**
何为沉浸式
**
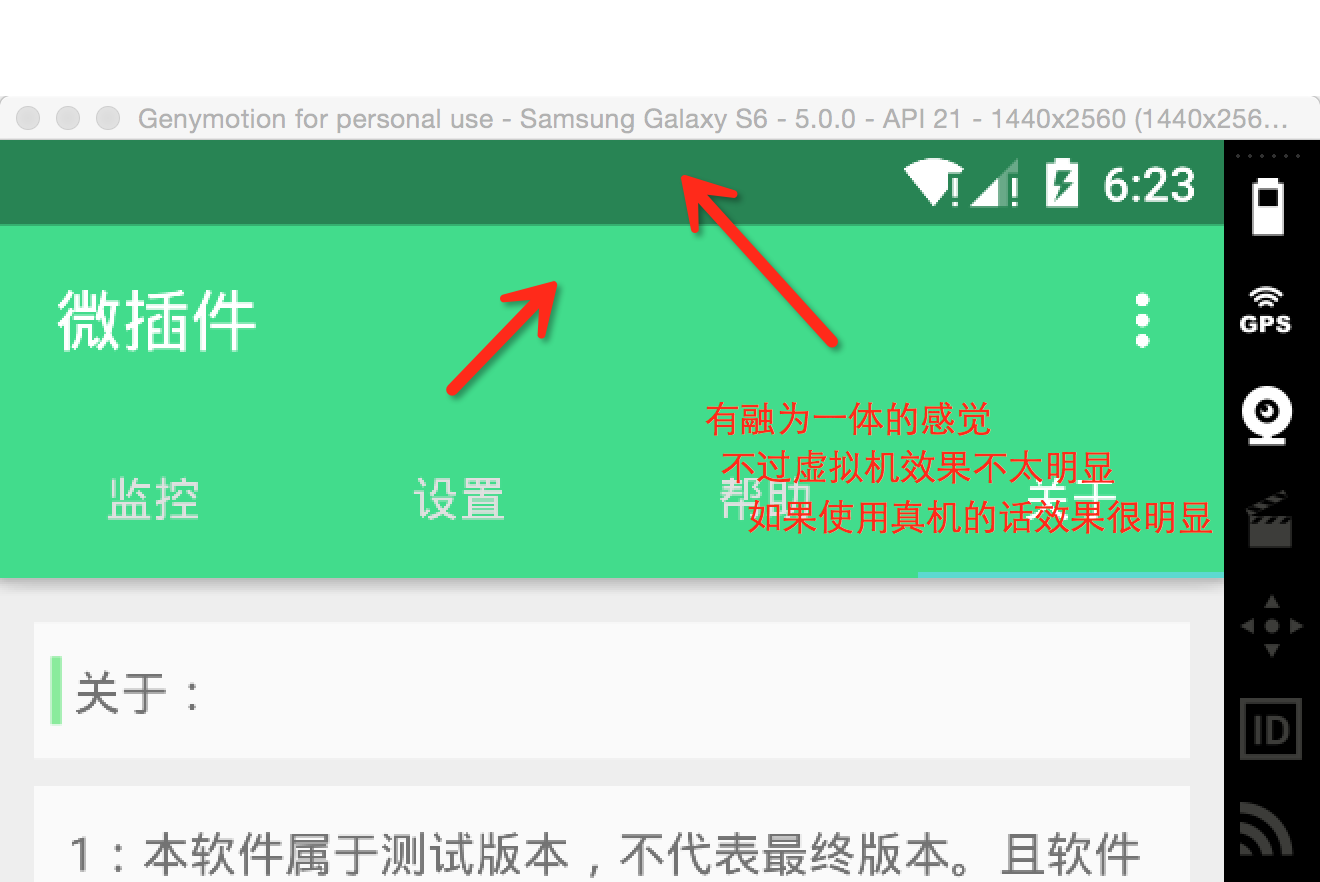
上图:
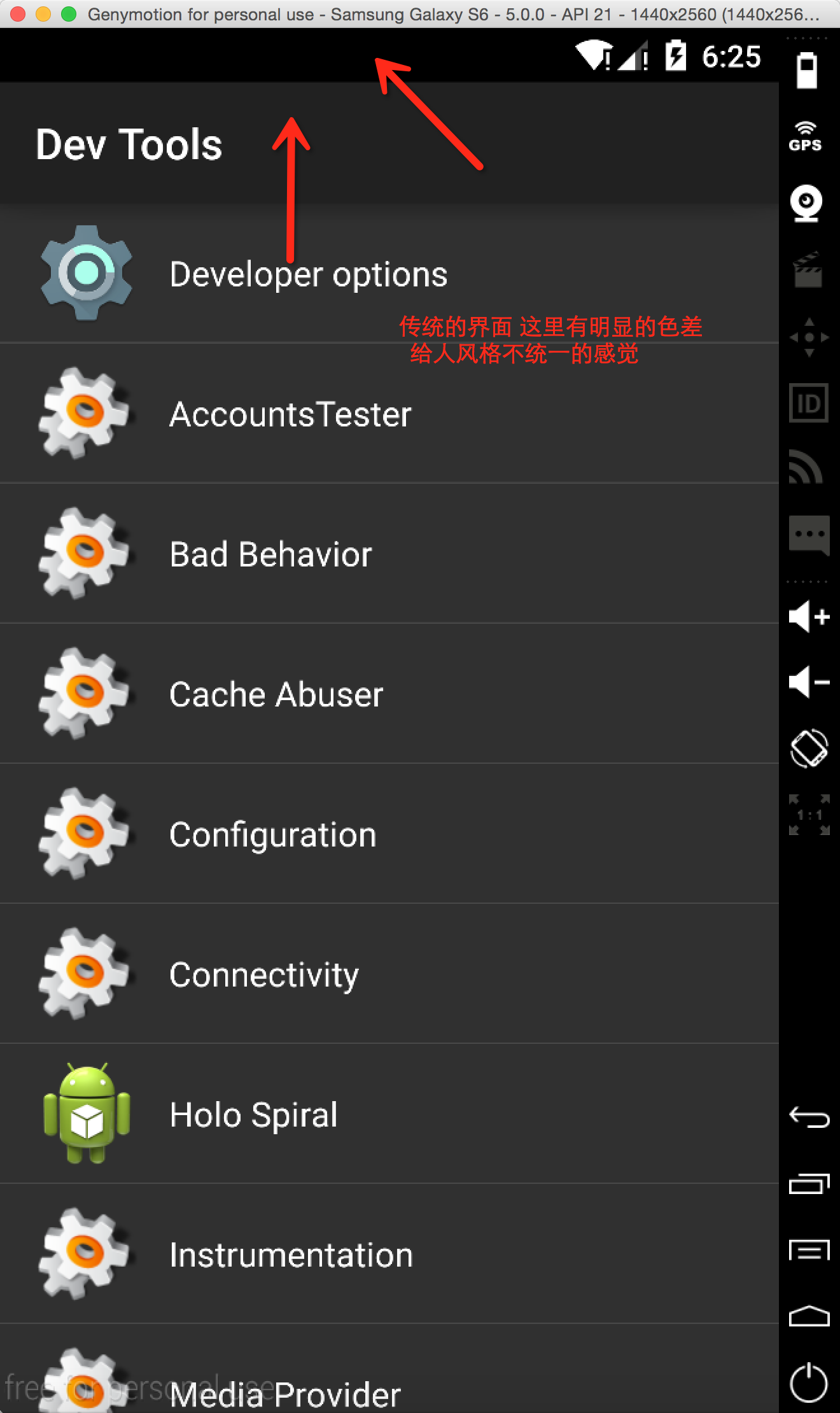
传统意义上的状态栏如下图:
当我们对界面要求非常苛刻(颜色要统一),我们就需要用沉浸式。值得注意的是,沉浸式状态栏只能用于4.4以上的设备。对于4.4一下的设备,我们并没有办法实现
我们先来看下git上关于该项目的使用方法。
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
// create our manager instance after the content view is set
SystemBarTintManager tintManager = new SystemBarTintManager(this);
// enable status bar tint
tintManager.setStatusBarTintEnabled(true);
// enable navigation bar tint
tintManager.setNavigationBarTintEnabled(true);
}我们首先获得了system bar tint manager,然后设置状态栏沉浸,最后一行代码还有关于导航栏的沉浸。不过这不重要。
如果你自己运行下demo你就会发现,这时候状态栏是透明了,但是,状态栏仅是透明色,并没有和主体颜色融为一体,所以,在设置状态栏沉浸的时候,你还需要设置下状态栏的颜色,如下:
// set a custom tint color for all system bars
tintManager.setTintColor(Color.parseColor("#99000FF"));
// set a custom navigation bar resource
tintManager.setNavigationBarTintResource(R.drawable.my_tint);
// set a custom status bar drawable
tintManager.setStatusBarTintDrawable(MyDrawable);不过我觉得,有些flag是针对4.4的,我们还是要加个if判断,比如笔者下面的代码(有些东西你直接忽略好了,这是我的工程代码)
