本文通过对Android SDK中DisplayBitmap Case的探究,来理解在Android中如何实现图片的异步加载、缓存机制等。下面进行具体的分析:
1 工程结构
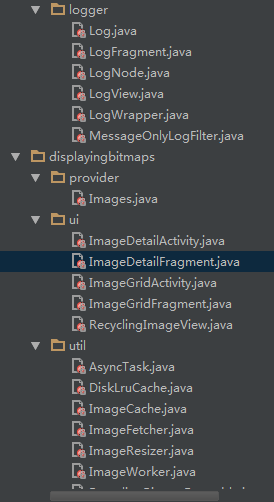
主要包含一个通用的日志包以及与图片显示相关的包。
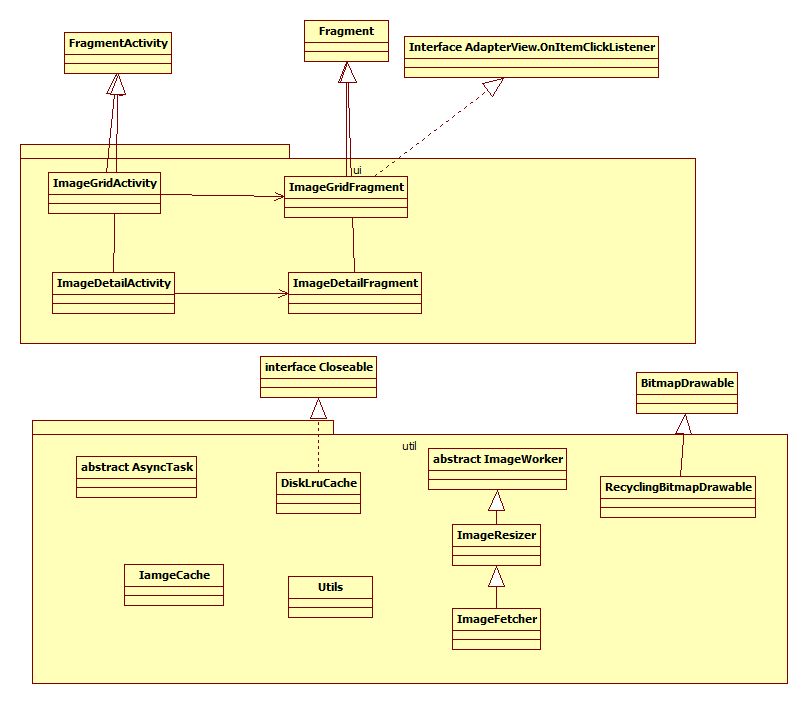
2 具体的结构图
3 类的具体分析
3.1 ui包
3.1.1 ImageGridActivity.java 类
该类提供了应用加载的主界面。该Activity持有一个Fragment,源码如下:
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
if (BuildConfig.DEBUG) {
Utils.enableStrictMode();
}
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
//TAG是给Fragment定义的标签
if (getSupportFragmentManager().findFragmentByTag(TAG) == null) {
final FragmentTransaction ft = getSupportFragmentManager().beginTransaction();
ft.add(android.R.id.content, new ImageGridFragment(), TAG);
ft.commit();
}
}该类很好理解。下面介绍ImageGridFragment.java类。
3.1.2 ImageGridFragment.java 类
首先看在onCreate()方法中干了什么?
