容!
























 9437
9437

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








