12.4-1
证明前先需要知道有
(44)=(33)
以及附录 C 的练习 C.1-7 需要证明的等式
(nk)=(n−1k)+(n−1k−1)
先证明附录 C 的练习 C.1-7
然后有:
12.4-2
首先给出第二个问题的答案,即渐进上界
O(nlgn−−−−−√)
。证明略,可以参考算法导论指导手册上此题的证明。
下面给出一个例子,
n
个结点的平均深度
Θ(lg(n−nlgn−−−−−√))+nlgn−−−−−√=Θ(nlgn−−−−−√)=ω(lgn)
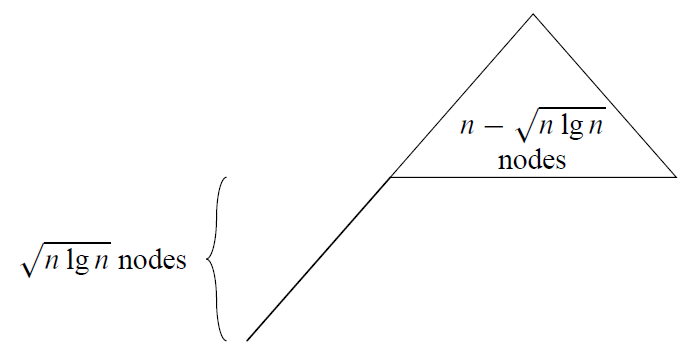
对此例的平均深度证明是
Θ(lgn)
同样略过。
12.4-3
先给出
n=3
构建出来的全部二叉搜索树。
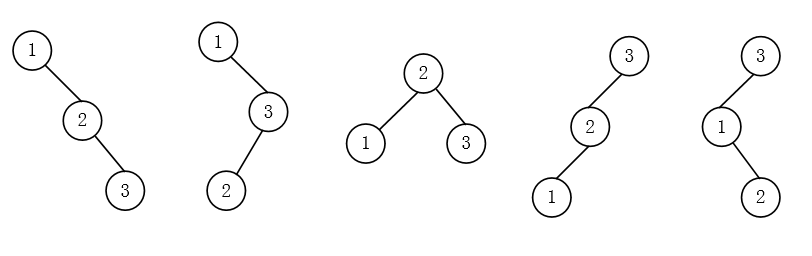
从左到右依次编号为
1,2,3,4,5
:
1;2;3
对应图1;
1;3;2
对应图2;
2;1;3
和
2;3;1
对应图3;
3;2;1
对应图4;
3;1;2
对应图5。
因此图3被创建的概率是
2/6
,其余的是
1/6
。而随机构建二叉搜索树都是
1/5
。
12.4-4
在书的附录里面有凸函数的定义(见中文版第三版的P701或英文版的P1199),然后国外的语意和国内相反,所以我们是要证明
f(x)=2x
是凹函数。
证明:根据凹函数定义:对于任意
x,y,λ∈(0,1)
,有
λ2x+(1−λ)2y≥2(λx+(1−λ)y)
……①
这里有个重要不等式,即对于任意
a,b,c
都有
ca≥cb+(a−b)(cb)lnc
。在这简单证明一下,根据
ex≥1+x
有:设
x=(a−b)lnc
带入
e((a−b)lnc)≥1+(a−b)lnc
即
c(a−b)≥1+(a−b)lnc
两边都乘以
cb
即得证。
这样用
2
代替
带入并化解得:
2x≥2z+(x−z)(2z)
….②同理,
a
变
把②和③式带入①式得:
由于 (λ(x−z)+(1−λ)(y−z))=0 ,所以 λ2x+(1−λ)2y≥2z=2(λx+(1−λ)y) ,得证!