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
//设置选项菜单
setHasOptionsMenu(true);
mImageThumbSize = getResources().getDimensionPixelSize(R.dimen.image_thumbnail_size);
mImageThumbSpacing = getResources().getDimensionPixelSize(R.dimen.image_thumbnail_spacing);
//创建ImageAdapter,用来适配GridView。可以通过getActivity()方法来获得Fragment依附的Activity(上下文环境)
mAdapter = new ImageAdapter(getActivity());
//设置图片缓存目录及缩放比
ImageCache.ImageCacheParams cacheParams =
new ImageCache.ImageCacheParams(getActivity(), IMAGE_CACHE_DIR);
//设置内存缓存大小,占应用缓存的25%
cacheParams.setMemCacheSizePercent(0.25f);
// 创建ImageFetcher对象,该对象只专注于实现异步加载图片
mImageFetcher = new ImageFetcher(getActivity(), mImageThumbSize);
//设置默认加载图片
mImageFetcher.setLoadingImage(R.drawable.empty_photo);
//设置加载缓存
mImageFetcher.addImageCache(getActivity().getSupportFragmentManager(), cacheParams);
}创建的ImageAdapter,用来在UI中显示图片,具体实现如下:
private class ImageAdapter extends BaseAdapter {
private final Context mContext;
private int mItemHeight = 0;//项的高度
private int mNumColumns = 0;//列数
private int mActionBarHeight = 0;//动作条(实现导航的)高度
private GridView.LayoutParams mImageViewLayoutParams;//GridView的布局参数对象
//Adapter构造器
public ImageAdapter(Context context) {
super();
mContext = context;
mImageViewLayoutParams = new GridView.LayoutParams(
LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT);
// 计算ActionBar的高度
//TypedValue是动态类型数据值的一个容器,主要用在持有value的Resource对象上
TypedValue tv = new TypedValue();
if (context.getTheme().resolveAttribute(
android.R.attr.actionBarSize, tv, true)) {
mActionBarHeight = TypedValue.complexToDimensionPixelSize(
tv.data, context.getResources().getDisplayMetrics());
}
}
//重载的getCount()方法
@Override
public int getCount() {
// 如果列数没有确定,就返回 0 .
if (getNumColumns() == 0) {
return 0;
}
// 数据大小加上顶部的空行,就得到要显示的总数
return Images.imageThumbUrls.length + mNumColumns;
}
//得到position位置的具体项
@Override
public Object getItem(int position) {
return position < mNumColumns ?
null : Images.imageThumbUrls[position - mNumColumns];
}
@Override
public long getItemId(int position) {
return position < mNumColumns ? 0 : position - mNumColumns;
}
//返回显示的View的类型,这儿主要有两种:一种是显示图片的ImageView,另一种是顶部空行的显示view,故返回2
@Override
public int getViewTypeCount() {
// Two types of views, the normal ImageView and the top row of empty views
return 2;
}
@Override
public int getItemViewType(int position) {
return (position < mNumColumns) ? 1 : 0;
}
@Override
public boolean hasStableIds() {
return true;
}
//重载的getView()方法
@Override
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup container) {
// 首先检查是不是顶行
if (position < mNumColumns) {
if (convertView == null) {
convertView = new View(mContext);
}
// 设置ActionBar空View的高度
convertView.setLayoutParams(new AbsListView.LayoutParams(
LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, mActionBarHeight));
return convertView;
}
// 下面处理主要的ImageView的显示
ImageView imageView;
if (convertView == null) { // 如果没有被回收,就实例化和初始化
imageView = new RecyclingImageView(mContext);
imageView.setScaleType(ImageView.ScaleType.CENTER_CROP);
imageView.setLayoutParams(mImageViewLayoutParams);
} else { // 否者重用convertView
imageView = (ImageView) convertView;
}
// 检验高度是否和计算的列宽匹配
if (imageView.getLayoutParams().height != mItemHeight) {
imageView.setLayoutParams(mImageViewLayoutParams);
}
// 异步加载图片
mImageFetcher.loadImage(Images.imageThumbUrls[position - mNumColumns], imageView);
return imageView;
}最终使用下面这行代码完成图片的异步加载,由于加载图片是耗时操作,所以一定不能在UI线程中加载图片。
