概述:
是针对一些经常分配并释放的对象,如进程描述符等,这些对象的大小一般比较小,如果直接采用伙伴系统来进行分配和释放,不仅会造成大量的内碎片,而且处理速度也太慢。而slab分配器是基于对象进行管理的,相同类型的对象归为一类(如进程描述符就是一类),每当要申请这样一个对象,slab分配器就从一个slab列表中分配一个这样大小的单元出去,而当要释放时,将其重新保存在该列表中,而不是直接返回给伙伴系统。slab分配对象时,会使用最近释放的对象内存块,因此其驻留在CPU高速缓存的概率较高。
slab分配把对象分组放进高速缓存,每个高速缓存都是同种类型对象的一种储备。
包含高速缓存的主内存被划分为多个slab,每个slab由一个或者多个页框组成。
高速缓存描述符:
struct kmem_cache {
/* 1) Cache tunables. Protected by cache_chain_mutex */
unsigned int batchcount;/*本地高速缓存转入或转出的大批对象数量*/
unsigned int limit; /*本地高速缓存中空闲对象的最大数目,可以调整*/
unsigned int shared;
unsigned int size; /*管理对象的大小*/
u32 reciprocal_buffer_size; /*buffer_size的倒数值*/
/* 2) touched by every alloc & free from the backend */
unsigned int flags; /* constant flags */ /* 高速缓存的永久标识*/
unsigned int num; /* # of objs per slab */ /* 一个slab所包含的对象数目 */
/* 3) cache_grow/shrink */
/* order of pgs per slab (2^n) */
unsigned int gfporder;/*一个slab包含的连续页框数的对数*/
/* force GFP flags, e.g. GFP_DMA */
gfp_t allocflags;/*与伙伴系统交互时所提供的分配标识*/
size_t colour; /* cache colouring range */ /* 颜色的个数*/
unsigned int colour_off; /* colour offset *//* 着色的偏移量 */
struct kmem_cache *slabp_cache;<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>/*如果将slab描述符存储在外部,该指针指向存储slab描述符的cache, 否则为NULL*/
unsigned int slab_size;<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>/*slab管理区的大小*/
unsigned int dflags; /* dynamic flags */
/* constructor func */
void (*ctor)(void *obj);
/* 4) cache creation/removal */
const char *name;
struct list_head list;<span style="white-space:pre"> /*用于将高速缓存链入cache chain*/ </span>
int refcount;
int object_size;
int align;
/* 5) statistics */
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_SLAB
unsigned long num_active;
unsigned long num_allocations;
unsigned long high_mark;
unsigned long grown;
unsigned long reaped;
unsigned long errors;
unsigned long max_freeable;
unsigned long node_allocs;
unsigned long node_frees;
unsigned long node_overflow;
atomic_t allochit;
atomic_t allocmiss;
atomic_t freehit;
atomic_t freemiss;
/*
* If debugging is enabled, then the allocator can add additional
* fields and/or padding to every object. size contains the total
* object size including these internal fields, the following two
* variables contain the offset to the user object and its size.
*/
int obj_offset;
#endif /* CONFIG_DEBUG_SLAB */
/* 6) per-cpu/per-node data, touched during every alloc/free */
/*
* We put array[] at the end of kmem_cache, because we want to size
* this array to nr_cpu_ids slots instead of NR_CPUS
* (see kmem_cache_init())
* We still use [NR_CPUS] and not [1] or [0] because cache_cache
* is statically defined, so we reserve the max number of cpus.
*/
struct kmem_list3 **nodelists; /*struct kmem_list3用于组织该高速缓存中的slab*/
struct array_cache *array[NR_CPUS];
/*<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>/*per-CPU数据,记录了本地高速缓存的信息,也用于跟踪最近释放的对象,每次分配和释放都要直接访问它*/
* Do not add fields after array[]
*/
};
/*
* The slab lists for all objects.