12.4-5
略。
附上本章的一些实现代码
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::stack;
struct BinTree
{
int key;
BinTree *parent;
BinTree *left;
BinTree *right;
};
void preOrder(BinTree *root)
{
if(root != NULL)
{
cout << root->key << ' ';
preOrder(root->left);
preOrder(root->right);
}
}
void non_recursive_preOrder(BinTree *root)
{
stack<BinTree *> ptr;
ptr.push(root);
while(root != NULL && !ptr.empty())
{
BinTree *p = ptr.top();
cout << p->key << ' ';
ptr.pop();
if(p->right != NULL)
ptr.push(p->right);
if(p->left != NULL)
ptr.push(p->left);
}
}
void inOrder(BinTree *root)
{
if(root != NULL)
{
inOrder(root->left);
cout << root->key << ' ';
inOrder(root->right);
}
}
void non_recursive_inOrder(BinTree *root)
{
stack<BinTree *> ptr;
BinTree *p = root;
while(p != NULL || !ptr.empty())
{
while(p != NULL) //找到最左孩子
{
ptr.push(p);
p = p->left;
}
if(!ptr.empty()) //弹出,然后向右
{
p = ptr.top();
ptr.pop();
cout << p->key << ' ';
p = p->right;
}
}
}
void postOrder(BinTree *root)
{
if(root != NULL)
{
postOrder(root->left);
postOrder(root->right);
cout << root->key << ' ';
}
}
void non_recursive_postOrder(BinTree *root)
{
stack<BinTree *> ptr;
BinTree *cur;
BinTree *pre = NULL;
ptr.push(root);
while(!ptr.empty())
{
cur = ptr.top();
//当前结点没孩子或者左(右)孩子已经访问过,则访问当前结点
if(cur->left == NULL && cur->right == NULL || pre != NULL && (pre == cur->left || pre == cur->right))
{
cout << cur->key << ' ';
ptr.pop();
pre = cur;
}
else
{
if(cur->right != NULL)
ptr.push(cur->right);
if(cur->left != NULL)
ptr.push(cur->left);
}
}
}
BinTree *TREE_SEARCH(BinTree *root,int value)
{
if(root == NULL)
return root;
if(root->key == value)
return root;
if(root->key < value)
TREE_SEARCH(root->right,value);
else TREE_SEARCH(root->left,value);
}
BinTree *non_recursive_TREE_SEARCH(BinTree *root,int value)
{
while(root != NULL && root->key != value)
{
if(root->key < value)
root = root->right;
else root = root->left;
}
return root;
}
BinTree *TREE_MINIMUM(BinTree *root)
{
if(root == NULL)
return root;
if(root->left == NULL)
return root;
else return TREE_MINIMUM(root->left);
}
BinTree *non_recursive_TREE_MINIMUM(BinTree *root)
{
if(root == NULL)
return root;
while(root->left != NULL)
root = root->left;
return root;
}
BinTree *TREE_MAXIMUM(BinTree *root)
{
if(root == NULL)
return root;
if(root->right == NULL)
return root;
else return TREE_MAXIMUM(root->right);
}
BinTree *non_recursive_TREE_MAXIMUM(BinTree *root)
{
if(root == NULL)
return root;
while(root->right != NULL)
root = root->right;
return root;
}
BinTree *TREE_SUCCESSOR(BinTree *p)
{
if(p == NULL)
return p;
if(p->right != NULL)
return TREE_MINIMUM(p->right);
BinTree *x = p->parent;
while(x != NULL && p == x->right)
{
p = x;
x = x->parent;
}
return x;
}
BinTree *TREE_PREDECESSOR(BinTree *p)
{
if(p == NULL)
return p;
if(p->left != NULL)
return TREE_MAXIMUM(p->left);
BinTree *x = p->parent;
while(x != NULL && p == x->left)
{
p = x;
x = x->parent;
}
return x;
}
void TREE_INSERT(BinTree **root,int key)
{
if(*root == NULL) //插入根节点
{
BinTree *z = new BinTree;
z->key = key;
z->left = z->right = NULL;
*root = z;
z->parent = NULL;
return;
}
BinTree *x = *root;
if(x->key > key) //左子树
{
if(x->left == NULL) //左子树为空
{
BinTree *z = new BinTree;
z->key = key;
z->left = z->right = NULL;
z->parent = x;
x->left = z;
}
else TREE_INSERT(&(x->left),key);//以左子树为根递归插入
}
else //右子树
{
if(x->right == NULL)
{
BinTree *z = new BinTree;
z->key = key;
z->left = z->right = NULL;
z->parent = x;
x->right = z;
}
else TREE_INSERT(&(x->right),key);
}
}
void non_recursive_TREE_INSERT(BinTree **root,int key)
{
BinTree *z = new BinTree;