mImageFetcher.loadImage(Images.imageThumbUrls[position - mNumColumns], imageView);接着创建了一个缓存参数对象,并设置了相应的属性,包括缓存目录和缓存大小。然后创建了ImageFetcher对象,主要用来关注于异步加载图片。
接下来分析onCreateView()方法:
public View onCreateView(
LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
//加载布局view
final View v = inflater.inflate(R.layout.image_grid_fragment, container, false);
//找到GridView对象
final GridView mGridView = (GridView) v.findViewById(R.id.gridView);
//设置适配器
mGridView.setAdapter(mAdapter);
//设置项点击事件
mGridView.setOnItemClickListener(this);
//设置滑动监听事件
mGridView.setOnScrollListener(new AbsListView.OnScrollListener() {
@Override
public void onScrollStateChanged(AbsListView absListView, int scrollState) {
// 当滑动的时候暂停加载,以使滑动更流畅
if (scrollState == AbsListView.OnScrollListener.SCROLL_STATE_FLING) {
if (!Utils.hasHoneycomb()) {
mImageFetcher.setPauseWork(true);
}
} else {
mImageFetcher.setPauseWork(false);
}
}上面完成了加载网格布局对象,注册适配器,并设置了监听器。
下面看看其他几个生命周期中的任务:
public void onResume() {
super.onResume();
mImageFetcher.setExitTasksEarly(false);
mAdapter.notifyDataSetChanged();
}
public void onPause() {
super.onPause();
mImageFetcher.setPauseWork(false);
mImageFetcher.setExitTasksEarly(true);
mImageFetcher.flushCache();
}
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
mImageFetcher.closeCache();
}上面处理的主要是伴随生命周期有关的资源的暂停和释放。
3.2 util包
3.2.1 分析 AsyncTask.java类
AsyncTask类是对https://android.googlesource.com/platform/frameworks/base/+/jb-release/core/java/android/os/AsyncTask.java的一个修改类。
首先它持有一个ThreadFactory类的引用,具体实现:
private static final ThreadFactory sThreadFactory = new ThreadFactory() {
private final AtomicInteger mCount = new AtomicInteger(1);
//实际就是开辟了一个新的线程
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
return new Thread(r, "AsyncTask #" + mCount.getAndIncrement());
}
};通过该工厂对象的工厂方法newThread(Runnable r)来创建线程,其返回一个线程对象。线程Thread类的构造方法的第二个参数代表线程名字。
下面是一个Runnable类型的队列, 并且限制了大小为10。
private static final BlockingQueue<Runnable> sPoolWorkQueue =
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(10);下面是一个Executor对象的引用,用来执行具体的任务
public static final Executor THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR
= new ThreadPoolExecutor(CORE_POOL_SIZE, MAXIMUM_POOL_SIZE, KEEP_ALIVE,
TimeUnit.SECONDS, sPoolWorkQueue, sThreadFactory,
new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy());可以看出它的构造方法含有7个参数。它们分别是核心池的大小,池中线程的最大数量,池中线程保持活跃状态的数量,时间单元以秒计 ,活跃线程队列,线程工厂对象,以及一个策略对象。它们中的一些在一开始就被初始化了。如下:
private static final int CORE_POOL_SIZE = 5;
private static final int MAXIMUM_POOL_SIZE = 128;
private static final int KEEP_ALIVE = 1;接下来就是其他用途的Excutor对象,以及一些对象和状态变量的初始化,其中包括一个Handler,如下:
public static final Executor SERIAL_EXECUTOR = Utils.hasHoneycomb() ? new SerialExecutor() :
Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(sThreadFactory);
public static final Executor DUAL_THREAD_EXECUTOR =
Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2, sThreadFactory);
private static final int MESSAGE_POST_RESULT = 0x1;
private static final int MESSAGE_POST_PROGRESS = 0x2;
private static final InternalHandler sHandler = new InternalHandler();
private static volatile Executor sDefaultExecutor = SERIAL_EXECUTOR;
private final WorkerRunnable<Params, Result> mWorker;
private final FutureTask<Result> mFuture;
private volatile Status mStatus = Status.PENDING;
private final AtomicBoolean mCancelled = new AtomicBoolean();
private final AtomicBoolean mTaskInvoked = new AtomicBoolean();该类中还包括了一个SerialExecutor子类,可以从上面的代码中看到针对版本问题的。一个内部InternalHandler类,其继承自Handler类,来看看它都做了什么:
private static class InternalHandler extends Handler {
