Largest Rectangle in a Histogram
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |
| Total Submissions: 14841 | Accepted: 4773 |
Description
A histogram is a polygon composed of a sequence of rectangles aligned at a common base line. The rectangles have equal widths but may have different heights. For example, the figure on the left shows the histogram that consists of rectangles with the heights 2, 1, 4, 5, 1, 3, 3, measured in units where 1 is the width of the rectangles:
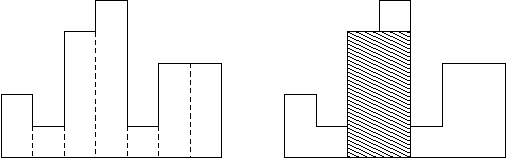
Usually, histograms are used to represent discrete distributions, e.g., the frequencies of characters in texts. Note that the order of the rectangles, i.e., their heights, is important. Calculate the area of the largest rectangle in a histogram that is aligned at the common base line, too. The figure on the right shows the largest aligned rectangle for the depicted histogram.

Usually, histograms are used to represent discrete distributions, e.g., the frequencies of characters in texts. Note that the order of the rectangles, i.e., their heights, is important. Calculate the area of the largest rectangle in a histogram that is aligned at the common base line, too. The figure on the right shows the largest aligned rectangle for the depicted histogram.
Input
The input contains several test cases. Each test case describes a histogram and starts with an integer
n, denoting the number of rectangles it is composed of. You may assume that
1<=n<=100000. Then follow
n integers
h1,...,hn, where
0<=hi<=1000000000. These numbers denote the heights of the rectangles of the histogram in left-to-right order. The width of each rectangle is
1. A zero follows the input for the last test case.
Output
For each test case output on a single line the area of the largest rectangle in the specified histogram. Remember that this rectangle must be aligned at the common base line.
Sample Input
7 2 1 4 5 1 3 3 4 1000 1000 1000 1000 0
Sample Output
8 4000
Hint
Huge input, scanf is recommended.
这道题是很显然对单调栈的应用,第一次写,先来练练手。
这道题用一个递增的栈来维护坐标,栈顶元素(坐标)表示从该坐标向右一直到目前正在决策入栈的位置,高度均为a[st[top]],这样很显然如果需要入栈的元素大于等于a[st[top]],那么就直接加入因为此时原栈顶仍然可以向右扩展,下标不变,这时只要维护新的栈顶下标,显然就是当前决策位置i;如果需要入栈的元素小于a[st[top]],这时候原栈顶已无法向右扩展,那就是直接计算面积左边界为st[top],右边界为i-1,高为a[st[top]],因此面积为(i-st[top])*a[st[top]],然后将该元素出栈,要知道栈中元素是递增的,因此其余栈中元素向右扩展的位置不变(出栈仅为减少元素个数,降低复杂度,实际上这块区域还是在的),这时候有了新的栈顶,重复上述步骤直到栈顶小于需要入栈的元素,这里注意一下,这时候入栈元素的下标不应该是i了,因为之前有出栈了一些下标,这些下标对应的矩形的高>=入栈的元素对应的矩形的高,因此这时候入栈元素的下标应该为最后一次弹出栈的元素下标,为了正确对应高,a[i]必须用a[此时的id]覆盖了。
注意a[n]=-1,这个是为了清空栈,计算最后的面积。
代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#define ll long long
#define Maxn 100010
using namespace std;
int a[Maxn],st[Maxn];
int main()
{
int n;
while(scanf("%d",&n),n){
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
scanf("%d",a+i);
a[n]=-1;
int top=-1;
ll ans,maxx=0;
for(int i=0;i<=n;i++){
int id=i;
while(top!=-1&&a[st[top]]>a[i]){
id=st[top];
ans=(ll)(i-st[top])*a[st[top--]];
maxx=max(maxx,ans);
}
st[++top]=id;
a[id]=a[i];
}
printf("%lld\n",maxx);
}
return 0;
}






















 304
304

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








