FragmentManager
实现类 FragmentManagerImpl
FragmentManager 定义的任务是由 FragmentManagerImpl 实现的。
主要成员
BackStackRecord 继承了 FragmentTransaction :
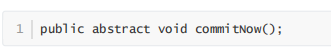
最终会调用 moveToState() ,我们直接来看它的实现:
f
.performDetach();
dispatchOnFragmentDetached(f, false);
if (!keepActive) {
if (!f.mRetaining) {
makeInactive(f);
} else {
f.mHost = null;
f.mParentFragment = null;
f.mFragmentManager = null;
}
}
}
}
}
}
i
f (f.mState != newState) {
Log.w(TAG, "moveToState: Fragment state for " + f + " not updated
inline; "
+ "expected state " + newState + " found " + f.mState);
f.mState = newState;
}
}
代码很长,但做的事情很简单:
1. 根据状态调用对应的生命周期方法
2. 如果是新创建的,就把布局添加到 ViewGroup 中
Fragment 是什么
Fragment 是什么,从官网、别人博客上看到的都是他人之言,我们还是得去看源码才能得到答案。
足时可以收到回调。
没有什么特别信息,我们还是去看看它的主要成员。
Fragment 的主要成员
| static final int INITIALIZING = 0; static final int CREATED = 1; | // Not yet created. // Created. |
| static final int ACTIVITY_CREATED = 2; // The activity has finished its | |
| creation. static final int STOPPED = 3; static final int STARTED = 4; static final int RESUMED = 5; | // Fully created, not started. // Created and started, not resumed. // Created started and resumed. |
//当前 Fragment 的状态值
int mState = INITIALIZING;
/...
// True if the fragment is in the list of added fragments.
boolean mAdded;
// If set this fragment is being removed from its activity.
boolean mRemoving;
// Set to true if this fragment was instantiated from a layout file.
boolean mFromLayout;
// Set to true when the view has actually been inflated in its layout.
boolean mInLayout;
// True if this fragment has been restored from previously saved state.
boolean mRestored;
// Number of active back stack entries this fragment is in.
int mBackStackNesting;
// Set to true when the app has requested that this fragment be hidden
// from the user.
boolean mHidden;
// Set to true when the app has requested that this fragment be
deactivated.
boolean mDetached;
// If set this fragment would like its instance retained across
// configuration changes.
boolean mRetainInstance;
// If set this fragment is being retained across the current config change.
boolean mRetaining;
// If set this fragment has menu items to contribute.
boolean mHasMenu;
// Set to true to allow the fragment's menu to be shown.
boolean mMenuVisible = true;
// Used to verify that subclasses call through to super class.
boolean mCalled;
一堆标志位和状态值。然后就是关键的成员了:
// The fragment manager we are associated with. Set as soon as the
// fragment is used in a transaction; cleared after it has been removed
// from all transactions.
FragmentManagerImpl mFragmentManager;
//Fragmemt 绑定的对象,一半就是 Activity 和 Fragment
FragmentHostCallback mHost;
//管理子 Fragment
FragmentManagerImpl mChildFragmentManager;
// For use when restoring fragment state and descendant fragments are
retained.
// This state is set by FragmentState.instantiate and cleared in onCreate.
FragmentManagerNonConfig mChildNonConfig;
//如果这个 Fragment 绑定的是另一个 Fragment,就需要设置这个值
Fragment mParentFragment;
//容器 Fragment 的ID
int mFragmentId;
//容器 View 的ID
int mContainerId;
//父布局
ViewGroup mContainer;
//当前 Fragment 的布局
View mView;
//真正保存状态的内部布局
View mInnerView;
看到这里,结合前面的,我们就清晰了一个 Fragment 的创建、添加过程:
在 onCreateView() 中返回一个 布局,然后在 FragmentManager 中拿到这个布局,添加到要绑定容
器(Activity/Fragment)的 ViewGroup 中,然后设置相应的状态值
生命周期方法
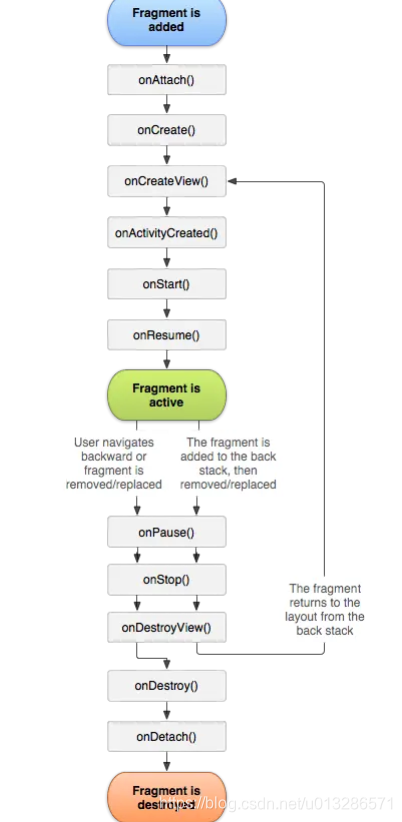
@CallSuper
public void onAttach(Context context) {
mCalled = true;
final Activity hostActivity = mHost == null ? null :
mHost.getActivity();
if (hostActivity != null) {
onAttach(hostActivity);
}
} @
Deprecated
@CallSuper
public void onAttach(Activity activity) {
