Collection接口:
public interface Collection<E> extends Iterable<E>超级接口:java.lang包下的Iterable<T>,实现这个接口允许对象成为"foreach"语句的目标,实现iterator方法,可以返回一个T类型的迭代器 基本作用:Collection表示一组对象,用于存储有序或则无序数据,对数据进行操作。 子类:LinkedList,ArrayList,Stack,TreeSet等
方法摘要:
boolean add(E e) 确保此 collection 包含指定的元素(可选操作)。 |
boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c)将指定 collection 中的所有元素都添加到此 collection 中(可选操作)。 |
| void clear() 移除此 collection 中的所有元素(可选操作)。 |
boolean contains(Object o)如果此 collection 包含指定的元素,则返回 true。 |
boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c) 如果此 collection 包含指定 collection 中的所有元素,则返回 true。 |
boolean equals(Object o) 比较此 collection 与指定对象是否相等。 |
int hashCode() 返回此 collection 的哈希码值。 |
boolean isEmpty() 如果此 collection 不包含元素,则返回 true。 |
Iterator<E> iterator() 返回在此 collection 的元素上进行迭代的迭代器。 |
boolean remove(Object o) 从此 collection 中移除指定元素的单个实例,如果存在的话(可选操作)。 |
boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) 移除此 collection 中那些也包含在指定 collection 中的所有元素(可选操作)。 |
boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) 仅保留此 collection 中那些也包含在指定 collection 的元素(可选操作)。 |
int size() 返回此 collection 中的元素数。 |
Object[] toArray() 返回包含此 collection 中所有元素的数组。 |
| <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) 返回包含此 collection 中所有元素的数组;返回数组的运行时类型与指定数组的运行时类型相同。 |
因为这个是一个接口,我们直接尝试这用一个类去实现这个接口,因为里面要传一个范型,我们暂时用String代替。
public class ICollection<String> implements Collection<String>
我们这边先参考使用了Collection接口的ArrayList来试着实现这个类,首先我们需要一个初始化的方法:
/**
* 当初始化一个当前对象时,初始化一个空的elementData
* (arrayList,164行)
*/
public ICollection(){
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} /**
* 一个可释放内存大小的Object数组
* (arrayList,134行)
*/
transient Object[] elementData;
我们知道,数组是一个线性表结构,也是一个强引用类型,在初始化的时候必须分配内存,并且不会被JVM强行GC掉,使用transient可以将内存大小动态回收掉,感觉是和static关键字正好相反的作用。
初始化时候的数组是另外一个数组,并不是这个elementData:
/** * 初始化一个默认为空的数组 * (arrayList,126行) */ private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA= {};
这里这样定义的好处就是使用了final关键字保证初始化时候的数组一定是空的,并不会发生任何的改变。
ArrayList里面还定义了一个变量,就是我们ArrayList能够存储数据最大的大小:
/** * 因为有些虚拟机会将数据放到数组的头部去,为了防止数据溢出,所以数组的最大大小为Integer减少8个 * (arrayList,244行) */ private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
这个Integer.MAX_VALUE的大小为2的31次方减1,int占4个字节,32位,减8是为了减去数据的头部有可能被JVM占用的空间。
还有三个变量就不多说了:
/** *默认数组elementData能够容纳的大小 *(arrayList,114行) */ private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;private int size;//数组的大小 private int modCount;//数组数据被修改的次数
我们按顺序来:
add方法:
/** * 添加一个元素 * true:元素添加成功 * false:元素添加失败 */ @Override public boolean add(String e) { ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); //确认容量大小 elementData[size++] = e; return true;}
我们要添加一个数据到elementData里面,首先要判断数组大小是否越界,并且动态的增加数组的大小,ArrayList里面是使用了ensureCapacityInternal方法实现的
/** * 确认elementData容量的大小 * (arrayList,222行) * @param minCapacity elementData容量大小的最小值 */ private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) { if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {//如果elementData大小为空 minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);//使容量大小为默认容量大小(DEFAULT_CAPACITY)和输入大小(minCapacity)最大值 }ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity); }
