基本概念
即处理器映射,它的主要作用就是根据 reqeust 获取 HandlerExecutionChain。
下面来看它的源码:
public interface HandlerMapping {
// 省略部分代码...
HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception;
}再来看它的继承关系:
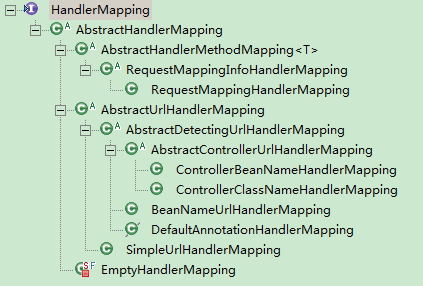
AbstractHandlerMapping
AbstractHandlerMapping 是该接口的抽象实现类,该类实现了 getHandler 方法。
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// 关键 -> 取得处理器,留给子类
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
// 取得默认处理器
if (handler == null) {
handler = getDefaultHandler();
}
if (handler == null) {
return null;
}
if (handler instanceof String) {
// 若处理器是 Bean 名称,则从 SpringMVC 容器手动取得该 Bean
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
// 关键 -> 取得 HandlerExecutionChain
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain =
getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
// 省略部分代码...
return executionChain;
}继续追踪到 getHandlerExecutionChain 方法
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandlerExecutionChain(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) {
// 1.取得 HandlerExecutionChain ,包含了处理器和拦截器,下面会详细分析
HandlerExecutionChain chain = (handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain ?
(HandlerExecutionChain) handler : newHandlerExecutionChain(handler));
// 2.获取请求路径
// 若完整请求地址为 http://localhost:8080/Demo/hello,则 lookupPath = /hello
String lookupPath = this.urlPathHelper.getLookupPathForRequest(request);
// 3.添加拦截器到 HandlerExecutionChain
// 遍历 SpringMVC 容器的所有拦截器
for (HandlerInterceptor interceptor : this.adaptedInterceptors) {
// 判断拦截器类型,属于 MappedInterceptor,则先匹配路径,否则直接添加
if (interceptor instanceof MappedInterceptor) {
MappedInterceptor mappedInterceptor = (MappedInterceptor) interceptor;
if (mappedInterceptor.matches(lookupPath, this.pathMatcher)) {
chain.addInterceptor(mappedInterceptor.getInterceptor());
}
}else {
chain.addInterceptor(interceptor);
}
}
return chain;
}分析代码可知, HandlerMapping 的主要职责是取得 HandlerExecutionChain,具体步骤如下:
- 取得 HandlerExecutionChain 的处理器,由不同子类作实现。
- 取得 HandlerExecutionChain 的拦截器
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
在介绍该类之前,先来看几个类:
RequestMapingInfo ,该类包含了 @ReuestMaping 的所有注解内容,包括 value,method,param,header,consumes,produces 等属性定义的内容 。
// 注解的所有内容被封装到它的成员变量中 // 包含了注解属性 value 的内容,如 "/hello" private final PatternsRequestCondition patternsCondition; // 包含了注解属性 method 的内容,如 GET private final RequestMethodsRequestCondition methodsCondition; // 省略部分代码...
MappingRegistry,它是 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 的内部类。它内有一个 Map,维护着 SpringMVC 中所有的 RequestMapingInfo 与 HandlerMethod 的映射关系。
// T 实际就是 RequestMapingInfo private final Map<T, HandlerMethod> mappingLookup = new LinkedHashMap<T, HandlerMethod>(); // 取得映射 public Map<T, HandlerMethod> getMappings() { return this.mappingLookup; }
Match,它是 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 的私有内部类,也称匹配者,封装了一个RequestMappingInfo ,以及对应的 HandlerMethod 。
private class Match { private final T mapping; private final HandlerMethod handlerMethod; public Match(T mapping, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) { this.mapping = mapping; this.handlerMethod = handlerMethod; } }
该类是 AbstractHandlerMapping 类的子类,也是个抽象类。它实现了取得处理器的具体过程,也就是对 getHandlerInternal 作了具体实现。
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// 省略部分代码...