*/
struct kmem_list3 {
struct list_head slabs_partial; /* partial list first, better asm code */
struct list_head slabs_full;<span style="white-space:pre"> /*slab链表,只包含非空闲的slab描述符*</span>
struct list_head slabs_free;<span style="white-space:pre"> /*slab链表,只包含空闲的slab描述符*/ </span>
unsigned long free_objects; /*高速缓存中空闲对象的个数*/
unsigned int free_limit;<span style="white-space:pre"> /*空闲对象的上限*/ </span>
unsigned int colour_next; /* Per-node cache coloring */ /*下一个slab使用的颜色*/
spinlock_t list_lock;
struct array_cache *shared; /* shared per node */ /*指向所有的cpu共享的一个本地高速缓存的指针*/
struct array_cache **alien; /* on other nodes */
unsigned long next_reap; /* updated without locking */
int free_touched; /* updated without locking */
};
/*
* struct slab
*
* Manages the objs in a slab. Placed either at the beginning of mem allocated
* for a slab, or allocated from an general cache.
* Slabs are chained into three list: fully used, partial, fully free slabs.
*/
struct slab {
union {
struct {
struct list_head list; /*用于将slab链入kmem_list3链表中的一个*/
unsigned long colouroff;/*该slab钟第一个对象的着色偏移*/
void *s_mem; /* including colour offset *//*指向slab中的第一个对象*/
unsigned int inuse; /* num of objs active in slab */ /*已分配出去的对象个数*/
kmem_bufctl_t free; /*下一个空闲对象的下标如果没有剩下空闲对象则为BUFCTL_RND*/
unsigned short nodeid;
};
struct slab_rcu __slab_cover_slab_rcu;
};
};
<pre name="code" class="cpp">/*
* struct array_cache
*
* Purpose:
* - LIFO ordering, to hand out cache-warm objects from _alloc
* - reduce the number of linked list operations
* - reduce spinlock operations
*
* The limit is stored in the per-cpu structure to reduce the data cache
* footprint.
*
*/
struct array_cache {
unsigned int avail;/*本地高速缓存中可用的空闲对象数*/
unsigned int limit;/*空闲对象的上限*/
unsigned int batchcount;/*一次转入和转出的对象数量*/
unsigned int touched; /*标识本地CPU最近是否被使用*/
spinlock_t lock;
void *entry[]; /*<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>/*这是一个伪数组,便于对后面用于跟踪空闲对象的指针数组的访问
* Must have this definition in here for the proper
* alignment of array_cache. Also simplifies accessing
* the entries.
*
* Entries should not be directly dereferenced as
* entries belonging to slabs marked pfmemalloc will
* have the lower bits set SLAB_OBJ_PFMEMALLOC
*/
};数组的元素个数对应了系统的CPU数,和伙伴系统中的每CPU页框高速缓存类似,该结构用来描述每个CPU的本地高速缓存,它可以减少SMP系统中对于自旋锁的竞争。在每个array_cache的末端都用一个指针数组记录了slab中的空闲对象,分配对象时,采用LIFO方式,也就是将该数组中的最后一个索引对应的对象分配出去,以保证该对象还驻留在高速缓存中的可能性。实际上,每次分配内存都是直接与本地CPU高速缓存进行交互,只有当其空闲内存不足时,才会从kmem_list中的slab中引入一部分对象到本地高速缓存中,而kmem_list中的空闲对象也不足了,那么就要从伙伴系统中引入新的页来建立新的slab了,这一点也和伙伴系统的每CPU页框高速缓存很类似。
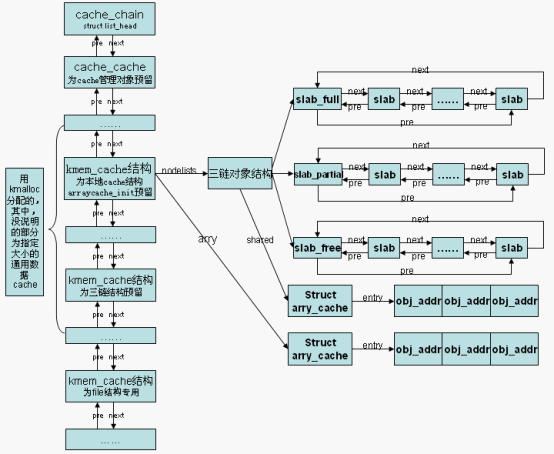
slab 相关结构之间的关系 来自 http://blog.csdn.net/vanbreaker/article/details/7664296

初始化时,cache对象、三链结构、本地cache对象预留了三个cache共分配。其他为通用数据cache,整体结构如下图
内核启动早期初始化
1.创建kmem_cache高速缓存用来存储所有的cache描述符
.2.创建array_cache和kmem_list3高速缓存用来存储slab数据结构中的这两个关键结构
此时slab尚未建立起来,如何用slab分配缓存??