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "RawUseOfParameterizedType"})
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
AsyncTaskResult result = (AsyncTaskResult) msg.obj;
switch (msg.what) {
case MESSAGE_POST_RESULT:
// There is only one result
result.mTask.finish(result.mData[0]);
break;
case MESSAGE_POST_PROGRESS:
result.mTask.onProgressUpdate(result.mData);
break;
}
}
}InternalHandler类的实例化工作,在前面的代码中已经看到。下面看看是何处发送了激活Handler的消息的呢?有两处:
其一
protected final void publishProgress(Progress... values) {
if (!isCancelled()) {
sHandler.obtainMessage(MESSAGE_POST_PROGRESS,
new AsyncTaskResult<Progress>(this, values)).sendToTarget();
}
}其二
private Result postResult(Result result) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Message message = sHandler.obtainMessage(MESSAGE_POST_RESULT,
new AsyncTaskResult<Result>(this, result));
message.sendToTarget();
return result;
}一个是publishProgress()一个是postResult(),两个方法的功能显而易见,都构建了一个Message消息对象,并调用了sendToTarget(),发送出去,激活handler及其他操作。
从这儿可以看出,实际上可以根据需求来定义自己的AsyncTask类(不是指继承自系统的AsyncTask,而是自己来重新构造一个这样的类)。同时如果要在异步线程中执行长时间的操作,上面的类是不满足要求的,这是就需要自己定义类来实现,可以参考java.util.concurrent包中的一些API,比如这些类:
java.util.concurrent.Executor
java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor
java.util.concurrent.FutureTask
其实这些类在上面也用到。
总结起来AsyncTask实际上就是结合线程池技术,来完成异步任务,并封装了Handler,使得感觉好像跨越了异步线程,而直接可以修改UI界面。其实不能在子线程中修改UI界面是始终保持的,这儿只不过将这部分工作封装了起来。
3.2.2 DiskLruCache.java类
明白该类首先要明白LRU是什么。LRU(Leasted Recently Used ) “最近最少使用”的意思。而LRU缓存也就使用了这样一种思想,LRU缓存把最近最少使用的数据移除,让给最新读取的数据。而往往最常读取的,也就是使用次数最多的。所以利用LRU缓存可以提高系统的性能。要实现LRU,就要用到一个LinkedHashMap。LinkedHashMap有什么特性呢?具体的可以参考JDK来了解。这儿简要的说明一下,该类继承自HashMap,由Map提供的集合通常是杂乱无章的,而LinkedHashMap与HashMap不同的是,它维护了一个双重链接表。此链接表维护了迭代顺序。通常该迭代顺序是插入顺序。然而其也提供了特殊的构造方法来创建链接哈希映射,可以按照访问顺序来排序。该构造方法API如下:
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity,
float loadFactor,
boolean accessOrder)构造一个带指定初始容量、加载因子和排序模式的空 LinkedHashMap 实例。
参数:
initialCapacity - 初始容量
loadFactor - 加载因子
accessOrder - 排序模式 - 对于访问顺序,为 true;对于插入顺序,则为 false
抛出:
IllegalArgumentException - 如果初始容量为负或者加载因子为非正
按照访问顺序来排序不正是LRU想要的结果吗!这种映射很适合构建 LRU 缓存。下面来详细看一下该类的具体实现:
static final String JOURNAL_FILE = "journal";
static final String JOURNAL_FILE_TMP = "journal.tmp";
static final String MAGIC = "libcore.io.DiskLruCache";
static final String VERSION_1 = "1";
static final long ANY_SEQUENCE_NUMBER = -1;
private static final String CLEAN = "CLEAN";
private static final String DIRTY = "DIRTY";
private static final String REMOVE = "REMOVE";
private static final String READ = "READ";
private static final Charset UTF_8 = Charset.forName("UTF-8");
private static final int IO_BUFFER_SIZE = 8 * 1024;上面是定义的一些常量,比如备忘文件名、版本、字符集,还有输入输出流的缓存大小8k。
private final File directory;
private final File journalFile;
private final File journalFileTmp;
private final int appVersion;
private final long maxSize;
private final int valueCount;
private long size = 0;
private Writer journalWriter;
private final LinkedHashMap<String, Entry> lruEntries
= new LinkedHashMap<String, Entry>(0, 0.75f, true);
private int redundantOpCount;定义了一些File对象,当然还有最重要的LinkedHashMap对象,lruEntries实例。注意构造器的第三个参数是true,说明是访问顺序。
从Reader中读取,并以字符串形式返回。
public static String readFully(Reader reader) throws IOException {
try {
StringWriter writer = new StringWriter();
char[] buffer = new char[1024];
int count;
while ((count = reader.read(buffer)) != -1) {
writer.write(buffer, 0, count);
}
return writer.toString();
} finally {
reader.close();
}