// 1.取得请求路径
String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request);
// 添加读锁,其他线程只能读不能写
this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock();
try {
// 关键 -> 2.取得 HandlerMethod
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request);
// 创建控制器并返回
return (handlerMethod != null ?
handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null);
}finally {
// 释放读锁
this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock();
}
}继续追踪到 lookupHandlerMethod 方法。
protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
List<Match> matches = new ArrayList<Match>();
// 1.取得 RequestMappingInfo,根据路径进行匹配
List<T> directPathMatches =
this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByUrl(lookupPath);
if (directPathMatches != null) {
// 2.构建 Match 并加入集合
addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request);
}
if (matches.isEmpty()) {
addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(),
matches, request);
}
// 3.选出最佳的 Match
if (!matches.isEmpty()) {
// 利用比较器进行排序
Comparator<Match> comparator =
new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(request));
Collections.sort(matches, comparator);
// 省略部分代码...
Match bestMatch = matches.get(0);
// 存在多个 Match 时,对前两个匹配者再比较,若相同则抛出异常
if (matches.size() > 1) {
// 省略部分代码...
Match secondBestMatch = matches.get(1);
if (comparator.compare(bestMatch, secondBestMatch) == 0) {
// 抛出异常...
}
}
// 将 相关信息添加到 reqeust 的属性。
handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request);
return bestMatch.handlerMethod;
} else {
// 处理没有 Match 的情况
return handleNoMatch(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(),
lookupPath, request);
}
}再来看看 addMatchingMappings 的实现过程:
private void addMatchingMappings(Collection<T> mappings, List<Match> matches, HttpServletRequest request) {
for (T mapping : mappings) {
// 关键 -> 取得匹配的 RequetMapingInfo,留给子类实现
T match = getMatchingMapping(mapping, request);
// 创建 Match 并加入集合
if (match != null) {
matches.add(new Match(match,
this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().get(mapping)));
}
}
}综上所述,该类的主要作用是负责找到相应的处理器,也就是 HandlerMethod。它的具体步骤如下:
1.取得 RequestMappingInfo。根据请求路径进行匹配。
2.构建 Match 并加入集合。过滤 RequestMappingInfo 与 rqeust 请求不符的内容,再从 MappingRegistry 找到对应的 HandlerMethod,最后添加进集合。
3.选出最佳的 Match。利用比较器筛选中最佳的 Match,再返回 Match 中的 HandlerMethod。
RequestMappingHandlerMapping
该类是 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 的子类。
若控制器采用了注解方法实现,则就会采用 RequestMappingHandlerMapping 来处理。在其内部实现了 getMatchingMapping 方法:
protected RequestMappingInfo getMatchingMapping(RequestMappingInfo info, HttpServletRequest request) {
// 将 info 的内容 rqeust 的内容进行匹配
// 假设 @RquestMapping 中 method 为 GET、POST
// 而 reqeuest 的请求类为 GET
// 经过匹配,RequestMappingInfo 中关于 method 的内容只剩下 GET
return info.getMatchingCondition(request);
}总结
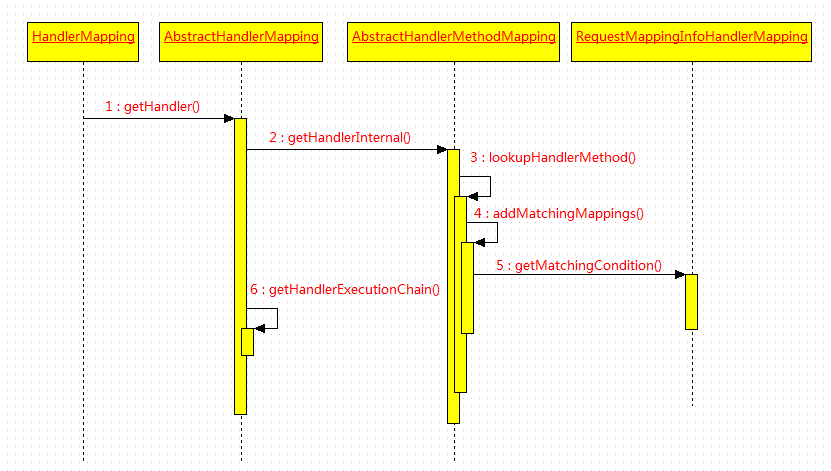
整个 HandlerMapping 的工作流程如下:
根据目的就是通过 reqeust 获取 HandlerExecutionChain 的 HandlerMethod、Interceptor。
而实现的重点又在获取 HandlerMethod 的过程,即根据请求获取 Controller 中处理方法的过程。

























 1679
1679











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