其实这个是为了更改默认的elementData的大小,当我们添加了一个元素进去,默认大小是10,直到你添加满10个,之后才会逐渐增加elementData的大小。当传入的参数minCapacity为15的时候,你默认的大小就为15了。
ensureExplicitCapacity是用来判断elementData的内容大小是否需要增大的:
/** * 判断elementData容量是否需要增大 * (arrayList,230行) * @param minCapacity elementData容量大小最小值 */ private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) { modCount++;//计算当前对象被修改的次数的,会在iterator当中返回回来,详见AbstractList,576行,暂时注释掉 // overflow-conscious code if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)//需求的最小值比当前容量大小大 grow(minCapacity);//增大容量 }
这个没什么好说的,当需求的最小值比当前容量大时,我们当然要增大当前的容量大小,下面说我们如何增大容量大小:
/**
* 增大elementData容量大小
* (arrayList,252行)
* @param minCapacity elementData容量大小最小值
*/
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);//新的容量大小增大一位
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)//新容量大小比最小大小小
newCapacity = minCapacity;//使其等于要求的最小大小
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)//判断容量大小是过大
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);//按照新容量大小生成一个新的拷贝对象
}
整体过程是这样的:当arrayList初始化后没有加入数据时,elementData大小为0,当加入1个数后,大小为10,直到加到11个时,oldCapacitiy=10,2进制为1010,newCapacity为 1010 + 0101 等于1111,即15,所以加到11个的时候ArrayList所占用的实际大小为15,虽然里面的size大小为11·。接下来就是判断新容量大小是否大于ArrayList能够容纳的最大大小,也就是2的32次方减1再减8
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) { if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow,内存溢出 throw new OutOfMemoryError(); return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : MAX_ARRAY_SIZE; }
addAll方法:
/** * 将指定collection当中的所有元素都添加到此collection当中 * true:添加成功 * false:添加失败 */ @Override public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends String> c) { Object[] a = c.toArray();//获取Collection当中的Object的数组 int numNew = a.length;//获取Object数组的大小 ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); //确定新数组大小不会越界 System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, size, numNew);//从elementData末尾添加a数组,添加a数组的起始位置为0,长度为numNew size += numNew; return numNew != 0;//添加的数组大小不能为0,为0表示添加失败 }
addAll方法主要就是先取出需要添加的Object数组a,然后判断添加过后的大小不会越界,最后,使用arrayCopy方法将数组添加到elementData数组的后面。
clear方法:
/** * 清除elementData当中的数据 * arrayList,553行 */ @Override public void clear() { modCount++;//计算数组数据更改的次数,暂时注释掉 //清除数据,让JVM执行GC操作 for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) elementData[i] = null; //设置elementData数组大小为0 size = 0; }
clear方法主要就是将所有elementData当中的数据全部置为null,让JVM执行GC操作
contains方法:
/** * 判断elementData里面是否有输入的Object对象 * */ @Override public boolean contains(Object o) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return indexOf(o) >=0; } //判断当前Object数组当中是否有该元素 (ArrayList,310行) public int indexOf(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) if (elementData[i]==null) return i; } else { for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) if (o.equals(elementData[i])) return i; } return -1; }
判断elementData当中是否有输入的Object对象时,首先要判断输入的对象是否为null,如果为null,先判断elementData当中是否有null元素存在;如果不为null,然后再使用equals判断当中的元素内容是否相等。
containsAll方法:
/** * arrayList当中并未实现该方法,可能是在AbstratList当中实现的,暂时不实现该方法 */ @Override public boolean containsAll(Collection<?> arg0) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return false; }