}从InputStream输入流中读取ASCII行数据(但不包括”\r\n”或”\n”),以字符串形式返回:
public static String readAsciiLine(InputStream in) throws IOException {
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder(80);
while (true) {
int c = in.read();
if (c == -1) {
throw new EOFException();
} else if (c == '\n') {
break;
}
result.append((char) c);
}
int length = result.length();
if (length > 0 && result.charAt(length - 1) == '\r') {
result.setLength(length - 1);
}
return result.toString();
}删除目录中的内容:
public static void deleteContents(File dir) throws IOException {
File[] files = dir.listFiles();
if (files == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("not a directory: " + dir);
}
for (File file : files) {
if (file.isDirectory()) {
deleteContents(file);
}
if (!file.delete()) {
throw new IOException("failed to delete file: " + file);
}
}
}该缓存使用后台的一个单线程来驱动实例:
private final ExecutorService executorService = new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, 1,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()); 初始化DiskLruCaxhe缓存,注意私有。并不能直接使用构造器来实例化该类:
private DiskLruCache(File directory, int appVersion, int valueCount, long maxSize) {
this.directory = directory;
this.appVersion = appVersion;
this.journalFile = new File(directory, JOURNAL_FILE);
this.journalFileTmp = new File(directory, JOURNAL_FILE_TMP);
this.valueCount = valueCount;
this.maxSize = maxSize;
}打开缓存,如果不存在就创建:
public static DiskLruCache open(File directory, int appVersion, int valueCount, long maxSize)
throws IOException {
if (maxSize <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("maxSize <= 0");
}
if (valueCount <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("valueCount <= 0");
}
//DiskLruCache缓存
DiskLruCache cache = new DiskLruCache(directory, appVersion, valueCount, maxSize);
if (cache.journalFile.exists()) {
try {
cache.readJournal();
cache.processJournal();
cache.journalWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(cache.journalFile, true),
IO_BUFFER_SIZE);
return cache;
} catch (IOException journalIsCorrupt) {
// System.logW("DiskLruCache " + directory + " is corrupt: "
// + journalIsCorrupt.getMessage() + ", removing");
cache.delete();
}
}
// create a new empty cache
directory.mkdirs();
cache = new DiskLruCache(directory, appVersion, valueCount, maxSize);
cache.rebuildJournal();
return cache;
}
读取备忘文件夹:
private void readJournal() throws IOException {
InputStream in = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(journalFile), IO_BUFFER_SIZE);
try {
String magic = readAsciiLine(in);
String version = readAsciiLine(in);
String appVersionString = readAsciiLine(in);
String valueCountString = readAsciiLine(in);
String blank = readAsciiLine(in);
if (!MAGIC.equals(magic)
|| !VERSION_1.equals(version)
|| !Integer.toString(appVersion).equals(appVersionString)
|| !Integer.toString(valueCount).equals(valueCountString)
|| !"".equals(blank)) {
throw new IOException("unexpected journal header: ["
+ magic + ", " + version + ", " + valueCountString + ", " + blank + "]");
}
while (true) {
try {
readJournalLine(readAsciiLine(in));
} catch (EOFException endOfJournal) {
break;
}
}
} finally {
closeQuietly(in);
}
}
读取备忘行:
private void readJournalLine(String line) throws IOException {
String[] parts = line.split(" ");
if (parts.length < 2) {
throw new IOException("unexpected journal line: " + line);
}
String key = parts[1];
if (parts[0].equals(REMOVE) && parts.length == 2) {
lruEntries.remove(key);
return;
}
Entry entry = lruEntries.get(key);