z->key = key;
z->left = z->right = NULL;
BinTree *y = NULL;
BinTree *x = *root;
while(x != NULL)
{
y = x;
if(x->key < z->key)
x = x->right;
else x = x->left;
}
z->parent = y;
if(y == NULL)
*root = z;
else if(y->key < z->key)
y->right = z;
else y->left = z;
}
void TRANSPLANT(BinTree **root,BinTree *u,BinTree *v)
{
if(u->parent == NULL)
*root = v;
else if(u == u->parent->left)
u->parent->left = v;
else u->parent->right = v;
if(v != NULL)
v->parent = u->parent;
}
void TREE_DELETE(BinTree **root,int key)
{
BinTree *p = TREE_SEARCH(*root,key);
if(p == NULL)
return;
if(p->left == NULL)
TRANSPLANT(root,p,p->right);
else if(p->right == NULL)
TRANSPLANT(root,p,p->left);
else{
BinTree *y = TREE_MINIMUM(p->right);
if(y->parent != p)
{
TRANSPLANT(root,y,y->right);
y->right = p->right;
y->right->parent = y;
}
TRANSPLANT(root,p,y);
y->left = p->left;
y->left->parent = y;
}
delete p;
}
int main()
{
BinTree *root = NULL;
int array[] = {8,2,-5,1,77,-6,45,0,5};
for(int i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
TREE_INSERT(&root,array[i]); //创建树
for(int i = 5; i < 9; ++i)
non_recursive_TREE_INSERT(&root,array[i]); //接上继续创建,在这只是为了测试
//分别用先中后序输出,包括每种顺序的递归和非递归
cout << "preOrder: ";
preOrder(root);
cout << endl;
cout << "non recursive preOrder: " ;
non_recursive_preOrder(root);
cout << endl;
cout << "inOrder: " ;
inOrder(root);
cout << endl;
cout << "non recursive inOrder: ";
non_recursive_inOrder(root);
cout << endl;
cout << "postOrder: ";
postOrder(root);
cout << endl;
cout << "non recursive postOrder: ";
non_recursive_postOrder(root);
cout << endl;
//查找元素,找到则输出并找到该元素的前驱和后继
BinTree *p = TREE_SEARCH(root,77);
if(p != NULL){
cout << "find " << p->key << endl;
cout << "it's predecessor and successor: ";
BinTree *pre = TREE_PREDECESSOR(p);
if(pre != NULL)
cout << pre->key << ' ';
else cout << "NULL" << ' ';
BinTree *succ = TREE_SUCCESSOR(p);
if(succ != NULL)
cout << succ->key << ' ';
else cout << "NULL" << ' ';
cout << endl;
}
else cout << "can not find in the tree" << endl;
p = TREE_SEARCH(root,66);
if(p != NULL){
cout << "find " << p->key << endl;
cout << "it's predecessor and successor: ";
BinTree *pre = TREE_PREDECESSOR(p);
if(pre != NULL)
cout << pre->key << ' ';
else cout << "NULL" << ' ';
BinTree *succ = TREE_SUCCESSOR(p);
if(succ != NULL)
cout << succ->key << ' ';
else cout << "NULL" << ' ';
cout << endl;
}
else cout << "can not find in the tree" << endl;
p = TREE_SEARCH(root,8);
if(p != NULL){
cout << "find " << p->key << endl;
cout << "it's predecessor and successor: ";
BinTree *pre = TREE_PREDECESSOR(p);
if(pre != NULL)
cout << pre->key << ' ';
else cout << "NULL" << ' ';
BinTree *succ = TREE_SUCCESSOR(p);
if(succ != NULL)
cout << succ->key << ' ';
else cout << "NULL" << ' ';
cout << endl;
}
else cout << "can not find in the tree" << endl;
//找到树的最小和最大值
p = TREE_MINIMUM(root);
if(p != NULL)
cout << "minimum is: " << p->key << endl;
p = TREE_MAXIMUM(root);
if(p != NULL)
cout << "maximum is: " << p->key << endl;
//删除操作
TREE_DELETE(&root,8);
p = TREE_SEARCH(root,8);
if(p != NULL){
cout << "find " << p->key << endl;
cout << "it's predecessor and successor: ";
BinTree *pre = TREE_PREDECESSOR(p);
if(pre != NULL)
cout << pre->key << ' ';
else cout << "NULL" << ' ';
BinTree *succ = TREE_SUCCESSOR(p);
if(succ != NULL)
cout << succ->key << ' ';
else cout << "NULL" << ' ';
cout << endl;
}
else cout << "can not find in the tree" << endl;
//删除后中序遍历
inOrder(root);
cout << endl;
return 0;
}




















 2214
2214











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