@Override
protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
ActivityCollector.addActivity(this);
m_activityComponent = DaggerActivityComponent.builder()
.applicationComponent(((MPApplication) getApplication()).getApplicationComponent())
.activityModule(new ActivityModule(this)).build();
//针对4.4以上的设备设置沉浸式状态栏
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.KITKAT) {
getWindow().addFlags(FLAG_TRANSLUCENT_STATUS);
SystemBarTintManager systemBarTintManager = m_activityComponent
.getSystemBarTintManager();
systemBarTintManager.setStatusBarTintColor(getResources()
.getColor(R.color.colorPrimary));
systemBarTintManager.setStatusBarTintEnabled(true);
}
initPresenter();
m_iPresenter = obtainIPresenter();
}可以看到,我们首先设置了window的flag,表面我们要透明状态栏:
getWindow().addFlags(FLAG_TRANSLUCENT_STATUS);这里的window其实是一个phone window实例,具体的已经设计到activity如何加载到屏幕上了,具体的读者可以参考相关的源码分析书籍
然后我们构造了一个system bar tint manager
SystemBarTintManager systemBarTintManager = m_activityComponent.getSystemBarTintManager();这是我写的代码,读者不必在乎,具体的代码如下:
@Provides
@PerActivity
public SystemBarTintManager provideSystemBarTintManager() {
return new SystemBarTintManager(m_activity);
}我们切进构造函数看下
@TargetApi(19)
public SystemBarTintManager(Activity activity) {
//获得window对象,其实是PhoneWindow
Window win = activity.getWindow();
//获得decor
ViewGroup decorViewGroup = (ViewGroup) win.getDecorView();
//一定要是4.4以上的设备
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.KITKAT) {
// check theme attrs
// 查看属性是否含有透明状态栏 透明导航栏
int[] attrs = {android.R.attr.windowTranslucentStatus,
android.R.attr.windowTranslucentNavigation};
TypedArray a = activity.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs);
try {
mStatusBarAvailable = a.getBoolean(0, false);
mNavBarAvailable = a.getBoolean(1, false);
} finally {
a.recycle();
}
// check window flags
// 看下window是否设置了状态栏透明
// 看下导航是否设置了透明
WindowManager.LayoutParams winParams = win.getAttributes();
int bits = WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_TRANSLUCENT_STATUS;
if ((winParams.flags & bits) != 0) {
mStatusBarAvailable = true;
}