if (entry == null) {
entry = new Entry(key);
lruEntries.put(key, entry);
}
if (parts[0].equals(CLEAN) && parts.length == 2 + valueCount) {
entry.readable = true;
entry.currentEditor = null;
entry.setLengths(copyOfRange(parts, 2, parts.length));
} else if (parts[0].equals(DIRTY) && parts.length == 2) {
entry.currentEditor = new Editor(entry);
} else if (parts[0].equals(READ) && parts.length == 2) {
// this work was already done by calling lruEntries.get()
} else {
throw new IOException("unexpected journal line: " + line);
}
}上面两种方法,与前面的两种写的形式相对应。
对备忘目录进行处理:
private void processJournal() throws IOException {
deleteIfExists(journalFileTmp);
for (Iterator<Entry> i = lruEntries.values().iterator(); i.hasNext(); ) {
Entry entry = i.next();
if (entry.currentEditor == null) {
for (int t = 0; t < valueCount; t++) {
size += entry.lengths[t];
}
} else {
entry.currentEditor = null;
for (int t = 0; t < valueCount; t++) {
deleteIfExists(entry.getCleanFile(t));
deleteIfExists(entry.getDirtyFile(t));
}
i.remove();
}
}
}计算初始大小,垃圾收部分缓存,以及一些脏数据。
private synchronized void rebuildJournal() throws IOException {
if (journalWriter != null) {
journalWriter.close();
}
Writer writer = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(journalFileTmp), IO_BUFFER_SIZE);
writer.write(MAGIC);
writer.write("\n");
writer.write(VERSION_1);
writer.write("\n");
writer.write(Integer.toString(appVersion));
writer.write("\n");
writer.write(Integer.toString(valueCount));
writer.write("\n");
writer.write("\n");
for (Entry entry : lruEntries.values()) {
if (entry.currentEditor != null) {
writer.write(DIRTY + ' ' + entry.key + '\n');
} else {
writer.write(CLEAN + ' ' + entry.key + entry.getLengths() + '\n');
}
}
writer.close();
journalFileTmp.renameTo(journalFile);
journalWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(journalFile, true), IO_BUFFER_SIZE);
}构建一个新的备忘录,代替当前存在的备忘文件。
public synchronized Snapshot get(String key) throws IOException {
checkNotClosed();
validateKey(key);
Entry entry = lruEntries.get(key);
if (entry == null) {
return null;
}
if (!entry.readable) {
return null;
}
InputStream[] ins = new InputStream[valueCount];
try {
for (int i = 0; i < valueCount; i++) {
ins[i] = new FileInputStream(entry.getCleanFile(i));
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// 如果手动删除了,就返回null
return null;
}
redundantOpCount++;
journalWriter.append(READ + ' ' + key + '\n');
if (journalRebuildRequired()) {
executorService.submit(cleanupCallable);
}
return new Snapshot(key, entry.sequenceNumber, ins);
}根据键得到Snapshot数据快照对象。
public synchronized boolean remove(String key) throws IOException {
checkNotClosed();
validateKey(key);
Entry entry = lruEntries.get(key);
if (entry == null || entry.currentEditor != null) {
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < valueCount; i++) {
File file = entry.getCleanFile(i);
if (!file.delete()) {
throw new IOException("failed to delete " + file);
}
size -= entry.lengths[i];
entry.lengths[i] = 0;
}
redundantOpCount++;
journalWriter.append(REMOVE + ' ' + key + '\n');
lruEntries.remove(key);
if (journalRebuildRequired()) {
executorService.submit(cleanupCallable);
}
return true;
}根据键移除实例。
下面是一个entries实例的数据快照:
public final class Snapshot implements Closeable {
private final String key;
private final long sequenceNumber;
private final InputStream[] ins;
private Snapshot(String key, long sequenceNumber, InputStream[] ins) {
this.key = key;
this.sequenceNumber = sequenceNumber;
this.ins = ins;
}
