创建slab主要由函数cache_grow()实现,满足以下两个条件时,slab分配器将为高速缓存创建新的slab
1.请求分配对象,但本地高速缓存没有空闲对象可以分配,需要填充
2.kmem_list3维护的链表中没有slab或者所有的slab都处于FULL链表中

图片来自:http://blog.csdn.net/vanbreaker/article/details/7673372
- /*使用一个或多个页面创建一个空slab。
- objp:页面虚拟地址,为空表示还未申请内存页,不为空
- ,说明已申请内存页,可直接用来创建slab*/
/*
* Grow (by 1) the number of slabs within a cache. This is called by
* kmem_cache_alloc() when there are no active objs left in a cache.
*/
static int cache_grow(struct kmem_cache *cachep,
gfp_t flags, int nodeid, void *objp)
{
struct slab *slabp;
size_t offset;
gfp_t local_flags;
struct kmem_list3 *l3;
/*
* Be lazy and only check for valid flags here, keeping it out of the
* critical path in kmem_cache_alloc().
*/
BUG_ON(flags & GFP_SLAB_BUG_MASK);
local_flags = flags & (GFP_CONSTRAINT_MASK|GFP_RECLAIM_MASK);
/* Take the l3 list lock to change the colour_next on this node */
check_irq_off();
l3 = cachep->nodelists[nodeid];/* 获得本内存节点的slab三链 */
spin_lock(&l3->list_lock);
/* Get colour for the slab, and cal the next value. */
offset = l3->colour_next;/*确定待创建的slab的颜色编号即着色区偏移*/
l3->colour_next++; /* 更新着色区偏移,使不同slab的着色偏移不同 */
if (l3->colour_next >= cachep->colour) /*颜色编号必须小于颜色数*/
l3->colour_next = 0;
spin_unlock(&l3->list_lock);
offset *= cachep->colour_off;/* 将着色单位区间的个数转换为着色区大小即 确定待创建的slab的颜色 */
if (local_flags & __GFP_WAIT)
local_irq_enable();
/*
* The test for missing atomic flag is performed here, rather than
* the more obvious place, simply to reduce the critical path length
* in kmem_cache_alloc(). If a caller is seriously mis-behaving they
* will eventually be caught here (where it matters).
*/
kmem_flagcheck(cachep, flags);
/*
* Get mem for the objs. Attempt to allocate a physical page from
* 'nodeid'.
*/
if (!objp) /*从伙伴系统分配页框,这是slab分配器与伙伴系统的接口
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>从本内存节点分配1<<cachep->gfporder个页面 ,objp为slab首页面的虚拟地址 */
objp = kmem_getpages(cachep, local_flags, nodeid);
if (!objp)
goto failed;
/* Get slab management. */* 分配slab管理对象 */
slabp = alloc_slabmgmt(cachep, objp, offset,
local_flags & ~GFP_CONSTRAINT_MASK, nodeid);
if (!slabp)
goto opps1;
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>
slab_map_pages(cachep, slabp, objp); /* 设置page到cache、slab的映射以便于根据obj迅速定位slab描述符和cache描述符 */
cache_init_objs(cachep, slabp);/*初始化slab对象*/
if (local_flags & __GFP_WAIT)
local_irq_disable();
check_irq_off();
spin_lock(&l3->list_lock);
/* Make slab active. */
list_add_tail(&slabp->list, &(l3->slabs_free)); /*将新创建的slab添加到free链表*/
STATS_INC_GROWN(cachep);
l3->free_objects += cachep->num;
spin_unlock(&l3->list_lock);
return 1;
opps1:
kmem_freepages(cachep, objp);
failed:
if (local_flags & __GFP_WAIT)
local_irq_disable();
return 0;
为slab分配页框
/*
* Interface to system's page allocator. No need to hold the cache-lock.
*
* If we requested dmaable memory, we will get it. Even if we
* did not request dmaable memory, we might get it, but that
* would be relatively rare and ignorable.
*/
static void *kmem_getpages(struct kmem_cache *cachep, gfp_t flags, int nodeid)
{
struct page *page;
int nr_pages;
int i;
#ifndef CONFIG_MMU
/*
* Nommu uses slab's for process anonymous memory allocations, and thus
* requires __GFP_COMP to properly refcount higher order allocations
*/
flags |= __GFP_COMP;
#endif
flags |= cachep->gfpflags;
if (cachep->flags & SLAB_RECLAIM_ACCOUNT)
flags |= __GFP_RECLAIMABLE;
/*从特定的节点分配2^gfporder个连续页*/
page = alloc_pages_exact_node(nodeid, flags | __GFP_NOTRACK, cachep->gfporder);
if (!page)
return NULL;
nr_pages = (1 << cachep->gfporder);
if (cachep->flags & SLAB_RECLAIM_ACCOUNT)
add_zone_page_state(page_zone(page),
NR_SLAB_RECLAIMABLE, nr_pages);
else
add_zone_page_state(page_zone(page),
NR_SLAB_UNRECLAIMABLE, nr_pages);
for (i = 0; i < nr_pages; i++)
__SetPageSlab(page + i);
if (kmemcheck_enabled && !(cachep->flags & SLAB_NOTRACK)) {
kmemcheck_alloc_shadow(page, cachep->gfporder, flags, nodeid);
if (cachep->ctor)
kmemcheck_mark_uninitialized_pages(page, nr_pages);
else
kmemcheck_mark_unallocated_pages(page, nr_pages);
}
/*返回首页的虚拟地址*/
return page_address(page);
}
对于释放分配给slab的页框
/*
* Interface to system's page release.