bits = WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_TRANSLUCENT_NAVIGATION;
if ((winParams.flags & bits) != 0) {
mNavBarAvailable = true;
}
}
//创建SystemBarConfig对象,我们一会儿看下有什么用处
mConfig = new SystemBarConfig(activity, mStatusBarAvailable, mNavBarAvailable);
// device might not have virtual navigation keys
// 注意 并不是所有的设备都有虚拟的导航键
// 所以这里还是要检查下
if (!mConfig.hasNavigtionBar()) {
mNavBarAvailable = false;
}
//开始安装用户需要的沉浸式导航,状态栏
if (mStatusBarAvailable) {
setupStatusBarView(activity, decorViewGroup);
}
if (mNavBarAvailable) {
setupNavBarView(activity, decorViewGroup);
}
}这里很多读者估计会很困惑什么事decor
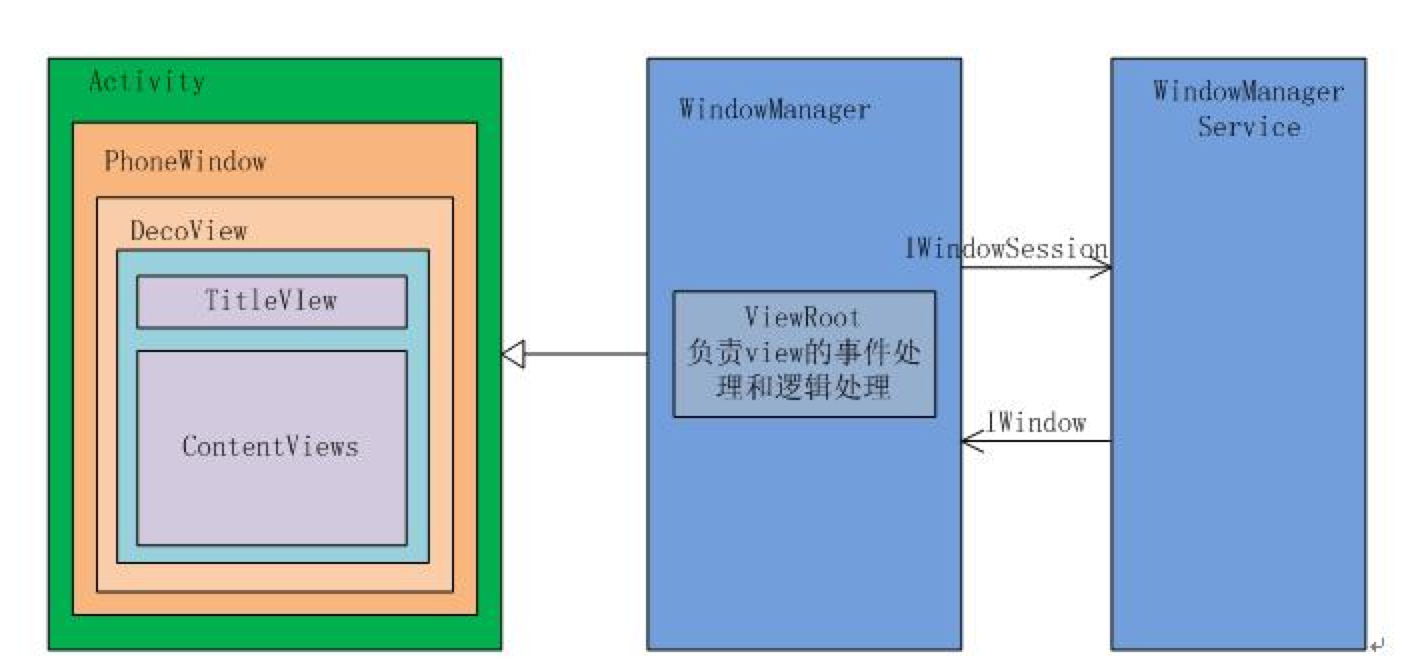
我引入一张图:
可以看到一个activity并不是很简单的,其中有包含一个PhoneWindow,而一个phone window里面有包含decor view,decor view其实是一个view group,它包含两个部分,一个是title view用于存放标题之类的内容,而content views 则是真正存放用户自定义的layout内容了。回想一下,我们在定义布局的时候,通常会使用:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:gravity="center"
android:background="@color/colorNormal"/>细想一下,我们的跟节点之外并无其它节点啊,为啥还要match_parent?现在看来,豁然开朗,不过这个参数只针对调用activity的setContentView有用哦!