public Editor edit() throws IOException {
return DiskLruCache.this.edit(key, sequenceNumber);
}
/**
* 返回为缓存的流
*/
public InputStream getInputStream(int index) {
return ins[index];
}
/**
* 返回index代表的String值
*/
public String getString(int index) throws IOException {
return inputStreamToString(getInputStream(index));
}
@Override public void close() {
for (InputStream in : ins) {
closeQuietly(in);
}
}
}上面就是该类的一些主要实现。总结:
其实该类中有很多值得学习的地方。比如文件读取,缓存机制等。LRU缓存机制的具体实现是应该着重关注的。
3.2.3 ImageCache.java类
图片缓存类,包括内存缓存和Disk缓存,以及对缓存的一些控制。下面看具体实现:
private static final String TAG = "ImageCache";
// 默认的内存缓存大小
private static final int DEFAULT_MEM_CACHE_SIZE = 1024 * 5; // 5k
// 默认的disk缓存大小
private static final int DEFAULT_DISK_CACHE_SIZE = 1024 * 1024 * 10; // 10MB
// 缓存图片到Disk时的压缩格式
private static final CompressFormat DEFAULT_COMPRESS_FORMAT = CompressFormat.JPEG;
private static final int DEFAULT_COMPRESS_QUALITY = 70;
private static final int DISK_CACHE_INDEX = 0;
// 常量,用来容易的控制各种缓存的开关
private static final boolean DEFAULT_MEM_CACHE_ENABLED = true;
private static final boolean DEFAULT_DISK_CACHE_ENABLED = true;
private static final boolean DEFAULT_INIT_DISK_CACHE_ON_CREATE = false;
private DiskLruCache mDiskLruCache;
private LruCache<String, BitmapDrawable> mMemoryCache;
private ImageCacheParams mCacheParams;
private final Object mDiskCacheLock = new Object();
private boolean mDiskCacheStarting = true;
private Set<SoftReference<Bitmap>> mReusableBitmaps;这儿声明类一些该类需要使用的状态变量和引用。注意该类中使用了两种Lru缓存,一种在Disk磁盘上DiskLruCache类型的mDiskLruCache,一个在内存里 LruCache类型的mMemoryCache,以及一个若引用对象。 默认的内存缓存大小是5K,默认的Disk缓存是10MB。private final Object mDiskCacheLock = new Object();作为同步锁的监视对象。图片默认的压缩格式JPEG。
其构造方法如下,同样它并没有将构造方法暴露给其他用户,
private ImageCache(ImageCacheParams cacheParams) {
init(cacheParams);
}而是通过getInstance()方法来获得实例。那是因为IamgeCache的构造不仅与自身有关,还与Fragment有关。即这样构造实例是有条件的构造实例,这正是工厂方法的好处之一(不熟悉工厂方法的,可以参考设计模式中的工厂方法)。
public static ImageCache getInstance(
FragmentManager fragmentManager, ImageCacheParams cacheParams) {
// 找到或创建以个非UI线程的RetainFragment实例
final RetainFragment mRetainFragment = findOrCreateRetainFragment(fragmentManager);
ImageCache imageCache = (ImageCache) mRetainFragment.getObject();
if (imageCache == null) {
imageCache = new ImageCache(cacheParams);
mRetainFragment.setObject(imageCache);
}
return imageCache;
}注意这儿使用的是单例模式,只有当IamgeCache不存在时,才会创建。
看下面这段初始化代码:
private void init(ImageCacheParams cacheParams) {
mCacheParams = cacheParams;
// 开始内存缓存
if (mCacheParams.memoryCacheEnabled) {
if (BuildConfig.DEBUG) {
Log.d(TAG, "Memory cache created (size = " + mCacheParams.memCacheSize + ")");
}
if (Utils.hasHoneycomb()) {
mReusableBitmaps =
Collections.synchronizedSet(new HashSet<SoftReference<Bitmap>>());
}
mMemoryCache = new LruCache<String, BitmapDrawable>(mCacheParams.memCacheSize) {
//通知移除缓存实例,不再使用
@Override
protected void entryRemoved(boolean evicted, String key,
BitmapDrawable oldValue, BitmapDrawable newValue) {
if (RecyclingBitmapDrawable.class.isInstance(oldValue)) {
((RecyclingBitmapDrawable) oldValue).setIsCached(false);
} else {
if (Utils.hasHoneycomb()) {
mReusableBitmaps.add(new SoftReference<Bitmap>(oldValue.getBitmap()));
}
}
}
@Override
protected int sizeOf(String key, BitmapDrawable value) {
final int bitmapSize = getBitmapSize(value) / 1024;
return bitmapSize == 0 ? 1 : bitmapSize;
}
};
}首先检查内存缓存是否可用。如果可用,在检查是否在Honeycomb版本以上,如果是则创建一个可重用的set集合。然后在内存中创建一个LRU机制的缓存。由于IamgeCache默认并不初始化一个Disk缓存,因此提供了initDiskCache()方法。
public void initDiskCache() {
// 开始Disk缓存