对于第一个问题: 定义一个cache_cache的kmem_cache结构,来管理所有的kmem_cahe的描述符,乳后建立普通高速缓存,在使用kmalloc分配普通高速缓存替代之前静态部分;
普通高速缓存是一组大小按几何倍数增长的高速缓存的合集;
/* Size description struct for general caches. */
struct cache_sizes {
size_t cs_size; /*general cache的大小*/
struct kmem_cache *cs_cachep; /*general cache的cache描述符指针*/
#ifdef CONFIG_ZONE_DMA
struct kmem_cache *cs_dmacachep;
#endif
};/*
* These are the default caches for kmalloc. Custom caches can have other sizes.
*/
struct cache_sizes malloc_sizes[] = {
#define CACHE(x) { .cs_size = (x) },
#include <linux/kmalloc_sizes.h>
CACHE(ULONG_MAX)
#undef CACHE
}; start_kernel()->mm_init()->kmem_cache_init()
1,初始化静态initkmem_list3三链;
2,初始化cache_cache的nodelists字段为1中的三链;
3,根据内存情况初始化每个slab占用的页面数变量slab_break_gfp_order;
4,将cache_cache加入cache_chain链表中,初始化cache_cache;
5,创建kmalloc所用的general cache:
1)cache的名称和大小存放在两个数据结构对应的数组中,对应大小的cache可以从size数组中找到;
2)先创建INDEX_AC和INDEX_L3下标的cache;
3)循环创建size数组中各个大小的cache;
6,替换静态本地cache全局变量:
1) 替换cache_cache中的arry_cache,本来指向静态变量initarray_cache.cache;
2) 替换malloc_sizes[INDEX_AC].cs_cachep的local cache,原本指向静态变量initarray_generic.cache;
7,替换静态三链
1)替换cache_cache三链,原本指向静态变量initkmem_list3;
2)替换malloc_sizes[INDEX_AC].cs_cachep三链,原本指向静态变量initkmem_list3;
8,更新初始化进度
/*
* Initialisation. Called after the page allocator have been initialised and
* before smp_init().
*/
void __init kmem_cache_init(void)
{
size_t left_over;
struct cache_sizes *sizes;
struct cache_names *names;
int i;
int order;
int node;
if (num_possible_nodes() == 1)
use_alien_caches = 0;
<span style="white-space:pre"> /* 在slab初始化好之前,无法通过kmalloc分配初始化过程中必要的一些对象
,只能使用静态的全局变量
,待slab初始化后期,再使用kmalloc动态分配的对象替换全局变量 */ </span>
for (i = 0; i < NUM_INIT_LISTS; i++) {
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span> <span style="white-space:pre"> /*<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>初始化全局变量initkmem_list3表示的slab三链
,每个内存节点对应一组slab三链。initkmem_list3是个slab三链数组,对于每个内存节点,包含三组
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>:struct kmem_cache的slab三链、struct arraycache_init的slab 三链、struct kmem_list3的slab三链
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>。这里循环初始化所有内存节点的所有slab三链 */ </span>
kmem_list3_init(&initkmem_list3[i]);
if (i < MAX_NUMNODES)
<span style="white-space:pre"> /* 全局变量cache_cache指向的slab cache包含所有struct kmem_cache对象,不包含cache_cache本身
</span> <span style="white-space:pre"> </span><span style="white-space:pre">。这里初始化所有内存节点的struct kmem_cache的slab三链为空。*/ </span>
cache_cache.nodelists[i] = NULL;
}
/* 设置struct kmem_cache的slab三链指向initkmem_list3中的一组slab三链,
CACHE_CACHE为cache在内核cache链表中的索引,
struct kmem_cache对应的cache是内核中创建的第一个cache
,故CACHE_CACHE为0 */
set_up_list3s(&cache_cache, CACHE_CACHE);
/*
* Fragmentation resistance on low memory - only use bigger
* page orders on machines with more than 32MB of memory if
* not overridden on the command line.