*/
static void kmem_freepages(struct kmem_cache *cachep, void *addr)
{
unsigned long i = (1 << cachep->gfporder);
struct page *page = virt_to_page(addr);
const unsigned long nr_freed = i;
kmemcheck_free_shadow(page, cachep->gfporder);
if (cachep->flags & SLAB_RECLAIM_ACCOUNT)
sub_zone_page_state(page_zone(page),
NR_SLAB_RECLAIMABLE, nr_freed);
else
sub_zone_page_state(page_zone(page),
NR_SLAB_UNRECLAIMABLE, nr_freed);
while (i--) {
BUG_ON(!PageSlab(page));
__ClearPageSlabPfmemalloc(page);
__ClearPageSlab(page);
page++;
}
if (current->reclaim_state)//执行内存回收
current->reclaim_state->reclaimed_slab += nr_freed;
free_pages((unsigned long)addr, cachep->gfporder);
}
对于slab管理区分配空间
static struct slab *alloc_slabmgmt(struct kmem_cache *cachep, void *objp,
int colour_off, gfp_t local_flags,
int nodeid)
{
struct slab *slabp;
/*如果slab管理区位于slab外,则在指定的slabp_cache中分配空间*/
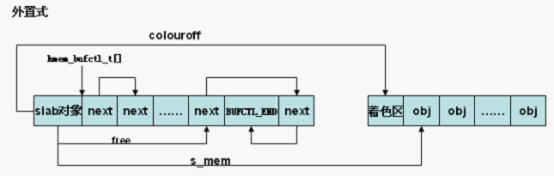
if (OFF_SLAB(cachep)) {
/* Slab management obj is off-slab. */
slabp = kmem_cache_alloc_node(cachep->slabp_cache,
local_flags, nodeid);
/*
* If the first object in the slab is leaked (it's allocated
* but no one has a reference to it), we want to make sure
* kmemleak does not treat the ->s_mem pointer as a reference
* to the object. Otherwise we will not report the leak.
*/
kmemleak_scan_area(slabp, offsetof(struct slab, list),
sizeof(struct list_head), local_flags);
if (!slabp)
return NULL;
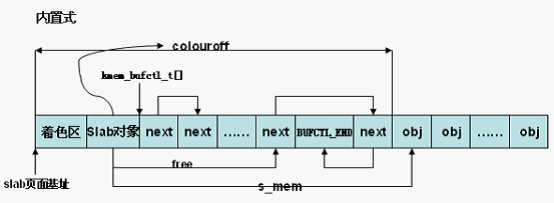
} else {/*slab管理区处于slab中*//* 内置式slab。objp为slab首页面的虚拟地址,加上着色偏移
,得到slab管理对象的虚拟地址 */
/*slab管理区从slab首部偏移颜色值的地方开始*/
slabp = objp + colour_off;
colour_off += cachep->slab_size;/* 计算slab中第一个对象的页内偏移,slab_size保存slab管理对象的大小 ,包含struct slab对象和kmem_bufctl_t数组 */
}
slabp->inuse = 0;/*对象全为空闲*/
slabp->colouroff = colour_off; /*刷新第一个对象的偏移*/ /* 第一个对象的页内偏移,可见对于内置式slab,colouroff成员不仅包括着色区
,还包括管理对象占用的空间 ,外置式slab,colouroff成员只包括着色区。*/
slabp->s_mem = objp + colour_off;/*确定第一个对象的位置*/
slabp->nodeid = nodeid;/*标识节点即 内存节点ID */
slabp->free = 0; /*下一个空闲对象位于s_mem起始处即kmem_bufctl_t数组的第一个元素 */
return slabp;
}1,从cache结构中获得并计算着色区偏移量;
2,从伙伴系统中获得1<<cachep->gfporder个页面用于slab;
3,初始化slab中相关变量,如果是外置式slab需要从新申请slab管理区的空间,由函数alloc_slabmgmt()实现
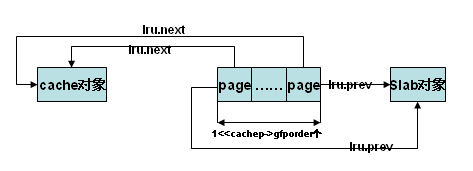
页描述结构的lru域建立页框到slab描述符和cache描述符的映射,实际就是使lru.next指向cache描述符,lru.prev指向slab描述符
static void slab_map_pages(struct kmem_cache *cache, struct slab *slab,
void *addr)
{
int nr_pages;
struct page *page;
page = virt_to_page(addr);
nr_pages = 1;
if (likely(!PageCompound(page)))
nr_pages <<= cache->gfporder;/*分配给slab的页框数*/
do {
page_set_cache(page, cache);/*建立到cache的映射*/
page_set_slab(page, slab); /*建立到slab的映射*/
page++;
} while (--nr_pages);
}