synchronized (mDiskCacheLock) {
if (mDiskLruCache == null || mDiskLruCache.isClosed()) {
File diskCacheDir = mCacheParams.diskCacheDir;
if (mCacheParams.diskCacheEnabled && diskCacheDir != null) {
if (!diskCacheDir.exists()) {
diskCacheDir.mkdirs();
}
if (getUsableSpace(diskCacheDir) > mCacheParams.diskCacheSize) {
try {
mDiskLruCache = DiskLruCache.open(
diskCacheDir, 1, 1, mCacheParams.diskCacheSize);
if (BuildConfig.DEBUG) {
Log.d(TAG, "Disk cache initialized");
}
} catch (final IOException e) {
mCacheParams.diskCacheDir = null;
Log.e(TAG, "initDiskCache - " + e);
}
}
}
}
mDiskCacheStarting = false;
mDiskCacheLock.notifyAll();
}
}下面这个方法将图片添加到内存缓存区和磁盘缓存区:
public void addBitmapToCache(String data, BitmapDrawable value) {
if (data == null || value == null) {
return;
}
// 添加内存缓存
if (mMemoryCache != null) {
if (RecyclingBitmapDrawable.class.isInstance(value)) {
//移除回收实例
((RecyclingBitmapDrawable) value).setIsCached(true);
}
mMemoryCache.put(data, value);
}
synchronized (mDiskCacheLock) {
// 添加到Disk缓存
if (mDiskLruCache != null) {
final String key = hashKeyForDisk(data);
OutputStream out = null;
try {
DiskLruCache.Snapshot snapshot = mDiskLruCache.get(key);
if (snapshot == null) {
final DiskLruCache.Editor editor = mDiskLruCache.edit(key);
if (editor != null) {
out = editor.newOutputStream(DISK_CACHE_INDEX);
value.getBitmap().compress(
mCacheParams.compressFormat, mCacheParams.compressQuality, out);
editor.commit();
out.close();
}
} else {
snapshot.getInputStream(DISK_CACHE_INDEX).close();
}
} catch (final IOException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "addBitmapToCache - " + e);
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e(TAG, "addBitmapToCache - " + e);
} finally {
try {
if (out != null) {
out.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {}
}
}
}
}与添加相对应的是获取,如下:
从内存中获取:
public BitmapDrawable getBitmapFromMemCache(String data) {
BitmapDrawable memValue = null;
if (mMemoryCache != null) {
memValue = mMemoryCache.get(data);
}
if (BuildConfig.DEBUG && memValue != null) {
Log.d(TAG, "Memory cache hit");
}
return memValue;
}从磁盘中获取:
public Bitmap getBitmapFromDiskCache(String data) {
final String key = hashKeyForDisk(data);
Bitmap bitmap = null;
synchronized (mDiskCacheLock) {
while (mDiskCacheStarting) {
try {
mDiskCacheLock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {}
}
if (mDiskLruCache != null) {
InputStream inputStream = null;
try {
final DiskLruCache.Snapshot snapshot = mDiskLruCache.get(key);
if (snapshot != null) {
if (BuildConfig.DEBUG) {
Log.d(TAG, "Disk cache hit");
}
inputStream = snapshot.getInputStream(DISK_CACHE_INDEX);
if (inputStream != null) {
FileDescriptor fd = ((FileInputStream) inputStream).getFD();
// 解码图片
bitmap = ImageResizer.decodeSampledBitmapFromDescriptor(
fd, Integer.MAX_VALUE, Integer.MAX_VALUE, this);
}
}
} catch (final IOException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "getBitmapFromDiskCache - " + e);
} finally {
try {
if (inputStream != null) {
inputStream.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {}
}
}
return bitmap;
}
}
通过对该demo的学习,应该很好地学习到:
1. 如何去自定义异步任务,从demo中可以学到如何来定制满足项目需求的AsyncTask的技巧。
2. 缓存机制,包括Lru、使用LinkedHashMap实现Lru机制等
3. 异步加载图片。有许多的第三方库具有加载图片的功能,但在具体项目中,也许只需要这样一个功能,如果将整个第三方库都加载进来,这是不和理的。会导致应用占用的内存增大,影响用户体验,也许用户在查看内存占用情况时,发现该应用占用的内存很大,显然会毫不犹豫的先卸载它。
4. 要注意资源的释放问题。
5. 文件读取,流的控制。
完整的demo可以看:http://github.com/Luise-li






















 1266
1266

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