*/ /* 全局变量slab_break_gfp_order为每个slab最多占用几个页面
,用来抑制碎片,比如大小为3360的对象
,如果其slab只占一个页面,碎片为736
,slab占用两个页面,则碎片大小也翻倍
。只有当对象很大
,以至于slab中连一个对象都放不下时
,才可以超过这个值
。有两个可能的取值
:当可用内存大于32MB时
,BREAK_GFP_ORDER_HI为1
,即每个slab最多占用2个页面
,只有当对象大小大于8192时
,才可以突破slab_break_gfp_order的限制
。小于等于32MB时BREAK_GFP_ORDER_LO为0。*/
if (!slab_max_order_set && totalram_pages > (32 << 20) >> PAGE_SHIFT)
slab_max_order = SLAB_MAX_ORDER_HI;
/* Bootstrap is tricky, because several objects are allocated
* from caches that do not exist yet:
* 1) initialize the cache_cache cache: it contains the struct
* kmem_cache structures of all caches, except cache_cache itself:
* cache_cache is statically allocated.
* Initially an __init data area is used for the head array and the
* kmem_list3 structures, it's replaced with a kmalloc allocated
* array at the end of the bootstrap.
* 2) Create the first kmalloc cache.
* The struct kmem_cache for the new cache is allocated normally.
* An __init data area is used for the head array.
* 3) Create the remaining kmalloc caches, with minimally sized
* head arrays.
* 4) Replace the __init data head arrays for cache_cache and the first
* kmalloc cache with kmalloc allocated arrays.
* 5) Replace the __init data for kmem_list3 for cache_cache and
* the other cache's with kmalloc allocated memory.
* 6) Resize the head arrays of the kmalloc caches to their final sizes.
*/
node = numa_mem_id();
/* 1) create the cache_cache */ /*初始化cache_cache的其余部分*/
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&slab_caches);
list_add(&cache_cache.list, &slab_caches);/* 将cache_cache加入到slab cache链表 */
cache_cache.colour_off = cache_line_size();/* 设置cache着色基本单位为cache line的大小:32字节 */
cache_cache.array[smp_processor_id()] = &initarray_cache.cache; /* 初始化cache_cache的local cache,同样这里也不能使用kmalloc,需要使用静态分配的全局变量initarray_cache */
cache_cache.nodelists[node] = &initkmem_list3[CACHE_CACHE + node];/* 初始化slab链表 ,用全局变量*/
/*
* struct kmem_cache size depends on nr_node_ids & nr_cpu_ids
*/
<span style="white-space:pre"> /* buffer_size保存slab中对象的大小,这里是计算struct kmem_cache的大小
, nodelists是最后一个成员
,nr_node_ids保存内存节点个数,UMA为1
,所以nodelists偏移加上1个struct kmem_list3 的大小即为struct kmem_cache的大小 */ </span>
cache_cache.size = offsetof(struct kmem_cache, array[nr_cpu_ids]) +
nr_node_ids * sizeof(struct kmem_list3 *);
cache_cache.object_size = cache_cache.size;/