初始化slab中kmem_bufctl_t[]数组,其中kmem_bufctl_t[]数组为一个静态链表,指定了slab对象(obj)的访问顺序。即kmem_bufctl_t[]中存放的是下一个访问的obj。在后面分析中slab_get_obj()函数从slab中提取一个空闲对象,他通过index_to_obj()函数找到空闲对象在kmem_bufctl_t[]数组中的下标,然后通过slab_bufctl(slabp)[slabp->free]获得下一个空闲对象的索引并用它更新静态链表。
static void cache_init_objs(struct kmem_cache *cachep,
struct slab *slabp)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < cachep->num; i++) { /* 逐一初始化slab中的对象 */
void *objp = index_to_obj(cachep, slabp, i);
#if DEBUG
/* need to poison the objs? */
if (cachep->flags & SLAB_POISON)
poison_obj(cachep, objp, POISON_FREE);
if (cachep->flags & SLAB_STORE_USER)
*dbg_userword(cachep, objp) = NULL;
if (cachep->flags & SLAB_RED_ZONE) {
*dbg_redzone1(cachep, objp) = RED_INACTIVE;
*dbg_redzone2(cachep, objp) = RED_INACTIVE;
}
/*
* Constructors are not allowed to allocate memory from the same
* cache which they are a constructor for. Otherwise, deadlock.
* They must also be threaded.
*/
if (cachep->ctor && !(cachep->flags & SLAB_POISON))
cachep->ctor(objp + obj_offset(cachep));
if (cachep->flags & SLAB_RED_ZONE) {
if (*dbg_redzone2(cachep, objp) != RED_INACTIVE)
slab_error(cachep, "constructor overwrote the"
" end of an object");
if (*dbg_redzone1(cachep, objp) != RED_INACTIVE)
slab_error(cachep, "constructor overwrote the"
" start of an object");
}
if ((cachep->size % PAGE_SIZE) == 0 &&
OFF_SLAB(cachep) && cachep->flags & SLAB_POISON)
kernel_map_pages(virt_to_page(objp),
cachep->size / PAGE_SIZE, 0);
#else
if (cachep->ctor)
cachep->ctor(objp);/*根据构造函数初始化对象*/
slab_bufctl(slabp)[i] = i + 1;/*确定下一个空闲对象为后面相邻的对象*/
}
slab_bufctl(slabp)[i - 1] = BUFCTL_END; /* 最后一个指向BUFCTL_END */
销毁slab;
/**
* slab_destroy - destroy and release all objects in a slab
* @cachep: cache pointer being destroyed
* @slabp: slab pointer being destroyed
*
* Destroy all the objs in a slab, and release the mem back to the system.
* Before calling the slab must have been unlinked from the cache. The
* cache-lock is not held/needed.
*/
static void slab_destroy(struct kmem_cache *cachep, struct slab *slabp)
{
/*用第一个对象的地址减去着色偏移量得到slab的起始地址*/
void *addr = slabp->s_mem - slabp->colouroff;
slab_destroy_debugcheck(cachep, slabp);
/*如果选择了RCU方式来销毁slab,则通过RCU进行销毁,这个表示还不太明白*/
if (unlikely(cachep->flags & SLAB_DESTROY_BY_RCU)) {
struct slab_rcu *slab_rcu;
slab_rcu = (struct slab_rcu *)slabp;
slab_rcu->cachep = cachep;
slab_rcu->addr = addr;
call_rcu(&slab_rcu->head, kmem_rcu_free);
} else {
/*将slab占用的页框释放回伙伴系统*/
kmem_freepages(cachep, addr);
/*如果slab的管理区位于外部,则需要从对应的缓存中释放管理区对象*/
if (OFF_SLAB(cachep))
kmem_cache_free(cachep->slabp_cache, slabp);
}
}






















 1607
1607











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