equals和hasCode方法是Object.class当中实现的内容,在java.lang包当中,后面讨论一下。
isEmpty方法:
/** * 判断数组大小是否为空 * arrayList,286行 */ @Override public boolean isEmpty() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return size == 0; }
判断element大小是否为0就行了
iterator方法:
/** * 暂时不太了解相关的内容,源码如下,有时间专门看一下 */ @Override public Iterator<String> iterator() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return new Itr(); } private class Itr implements Iterator<String> { int cursor; // index of next element to return int lastRet = -1; // index of last element returned; -1 if no such int expectedModCount = modCount; public boolean hasNext() { return cursor != size; } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public String next() { checkForComodification(); int i = cursor; if (i >= size) throw new NoSuchElementException(); Object[] elementData = ICollection.this.elementData; if (i >= elementData.length) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); cursor = i + 1; return (String) elementData[lastRet = i]; } public void remove() { if (lastRet < 0) throw new IllegalStateException(); checkForComodification(); try { ICollection.this.remove(lastRet); cursor = lastRet; lastRet = -1; expectedModCount = modCount; } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } } @Override @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super String> consumer) { Objects.requireNonNull(consumer); final int size = ICollection.this.size; int i = cursor; if (i >= size) { return; } final Object[] elementData = ICollection.this.elementData; if (i >= elementData.length) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } while (i != size && modCount == expectedModCount) { consumer.accept((String) elementData[i++]); } // update once at end of iteration to reduce heap write traffic cursor = i; lastRet = i - 1; checkForComodification(); } final void checkForComodification() { if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } }
remove方法:
/** * 移除elementData当中的数据 * arrayList,519行 * @param o 需要移除的内容对象 */ @Override public boolean remove(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) if (elementData[index] == null) { fastRemove(index); return true; } } else { for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) if (o.equals(elementData[index])) { fastRemove(index); return true; } } return false; }
跟contains方法有点类似,都是需要先判断对象是否为null,如果为null,先查找elementData当中的null进行移除;如果不为null,则使用equals判断是否相等,然后进行移除
fastRemove方法的实现如下:
/** * 在elementData数组当中移除一个元素 * @param index */ private void fastRemove(int index) { modCount++; int numMoved = size - index - 1; if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved);//将要移除的位置index后面的数据全部前移一位,替换前面的数据(最后一位为特殊位,需要清除掉) elementData[--size] = null; //将最后一位清除 }
因为数组实现的方式是一个线性表,要对中间的元素进行删除操作,必须要将删除数据后面的所有数据前移一位,并且将最后一位清除。
removeAll方法:
/** * 在elementData数组当中移除一个Collection * arrayList,688行 * @param c 需要移除的所有数据的集合 */ @Override public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) { Objects.requireNonNull(c);//判断c是否为空,为空会抛出NullPointerException异常 return batchRemove(c, false); }
retainAll方法:
/** * 相当于当前elementData和输入的Collection取交集,留下相同的部分 * arrayList,706行 * @param c 取交集的集合 */ @Override public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) { Objects.requireNonNull(c); return batchRemove(c, true); }
首先要判断要移除和留下的集合是否为null,然后进行操作,batchRemove方法如下:
/** * 对需要移除的数据进行处理 */ private boolean batchRemove(Collection<?> c, boolean complement) { final Object[] elementData = this.elementData;//把数据定义成final保证数据在遍历的过程此方法当中的elementData的地址不会发生任何的变化 int r = 0, w = 0; boolean modified = false; try { for (; r < size; r++) if (c.contains(elementData[r]) == complement) elementData[w++] = elementData[r];//如果complement为false,就相当于将elementData和c取补集,放入elementData当中; //如果complement为true,就相当于是取交集 } finally { // Preserve behavioral compatibility with AbstractCollection, // even if c.contains() throws. if (r != size) {//中途出现了异常,r为出错时elementData正在遍历的位置,w为遍历后结果存储的位置 System.arraycopy(elementData, r, elementData, w, size - r);//出错过后,将出错后没有遍历的数据直接添加到结果的后面输出出来 w += size - r; } if (w != size) {//如果输出结果跟原来的elementData不相同 // clear to let GC do its work for (int i = w; i < size; i++)//将遍历停止位置w后面没有用的数据空间GC掉 elementData[i] = null; modCount += size - w; size = w; modified = true; } } return modified; }
这一段的代码比较难懂,首先要把方法当中的elementData定义为final,主要还是为了使该动态变量在编译器里面是静态链接的,也就是地址是固定的,保证遍历的过程当中不会发生变化,然后就是判断输入的Collection当中的数据是否和elementData当中的相等,判断的结果是放在从elementData[0]开始到elementData[w]的位置,结束遍历判断的位置为r,最后将elementData[w]后面的数据清空掉,就是最终的结果了。
下面两个都没什么好说的:
size方法:
/** * 返回当前elementData的大小 */ @Override public int size() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return size; }
toArray方法:
/** * 返回当前elementData等长的一个数组副本 */ @Override public Object[] toArray() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size); }
toArrray泛型方法:
/** * 将elementData转化为对应泛型的数组副本 */ @Override public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) { if (a.length < size) // Make a new array of a's runtime type, but my contents: return (T[]) Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, a.getClass()); System.arraycopy(elementData, 0, a, 0, size); if (a.length > size) a[size] = null;// return a; }
当输入a的长度小于现在elementData的大小时,会将elementData转化为a类型的数组,长度不变;当a长度大于elementData的大小时,a[size] = null,确实没看懂(System.arraycopy和Arrays.copyof的区别等会也看一下)。
看了一下网上的翻译:
返回数组的运行时类型是指定数组的。如果列表中指定的数组能容纳,则在其中返回。否则,一个新的数组分配具有指定数组的运行时类型和此列表的大小。如果列表中指定的数组能容纳更加节省空间(即数组的元素比列表元素多),那么会将紧挨着collection尾部的元素设置为null。
如果是这样解释的话这段代码就没有任何的问题了。
下面我们对我们写出来的Icollection进行结果的测试:
首先有一个main函数:
public static void main(String args[]){ //生成一个自定义的ICollection对象 ICollection icollection = new ICollection(); testAdd(icollection); }
测试Add方法:
/** * 测试Add方法 * @param icollection */ public static void testAdd(ICollection icollection){ String a1 = "a1"; String a2 = "a2"; icollection.add(a1); icollection.add(a2); for(int i=0;i<icollection.size();i++){ System.out.println(String.format("elementData的第%d个元素是:%s", i,icollection.toArray()[i])); } }
结果为:
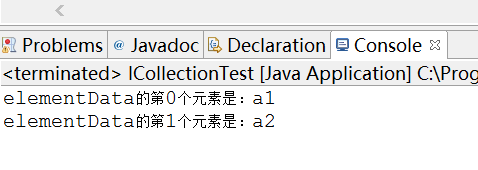
证明add,size和toArray方法都没有什么问题。
测试addAll方法:
/** * 测试addAll方法 * @param icollection */ public static void testAddAll(ICollection icollection){ String a1 = "a1"; String a2 = "a2"; String a3 = "a3"; //初始化一个Collection当中放两个元素 ICollection<String> tempCollection = new ICollection(); tempCollection.add(a1); tempCollection.add(a2); //输入的iCollection当中放一个元素 icollection.add(a3); //使用addAll方法 icollection.addAll(tempCollection); //打印输出结果 for(int i=0;i<icollection.size();i++){ System.out.println(String.format("iCollection当中的元素有:%s", icollection.toArray()[i])); } }
结果为:
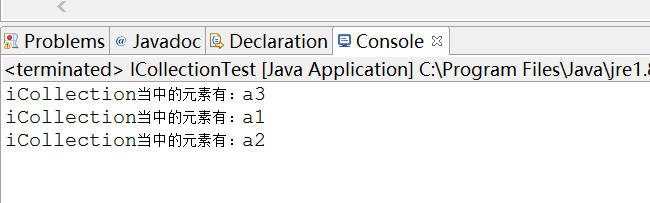
测试clear方法:
public static void testClear(ICollection icollection){ String a1 = "a1"; String a2 = "a2"; //添加两个元素 icollection.add("a1"); icollection.add("a2"); //打印当前内容: for(int i=0;i<icollection.size();i++){ System.out.println(String.format("iCollection当中的元素有:%s", icollection.toArray()[i])); } //清除数据 icollection.clear(); System.out.println("清除之后iCollection的大小为:"+ icollection.size()); }
结果为:
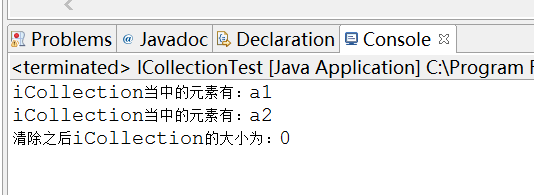
测试contains方法:
/** * 测试contains方法 */ public static void testContains(ICollection icollection){ String a1 = "a1"; String a2 = "a2"; String a3 = "a3"; //添加两个元素 icollection.add(a1); icollection.add(a2); System.out.println("icollection中是否含有a1:"+icollection.contains(a1)); System.out.println("icollection中是否含有a2:"+icollection.contains(a2)); System.out.println("icollection中是否含有a3:"+icollection.contains(a3)); }
结果为:
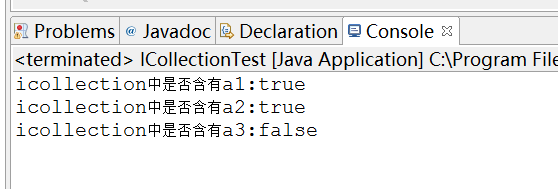
测试isEmpty方法:
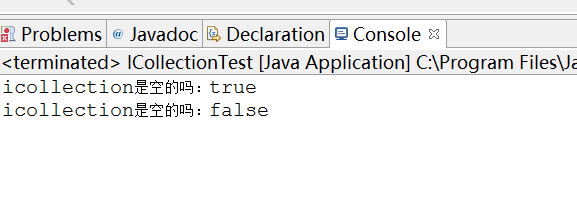
/** * 测试empty方法 * @param icollection */ public static void testEmpty(ICollection icollection){ System.out.println("icollection是空的吗:" + icollection.isEmpty()); icollection.add("a1"); System.out.println("icollection是空的吗:" + icollection.isEmpty()); }
结果为:
测试toArray方法:
/** * 测试toArray方法 */ public static void testToArray(ICollection icollection){ String a1 = "a1"; String a2 = "a2"; String a3 = "a3"; String a4 = "a4"; //添加2个元素 icollection.add(a1); icollection.add(a2); //调用toArray方法 System.out.println("toArray:" + icollection.toArray()); //打icollection当中的内容: for(int i=0;i<icollection.size();i++){ System.out.println(String.format("iCollection中的元素有:%s", icollection.toArray()[i])); } //创建一个中间tempCollection ICollection<String> tempCollection = new ICollection<String>(); tempCollection.add(a1); tempCollection.add(a2); tempCollection.add(a3); tempCollection.add(a4); //当icollection中的数组比tempCollection当中的小 Object[] tempArray = icollection.toArray(tempCollection.toArray()); //打印tempArray当中的内容: for(int i=0;i<tempArray.length;i++){ System.out.println(String.format("iCollection中的数组小:%s", tempArray[i])); } //清除tempCollection当中的数据 tempCollection.clear(); //向tempCollection当中添加一个数据 tempCollection.add(a1); //当icollection中的数组比tempCollection当中的大 tempArray = icollection.toArray(tempCollection.toArray()); //打印tempArray当中的内容: for(int i=0;i<tempArray.length;i++){ System.out.println(String.format("iCollection中的数组大:%s", tempArray[i])); } }
结果为:

这个先是icollection里放了a1,a2,tempCollection当中放了a1,a2,a3,a4,先icollection toArray tempCollection,然后是icollection中还是a1,a2,tempCollection当中放了a1,再toArray的结果。
萌新初学java,有什么写的不对的地方还请多指教,边工作边学这个也不容易,就这样了,谢谢大家的光临。






















 375
375











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








