参考:
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_5e99b41e0100rxgf.html
http://hi.baidu.com/shiftedmind/blog/item/1a7c8381e6a67fa56d8119da.html
在Linux内核源码中,经常要对链表进行操作,其中一个很重要的宏是list_for_each_entry:
意思大体如下:
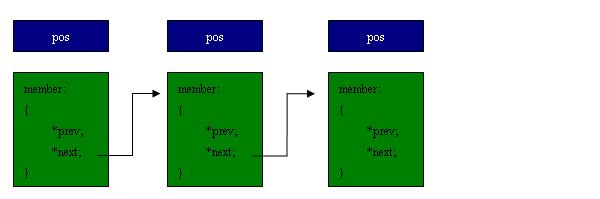
假设下面几个结点,则第一个member代表head,list_for_each_entry的作用就是循环遍历每一个pos中的member子项。
list_for_each_entry应用:
它实际上是一个 for 循环,利用传入的 pos 作为循环变量,从表头 head 开始,逐项向后(next 方向)移动 pos,直至又回head(prefetch() 可以不考虑,用于预取以提高遍历速度 )。
在程序中的使用如下:
list_for_each_entry(pos , head,member)
{
………………
addr = pos; //对返回值pos的操作,这样更容易去理解list_for_each_entry,可以把它看作for()循环
………………
}
宏list_for_each_entry的实现:
对程序中for循环的三步分析:
(1),pos = list_entry((head)->next, typeof(*pos), member)
pos相当于循环中返回的循环变量,这里就是返回一个结构体指针。实现过程如下:
函数list_entry():
跟进:container_of这个函数:
这个不做重点分析,这个函数的做用是:它的作用显而易见,那就是根据一个结构体变量中的一个域成员变量的指针来获取指向整个结构体变量的指针。
所以list_entry()的作用为:如上图所示,可以以通过已知的指向member子项的指针,获得整个结构体的指针(地址)
(2), prefetch(pos->member.next),&pos->member!= (head);
prefetch的含义是告诉cpu那些元素有可能马上就要用到,告诉cpu预取一下,这样可以提高速度,用于预取以提高遍历速度;
&pos->member !=(head) ,这个判断循环条件。
(3), pos= list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member))
和第(1)实现相似,用于逐项向后(next 方向)移动 pos。






















 1048
1048

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