cache_cache.size = ALIGN(cache_cache.size,
cache_line_size());/* 将对象大小与cache line大小对齐 *
cache_cache.reciprocal_buffer_size =
reciprocal_value(cache_cache.size);
for (order = 0; order < MAX_ORDER; order++) {/* 计算cache_cache中的对象数目 */
cache_estimate(order, cache_cache.size,
cache_line_size(), 0, &left_over, &cache_cache.num);
if (cache_cache.num)
break;
}
BUG_ON(!cache_cache.num);
cache_cache.gfporder = order; /* gfporder表示本slab包含2^gfporder个页面 */
cache_cache.colour = left_over / cache_cache.colour_off;
cache_cache.slab_size = ALIGN(cache_cache.num * sizeof(kmem_bufctl_t) +
sizeof(struct slab), cache_line_size()); /* slab管理对象的大小 即slab描述符以及kmem_bufctl_t数组*/
/* 2+3) create the kmalloc caches */
<span style="white-space:pre"> /* 第二步,创建kmalloc所用的general cache
,kmalloc所用的对象按大小分级
,malloc_sizes保存大小,cache_names保存cache名 */ </span>
sizes = malloc_sizes; //全局数组 存的size为32 64 等
names = cache_names;
/*
* Initialize the caches that provide memory for the array cache and the
* kmem_list3 structures first. Without this, further allocations will
* bug.
*/ /*为了后面能够调用kmalloc()创建per-CPU高速缓存和kmem_list3高速缓存,
这里必须先创建大小相应的general cache*/
/*其大小分别为32 64 128 256 512 。。。。。。*/
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>/*
<span style="white-space:pre"> #define INDEX_AC index_of(sizeof(struct arraycache_init))
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>#define INDEX_L3 index_of(sizeof(struct kmem_list3)</span> 找出是属于其内存大小对应的最合适的下标; 比如 大小为60bytes 分配其内存大小为64bytes
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>*/
sizes[INDEX_AC].cs_cachep = __kmem_cache_create(names[INDEX_AC].name,
sizes[INDEX_AC].cs_size,
ARCH_KMALLOC_MINALIGN,
ARCH_KMALLOC_FLAGS|SLAB_PANIC,
NULL);
if (INDEX_AC != INDEX_L3) {/*如果AC和L3在malloc_sizes中的偏移不一样,也就是说它们的大小不属于同一级别,
则创建L3的gerneral cache,否则两者共用一个gerneral cache*/
sizes[INDEX_L3].cs_cachep =
__kmem_cache_create(names[INDEX_L3].name,
sizes[INDEX_L3].cs_size,
ARCH_KMALLOC_MINALIGN,
ARCH_KMALLOC_FLAGS|SLAB_PANIC,
NULL);
}
slab_early_init = 0;
/*创建各级的gerneral cache*/
while (sizes->cs_size != ULONG_MAX) {
/*
* For performance, all the general caches are L1 aligned.
* This should be particularly beneficial on SMP boxes, as it
* eliminates "false sharing".
* Note for systems short on memory removing the alignment will
* allow tighter packing of the smaller caches.