mCalled = true;
}
onAttach() 是一个 Fragment 和它的 Context 关联时第一个调用的方法,这里我们可以获得对应的
Context 或者 Activity ,可以看到这里拿到的 Activity 是 mHost.getActivity() ,后面我们介绍
FragmentManager 时介绍这个方法。
public void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
mCalled = true;
restoreChildFragmentState(savedInstanceState);
if (mChildFragmentManager != null
&& !mChildFragmentManager.isStateAtLeast(Fragment.CREATED)) {
mChildFragmentManager.dispatchCreate();
}
} v
oid restoreChildFragmentState(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
if (savedInstanceState != null) {
Parcelable p = savedInstanceState.getParcelable(
FragmentActivity.FRAGMENTS_TAG);
if (p != null) {
if (mChildFragmentManager == null) {
instantiateChildFragmentManager();
} m
ChildFragmentManager.restoreAllState(p, mChildNonConfig);
mChildNonConfig = null;
mChildFragmentManager.dispatchCreate();
}
}
}
需要注意的是,Fragment 的 onCreate() 调用时关联的 Activity 可能还没创建好,所以这里不要有依
赖外部 Activity 布局的操作。如果有依赖 Activity 的操作,可以放在 onActivityCreate() 中。
从上面的代码还可以看到,如果是从旧状态中恢复,会执行子 Fragment 状态的恢复,此外还在
onCreate() 中调用了子 Fragment 管理者的创建。
@Nullable
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, @Nullable ViewGroup
container,
@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
return null;
}
当我们需要在 Fragment 中显示布局时,需要重写这个方法,返回要显示的布局。
后面布局销毁时就会调用 onDestroyView()
}
onViewCreate() 不是生命周期中的方法,但是却很有用。
它会在 onCreateView() 返回后立即执行,参数中的 view 就是之前创建的 View,因此我们可以在
onViewCreate() 中进行布局的初始化,比如这样:
public void onViewCreated(final View view, @Nullable final Bundle
savedInstanceState) {
if (view == null) {
return;
} m
TextView = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.tv_content);
mBtnSwitchChild = (Button) view.findViewById(R.id.btn_switch_child);
Bundle arguments = getArguments();
if (arguments != null && mTextView != null &&
!TextUtils.isEmpty(arguments.getString(KEY_TITLE))) {
mTextView.setText(arguments.getString(KEY_TITLE));
} m
BtnSwitchChild.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(final View v) {
//...
});
}
public void onActivityCreated(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
mCalled = true;
}
调用。
可以在这个方法里做些和布局、状态恢复有关的操作。
@CallSuper
public void onViewStateRestored(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
mCalled = true;
}
onViewStateRestored() 方法会在 onActivityCreated() 结束后调用,用于一个 Fragment 在从
旧的状态恢复时,获取状态 saveInstanceState 恢复状态,比如恢复一个 check box 的状态。
经过这四步,Fragment 创建完成,同步于 Activity 的创建过程
public void onStart() {
mCalled = true;
if (!mLoadersStarted) {
mLoadersStarted = true;
if (!mCheckedForLoaderManager) {
mCheckedForLoaderManager = true;
mLoaderManager = mHost.getLoaderManager(mWho, mLoadersStarted,
false);
} i
f (mLoaderManager != null) {
mLoaderManager.doStart();
}
}
}
@CallSuper
public void onResume() {
mCalled = true;
}
它和 Activity 的 onResume() 同步。
7. onPause()
public void onPause() {
mCalled = true;
}
也和 Activity 的 onPause() 同步。
@CallSuper
public void onStop() {
mCalled = true;
}
public void onDestroyView() {
mCalled = true;
}
当 onCreateView() 返回的布局(不论是不是 null)从 Fragment 中解除绑定时调用
onDestroyView() 。
下次 Fragment 展示时,会重新创建布局。
public void onDestroy() {
mCalled = true;
//Log.v("foo", "onDestroy: mCheckedForLoaderManager=" +
mCheckedForLoaderManager
// + " mLoaderManager=" + mLoaderManager);
if (!mCheckedForLoaderManager) {
mCheckedForLoaderManager = true;
mLoaderManager = mHost.getLoaderManager(mWho, mLoadersStarted,
false);
} i
f (mLoaderManager != null) {
mLoaderManager.doDestroy();
}
}
可以看到这里,调用了 mLoaderManager.doDestroy() ,后面介绍它。
public void onDetach() {
mCalled = true;
}
Fragment 的 onDestroyView() , onDestroy() , onDetach() 三个对应 Activity 的 onDestroyed()