//继续跟踪 看下 status bar 是如何安装的
private void setupStatusBarView(Context context, ViewGroup decorViewGroup) {
//创建了一个view
mStatusBarTintView = new View(context);
//设置下宽高 不过到这里 我们确实好像有必要看下SystemBarConfig是啥了
LayoutParams params = new LayoutParams(
LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, mConfig.getStatusBarHeight());
params.gravity = Gravity.TOP;
//看下导航栏是否存在 如果存在 并且 还不在底部 那就可能旋转了屏幕 出现在
//屏幕的右端 这时候就要设置下right margin
if (mNavBarAvailable && !mConfig.isNavigationAtBottom()) {
params.rightMargin = mConfig.getNavigationBarWidth();
}
//设置下布局参数
mStatusBarTintView.setLayoutParams(params);
//设置下背景颜色 其实这里是可以自定义的
mStatusBarTintView.setBackgroundColor(DEFAULT_TINT_COLOR);
//设置它为不可见
mStatusBarTintView.setVisibility(View.GONE);
//把他添加到decor中
decorViewGroup.addView(mStatusBarTintView);
}我们看下SystemBarConfig:
//为了方便读者阅读 我都贴出了所有的field
private static final String STATUS_BAR_HEIGHT_RES_NAME = "status_bar_height";
private static final String NAV_BAR_HEIGHT_RES_NAME = "navigation_bar_height";
private static final String
NAV_BAR_HEIGHT_LANDSCAPE_RES_NAME = "navigation_bar_height_landscape";
private static final String NAV_BAR_WIDTH_RES_NAME = "navigation_bar_width";
private static final String SHOW_NAV_BAR_RES_NAME = "config_showNavigationBar";
private final boolean mTranslucentStatusBar;
private final boolean mTranslucentNavBar;
private final int mStatusBarHeight;
private final int mActionBarHeight;
private final boolean mHasNavigationBar;
private final int mNavigationBarHeight;
private final int mNavigationBarWidth;
private final boolean mInPortrait;
private final float mSmallestWidthDp;
private SystemBarConfig(Activity activity,
boolean translucentStatusBar, boolean traslucentNavBar) {
Resources res = activity.getResources();
//获得现在屏幕的方向
mInPortrait = (res.getConfiguration().orientation == Configuration.ORIENTATION_PORTRAIT);
//获得下屏幕的最小dp值
mSmallestWidthDp = getSmallestWidthDp(activity);
//获得状态栏的高度
mStatusBarHeight = getInternalDimensionSize(res, STATUS_BAR_HEIGHT_RES_NAME);
//获得action bar的高度
mActionBarHeight = getActionBarHeight(activity);
//获得导航栏的高度 宽度
mNavigationBarHeight = getNavigationBarHeight(activity);
mNavigationBarWidth = getNavigationBarWidth(activity);
//测试是否含有虚拟的导航栏
mHasNavigationBar = (mNavigationBarHeight > 0);
//这两个数值是由外部传入的
mTranslucentStatusBar = translucentStatusBar;
mTranslucentNavBar = traslucentNavBar;
}好像不是太复杂 都是一大堆获得系统配置的函数 我们一个个的看吧
//好像不是很复杂
@SuppressLint("NewApi")
private float getSmallestWidthDp(Activity activity) {
DisplayMetrics metrics = new DisplayMetrics();