*/
if (!sizes->cs_cachep) {
sizes->cs_cachep = __kmem_cache_create(names->name,
sizes->cs_size,
ARCH_KMALLOC_MINALIGN,
ARCH_KMALLOC_FLAGS|SLAB_PANIC,
NULL);
}
#ifdef CONFIG_ZONE_DMA
sizes->cs_dmacachep = __kmem_cache_create(
names->name_dma,
sizes->cs_size,
ARCH_KMALLOC_MINALIGN,
ARCH_KMALLOC_FLAGS|SLAB_CACHE_DMA|
SLAB_PANIC,
NULL);
#endif
sizes++;
names++;
} /* 至此,kmalloc general cache已经创建完毕,可以拿来使用了 */
/* 4) Replace the bootstrap head arrays */
{/*用kmalloc对象替换静态分配的全局变量
。到目前为止一共使用了两个全局local cache
,一个是cache_cache的local cache指向initarray_cache.cache
,另一个是malloc_sizes[INDEX_AC].cs_cachep的local cache指向initarray_generic.cache
,参见setup_cpu_cache函数。这里替换它们。*/
struct array_cache *ptr;
<span style="white-space:pre"> /*这里调用kmalloc()为cache_cache创建per-CPU高速缓存*/ /* 申请cache_cache所用local cache的空间 */ </span>
ptr = kmalloc(sizeof(struct arraycache_init), GFP_NOWAIT);
BUG_ON(cpu_cache_get(&cache_cache) != &initarray_cache.cache);
memcpy(ptr, cpu_cache_get(&cache_cache),
sizeof(struct arraycache_init));
/*
* Do not assume that spinlocks can be initialized via memcpy:
*/
spin_lock_init(&ptr->lock);
cache_cache.array[smp_processor_id()] = ptr;
ptr = kmalloc(sizeof(struct arraycache_init), GFP_NOWAIT); /* 申请malloc_sizes[INDEX_AC].cs_cachep所用local cache的空间 *
BUG_ON(cpu_cache_get(malloc_sizes[INDEX_AC].cs_cachep)
!= &initarray_generic.cache);
memcpy(ptr, cpu_cache_get(malloc_sizes[INDEX_AC].cs_cachep),
sizeof(struct arraycache_init));
/*
* Do not assume that spinlocks can be initialized via memcpy:
*/
spin_lock_init(&ptr->lock);
malloc_sizes[INDEX_AC].cs_cachep->array[smp_processor_id()] =
ptr;
}
/* 5) Replace the bootstrap kmem_list3's 用kmalloc的空间替换静态分配的slab三链 */ */
{
int nid;
for_each_online_node(nid) {
init_list(&cache_cache, &initkmem_list3[CACHE_CACHE + nid], nid);
init_list(malloc_sizes[INDEX_AC].cs_cachep,
&initkmem_list3[SIZE_AC + nid], nid);
if (INDEX_AC != INDEX_L3) {
init_list(malloc_sizes[INDEX_L3].cs_cachep,
&initkmem_list3[SIZE_L3 + nid], nid);
}
}
}
slab_state = UP;
}
/*
* For setting up all the kmem_list3s for cache whose buffer_size is same as
* size of kmem_list3.
*/
static void __init set_up_list3s(struct kmem_cache *cachep, int index)
{
int node;
for_each_online_node(node) {
cachep->nodelists[node] = &initkmem_list3[index + node]; /* 全局变量initkmem_list3是初始化阶段使用的slab三链 */
cachep->nodelists[node]->next_reap = jiffies +
REAPTIMEOUT_LIST3 +
((unsigned long)cachep) % REAPTIMEOUT_LIST3;/* 设置回收时间 */
}
}计算每个slab中的对象
hjgh
/*
* Calculate the number of objects and left-over bytes for a given buffer size.
*/
/*计算每个slab中对象的数目。*/
/*
1) gfporder:slab由2gfporder个页面组成。
2) buffer_size:对象的大小。
3) align:对象的对齐方式。
4) flags:内置式slab还是外置式slab。
5) left_over:slab中浪费空间的大小。
6) num:slab中的对象数目。
*/
static void cache_estimate(unsigned long gfporder, size_t buffer_size,
size_t align, int flags, size_t *left_over,
unsigned int *num)
{
int nr_objs;
size_t mgmt_size;
/* slab大小为1<<order个页面 */
size_t slab_size = PAGE_SIZE << gfporder;
/*
* The slab management structure can be either off the slab or
* on it. For the latter case, the memory allocated for a
* slab is used for:
*
* - The struct slab
* - One kmem_bufctl_t for each object
* - Padding to respect alignment of @align
* - @buffer_size bytes for each object
*
* If the slab management structure is off the slab, then the
* alignment will already be calculated into the size. Because
* the slabs are all pages aligned, the objects will be at the
* correct alignment when allocated.
