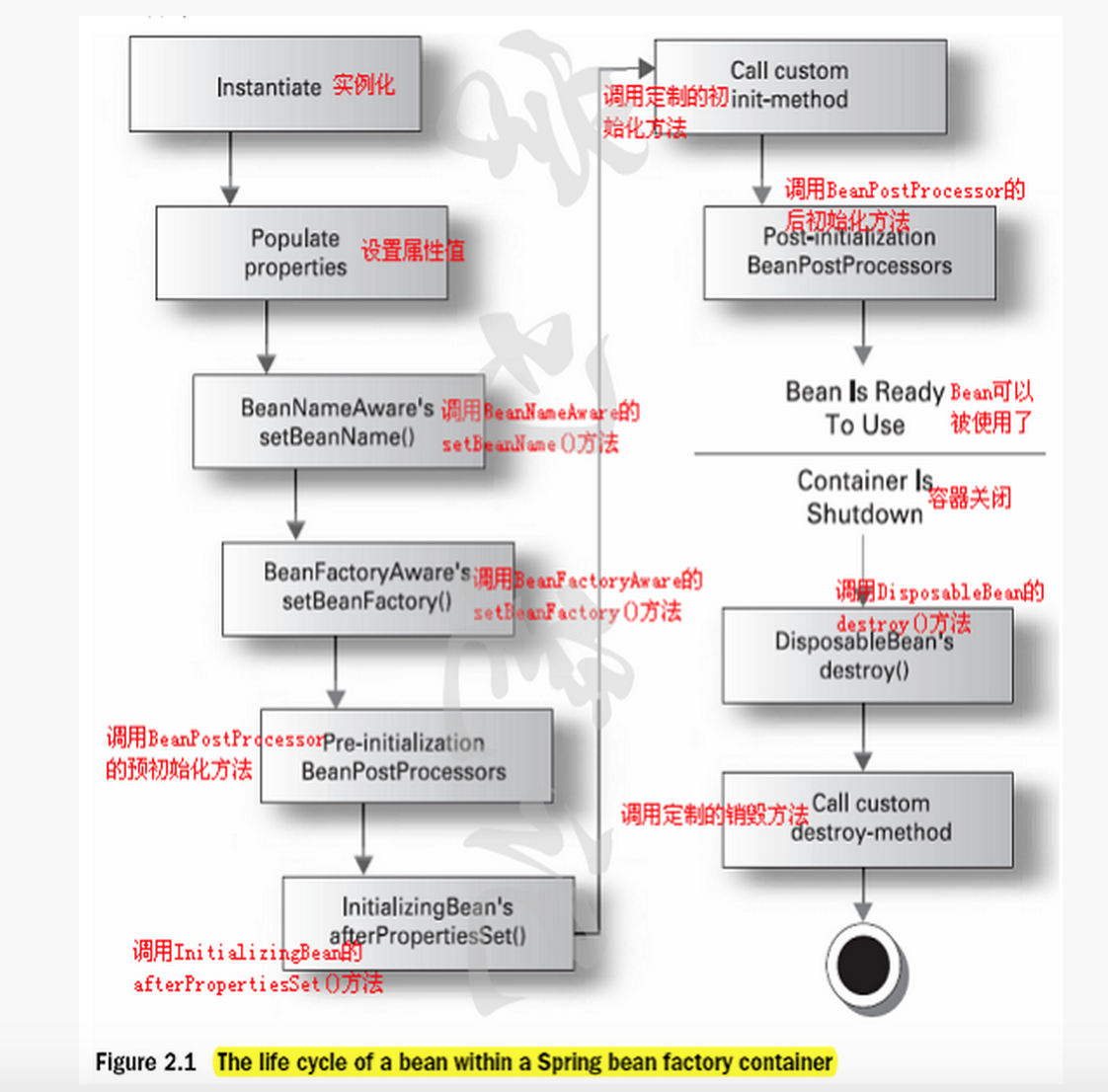
对于单例的bean生命周期图
bean周期详解
对于单例的bean,生命周期有11个步骤:
1.instantiate bean对象实例化,bean对象实例化,是在加载配置文件的时候实例的。即,我们启动spring容器的时候,加载配置文件,此时就实例化bean了。
2.populate properties 封装属性
3.如果Bean实现BeanNameAware, 执行 setBeanName
4.如果Bean实现BeanFactoryAware 或者 ApplicationContextAware,设置工厂 setBeanFactory 或者上下文对象 setApplicationContext
5.如果存在类实现 BeanPostProcessor(后处理Bean) ,执行postProcessBeforeInitialization(此点常常用来增强bean)
6.如果Bean实现InitializingBean 执行 afterPropertiesSet
7.调用<bean init-method="init"> 指定初始化方法 init
8.如果存在类实现 BeanPostProcessor(后处理Bean) ,执行postProcessAfterInitialization(此点常常用来增强bean)
9.执行业务处理
10.如果Bean实现 DisposableBean 执行 destroy
11.调用<bean destroy-method="customerDestroy"> 指定销毁方法
示例:
CustomerService接口
/**
* Created by enyilr on 15/9/4.