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.JELLY_BEAN) {
//获得一些显示的参数
activity.getWindowManager().getDefaultDisplay().getRealMetrics(metrics);
} else {
// TODO this is not correct, but we don't really care pre-kitkat
activity.getWindowManager().getDefaultDisplay().getMetrics(metrics);
}
float widthDp = metrics.widthPixels / metrics.density;
float heightDp = metrics.heightPixels / metrics.density;
return Math.min(widthDp, heightDp);
} //获得内部的面积
private int getInternalDimensionSize(Resources res, String key) {
int result = 0;
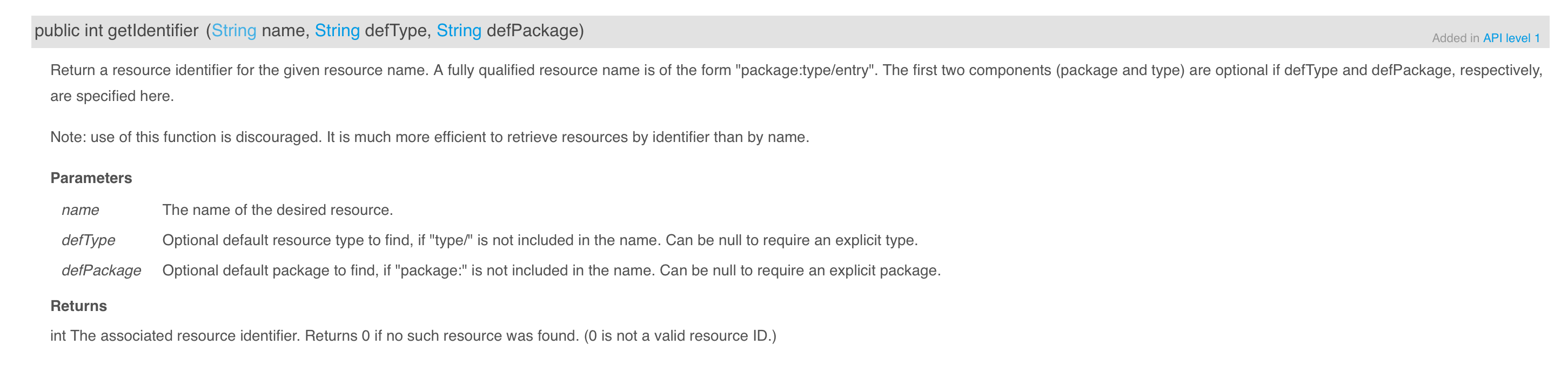
int resourceId = res.getIdentifier(key, "dimen", "android");
if (resourceId > 0) {
result = res.getDimensionPixelSize(resourceId);
}
return result;
}关于resource的getIdentifier函数,我们看下说明:
@TargetApi(14)
private int getActionBarHeight(Context context) {
int result = 0;
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.ICE_CREAM_SANDWICH) {
TypedValue tv = new TypedValue();
//感觉涨了好多姿势
context.getTheme().resolveAttribute(android.R.attr.actionBarSize, tv, true);
result = context.getResources().getDimensionPixelSize(tv.resourceId);
}
return result;
} @TargetApi(14)
private int getNavigationBarHeight(Context context) {
Resources res = context.getResources();
int result = 0;
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.ICE_CREAM_SANDWICH) {
if (hasNavBar(context)) {
String key;
if (mInPortrait) {
key = NAV_BAR_HEIGHT_RES_NAME;
} else {
key = NAV_BAR_HEIGHT_LANDSCAPE_RES_NAME;
}
//调用和计算status bar高度一样的函数
return getInternalDimensionSize(res, key);
}
}
return result;
}分析完了沉浸式状态栏是如何做的 我们看下导航栏
同样是调用的安装函数:
private void setupNavBarView(Context context, ViewGroup decorViewGroup) {
mNavBarTintView = new View(context);
LayoutParams params;
if (mConfig.isNavigationAtBottom()) {
params = new LayoutParams(LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, mConfig.getNavigationBarHeight());
params.gravity = Gravity.BOTTOM;
} else {
//可能显示在右边
params = new LayoutParams(mConfig.getNavigationBarWidth(), LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT);
params.gravity = Gravity.RIGHT;
}
mNavBarTintView.setLayoutParams(params);
mNavBarTintView.setBackgroundColor(DEFAULT_TINT_COLOR);
mNavBarTintView.setVisibility(View.GONE);
decorViewGroup.addView(mNavBarTintView);
}并没有什么难点,不过,读者看到decor view group一直在addView,不会发生错乱吗?其实并不会,decor 是frame layout,当帮导航栏透明后,mNavBarTintView变回布局到系统的导航栏后面,这时候用户便可以看到自己定义的导航栏了






















 147
147











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