*/
if (flags & CFLGS_OFF_SLAB) {
/* 外置式slab */
mgmt_size = 0;
/* slab页面不含slab管理对象,全部用来存储slab对象 */
nr_objs = slab_size / buffer_size;
/* 对象数不能超过上限 */
if (nr_objs > SLAB_LIMIT)
nr_objs = SLAB_LIMIT;
} else {
/*
* Ignore padding for the initial guess. The padding
* is at most @align-1 bytes, and @buffer_size is at
* least @align. In the worst case, this result will
* be one greater than the number of objects that fit
* into the memory allocation when taking the padding
* into account.
*//* 内置式slab,slab管理对象与slab对象在一起
,此时slab页面中包含:一个struct slab对象,一个kmem_bufctl_t数组,slab对象。
kmem_bufctl_t数组大小与slab对象数目相同 */
nr_objs = (slab_size - sizeof(struct slab)) /
(buffer_size + sizeof(kmem_bufctl_t));
/*
* This calculated number will be either the right
* amount, or one greater than what we want.
*//* 计算cache line对齐后的大小,如果超出了slab总的大小,则对象数减一 */
if (slab_mgmt_size(nr_objs, align) + nr_objs*buffer_size
> slab_size)
nr_objs--;
if (nr_objs > SLAB_LIMIT)
nr_objs = SLAB_LIMIT;
/* 计算cache line对齐后slab管理对象的大小 */
mgmt_size = slab_mgmt_size(nr_objs, align);
}
*num = nr_objs;/* 保存slab对象数目 */
/* 计算浪费空间的大小 */
*left_over = slab_size - nr_objs*buffer_size - mgmt_size;
}slab 三链初始化
设置cache的slab三链指向静态分配的全局变量
static void __init set_up_list3s(struct kmem_cache *cachep, int index)
{
int node;
/* UMA只有一个节点 */
for_each_online_node(node) {
/* 全局变量initkmem_list3是初始化阶段使用的slab三链 */
cachep->nodelists[node] = &initkmem_list3[index + node];
/* 设置回收时间 */
cachep->nodelists[node]->next_reap = jiffies +
REAPTIMEOUT_LIST3 +
((unsigned long)cachep) % REAPTIMEOUT_LIST3;
}
}static void kmem_list3_init(struct kmem_list3 *parent)
{
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&parent->slabs_full);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&parent->slabs_partial);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&parent->slabs_free);
parent->shared = NULL;
parent->alien = NULL;
parent->colour_next = 0;
spin_lock_init(&parent->list_lock);
parent->free_objects = 0;
parent->free_touched = 0;
}/*
* Calculate the number of objects and left-over bytes for a given buffer size.
*/
/*计算每个slab中对象的数目。*/
/*
1) gfporder:slab由2gfporder个页面组成。
2) buffer_size:对象的大小。
3) align:对象的对齐方式。
4) flags:内置式slab还是外置式slab。
5) left_over:slab中浪费空间的大小。
6) num:slab中的对象数目。
*/
static void cache_estimate(unsigned long gfporder, size_t buffer_size,
size_t align, int flags, size_t *left_over,
unsigned int *num)
{
int nr_objs;
size_t mgmt_size;
/* slab大小为1<<order个页面 */
size_t slab_size = PAGE_SIZE << gfporder;
/*
* The slab management structure can be either off the slab or
* on it. For the latter case, the memory allocated for a
* slab is used for:
*
* - The struct slab
* - One kmem_bufctl_t for each object
* - Padding to respect alignment of @align
* - @buffer_size bytes for each object
*
* If the slab management structure is off the slab, then the
* alignment will already be calculated into the size. Because
* the slabs are all pages aligned, the objects will be at the
* correct alignment when allocated.