*/
public interface CustomerService {
void add();
void find();
}接口的实现类,此类实现了BeanNameAware,ApplicationContextAware,InitializingBean,DisposableBean
/**
* Created by enyilr on 15/9/4.
*/
public class CustomerServiceImpl implements BeanNameAware, ApplicationContextAware, InitializingBean, DisposableBean, CustomerService {
private String name;
public CustomerServiceImpl() {
super();
System.out.println("第一步:实例化类");
}
public void add() {
System.out.println("添加客户...");
}
public void find() {
System.out.println("查找客户...");
}
public void setup() {
System.out.println("第七步:调用手动设置的初始化的方法");
}
public void setName(String name) {
System.out.println("第二步:注入属性");
this.name = name;
}
//<bean id="customerService" class="demo4.CustomerService">
// 把id的值注入进来
public void setBeanName(String name) {
System.out.println("第三步:注入配置的类的名称" + name);
}
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("第四步:注入applicationContext" + applicationContext);
}
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("第六步:属性设置后执行...");
}
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("第十步:调用销毁的方法...");
}
public void teardown() {
System.out.println("第十一步:调用手动销毁的方法...");
}
}import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
/**
* Created by enyilr on 15/9/4.
*/
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
/**
* @param bean 实例对象
* @param beanName 在配置文件中配置类的标识
* @return
* @throws BeansException
*/
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("第五步:初始化之前执行");
// 在此处可以增强bean
return bean;
}
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(final Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("第八步:在初始化后执行");
if (beanName.equals("customerService")) {
Object proxyInstance = Proxy.newProxyInstance(bean.getClass().getClassLoader(), bean.getClass().getInterfaces(), new InvocationHandler() {
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
if("add".equals(method.getName())){
System.out.println("权限校验...");
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis());
Object result = method.invoke(bean, args);
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis());
return result;
}
return method.invoke(bean, args);
}
});
return proxyInstance;
}
if (beanName.equals("customer")){
System.out.println("beanName为:customer,不做任何操作!");
}
return bean;
}
}
spring配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="customerService" class="demo4.CustomerServiceImpl" init-method="setup" destroy-method="teardown">
<property name="name" value="enyi"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 实现BeanPostProcessor的类也要注册bean,只不过不需要写id -->
<bean class="demo4.MyBeanPostProcessor"/>
</beans>@Test
// 测试bean的完整生命周期
public void test1(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("demo4/demo4.xml");
CustomerService customerService = (CustomerService)applicationContext.getBean("customerService");
customerService.add();
customerService.find();
applicationContext.close();
}生命周期的实际应用
如果存在类实现BeanPostProcessor,那么spring每实例化一个类,都会执行postProcessBeforeInitialization,postProcessAfterInitialization方法,我们可以在这两个方法中做很多,比如我们用动态代理来增强bean,选择不同的操作做权限判断等等。我们可以选择性的增强一些bean
其他
上面的生命周期,是针对bean是单例的,对于多例的,则销毁操作是由调用者完成的。






















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