*/
if (flags & CFLGS_OFF_SLAB) {
/* 外置式slab */
mgmt_size = 0;
/* slab页面不含slab管理对象,全部用来存储slab对象 */
nr_objs = slab_size / buffer_size;
/* 对象数不能超过上限 */
if (nr_objs > SLAB_LIMIT)
nr_objs = SLAB_LIMIT;
} else {
/*
* Ignore padding for the initial guess. The padding
* is at most @align-1 bytes, and @buffer_size is at
* least @align. In the worst case, this result will
* be one greater than the number of objects that fit
* into the memory allocation when taking the padding
* into account.
*//* 内置式slab,slab管理对象与slab对象在一起
,此时slab页面中包含:一个struct slab对象,一个kmem_bufctl_t数组,slab对象。
kmem_bufctl_t数组大小与slab对象数目相同 */
nr_objs = (slab_size - sizeof(struct slab)) /
(buffer_size + sizeof(kmem_bufctl_t));
/*
* This calculated number will be either the right
* amount, or one greater than what we want.
*//* 计算cache line对齐后的大小,如果超出了slab总的大小,则对象数减一 */
if (slab_mgmt_size(nr_objs, align) + nr_objs*buffer_size
> slab_size)
nr_objs--;
if (nr_objs > SLAB_LIMIT)
nr_objs = SLAB_LIMIT;
/* 计算cache line对齐后slab管理对象的大小 */
mgmt_size = slab_mgmt_size(nr_objs, align);
}
*num = nr_objs;/* 保存slab对象数目 */
/* 计算浪费空间的大小 */
*left_over = slab_size - nr_objs*buffer_size - mgmt_size;
}从上面的初始化过程中我们看到,创建的cache与用途主要有:
1,cache_cache用于cache管理结构空间申请,对象大小为cache管理结构大小;2,sizes[INDEX_AC].cs_cachep用于local cache;
3,sizes[INDEX_L3].cs_cachep用于三链;
4.其他的主要用于指定大小的通用数据cache。
- 前面大部分的代码都是围绕cache_cache展开的,主要是将cache_cache同静态kmem_list3进行关联,将cache_cache添加到cache_chain链表中,并且计算初始化内部的一些数据项
- 现在还没有高速缓存来存储cache_cache中的kmem_list3描述符和array_cache描述符,因此下面就要调用kmem_cache_create()建立高速缓存来存储这两种描述符
- 内核使用g_cpucache_up这个枚举量来表示slab分配器的初始化进度
这个值的更新是在kmem_cache_create()-->setup_cpu_cache()函数中进行更新的,每调用一次kmem_cache_create(),g_cpucache_up的值就加1,直到它等于EARLY,比如说第一次调用kmem_cache_create()创建了AC(array_cache)的高速缓存,那么g_cpucache_up由NONE变为PARTIAL_AC,那么下次调用kmem_cache_create()创建L3高速缓存时,内核就知道AC高速缓存已经准备好了,也就是说可以在array_cache高速缓存中为L3高速缓存描述符的array_cache描述符分配高速缓存空间了。
- 创建了AC和L3高速缓存后就循环创建各级普通高速缓存,此时创建的高速缓存都是完整的了!也就是说里面的结构变量都已经是存储在相应的高速缓存中
- 由于AC高速缓存已经创建,因此kmalloc()动态创建一个array_cache对象替换cache_cache的静态array_cache
- 由于AC高速缓存描述符本身的array_cache描述符还未动态创建,因此同样kmalloc()动态创建一个array_cache替换AC高速缓存的静态array_cache
- 为cache_cache,AC,L3高速缓存分别动态创建kmem_list描述符对象,替换静态的initkmem_list3
- 将g_cpucache_up置为EARLY,表示slab分配器的初始化已初步完成
Start_kernel()->kmem_cache_init_late()
slab分配器初始化工作的最后一步由kmem_cache_init_late()函数完成;它的工作就是设置cache_cache和各级普通高速缓存中的array_cache本地高速缓存的相关属性;
其中会调用_kmem_cache_create()是什么鬼????
创建新的缓存必须通过kmem_cache_create()函数来完成,原型如下






















 2993
2993

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