方法。
总结
OK,看完这篇文章,相信对开头提出的问题你已经有了答案,这里再总结一下。
Fragment、FragmentManager、
FragmentTransaction 关系
Fragment
其实是对 View 的封装,它持有 view, containerView, fragmentManager,
childFragmentManager 等信息
FragmentManager
是一个抽象类,它定义了对一个 Activity/Fragment 中 添加进来的 Fragment 列表、
Fragment 回退栈的操作、管理方法
还定义了获取事务对象的方法
具体实现在 FragmentImpl 中
FragmentTransaction
定义了对 Fragment 添加、替换、隐藏等操作,还有四种提交方法
具体实现是在 BackStackRecord 中
Fragment 如何实现布局的添加替换
通过获得当前 Activity/Fragment 的 FragmentManager/ChildFragmentManager,进而拿到事务的实
现类 BackStackRecord,它将目标 Fragment 构造成 Ops(包装Fragment 和状态信息),然后提交给
FragmentManager 处理。
如果是异步提交,就通过 Handler 发送 Runnable 任务,FragmentManager 拿到任务后,先处理 Ops
状态,然后调用 moveToState() 方法根据状态调用 Fragment 对应的生命周期方法,从而达到
Fragment 的添加、布局的替换隐藏等。
下面这张图从下往上看就是一个 Fragment 创建经历的方法: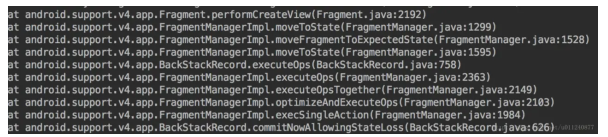
FRAGMENT管理整体结构图

public FragmentManager getSupportFragmentManager() {
return mFragments.getSupportFragmentManager();
}进入FragmentController中持有FragmentHostCallback对象private final FragmentHostCallback<?> mHost;public FragmentManager getSupportFragmentManager() {
return mHost.mFragmentManager;
}
进入FragmentHostCallback
public abstract class FragmentHostCallback<E> extends FragmentContainerfinal FragmentManager mFragmentManager = new FragmentManagerImpl();所以这一步实际上是拿到FragmentManagerImpl这个实现对象。
(2)beginTransaction
public FragmentTransaction beginTransaction() {
return new BackStackRecord(this);
}final class BackStackRecord extends FragmentTransaction implements
FragmentManager.BackStackEntry, FragmentManager.OpGenerator {可以看到这步是拿到事务,继承于FragmentTransaction
(3)add()
FragmentTransaction中@NonNull
public FragmentTransaction add(@NonNull Fragment fragment, @Nullable String tag) {
doAddOp(0, fragment, tag, OP_ADD);
return this;
}FragmentTransaction中void doAddOp(int containerViewId, Fragment fragment, @Nullable String tag, int opcmd) {
final Class<?> fragmentClass = fragment.getClass();
final int modifiers = fragmentClass.getModifiers();
if (fragmentClass.isAnonymousClass() || !Modifier.isPublic(modifiers)
|| (fragmentClass.isMemberClass() && !Modifier.isStatic(modifiers))) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Fragment " + fragmentClass.getCanonicalName()
+ " must be a public static class to be properly recreated from"
+ " instance state.");
}
if (tag != null) {
if (fragment.mTag != null && !tag.equals(fragment.mTag)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Can't change tag of fragment "
+ fragment + ": was " + fragment.mTag
+ " now " + tag);
}
fragment.mTag = tag;
}
if (containerViewId != 0) {
if (containerViewId == View.NO_ID) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Can't add fragment "
+ fragment + " with tag " + tag + " to container view with no id");
}
if (fragment.mFragmentId != 0 && fragment.mFragmentId != containerViewId) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Can't change container ID of fragment "
+ fragment + ": was " + fragment.mFragmentId
+ " now " + containerViewId);
}
fragment.mContainerId = fragment.mFragmentId = containerViewId;
}
addOp(new Op(opcmd, fragment));
}void addOp(Op op) {
mOps.add(op);
op.mEnterAnim = mEnterAnim;
op.mExitAnim = mExitAnim;
op.mPopEnterAnim = mPopEnterAnim;
op.mPopExitAnim = mPopExitAnim;
}
看下中mOps是什么
ArrayList<Op> mOps = new ArrayList<>();这一步把一些fragment状态值保存
(4)commit()
public abstract int commit();实现在BackStackRecord中
public int commit() {
return commitInternal(false);
}BackStackRecord中
int commitInternal(boolean allowStateLoss) {
if (mCommitted) throw new IllegalStateException("commit already called");
if (FragmentManager.isLoggingEnabled(Log.VERBOSE)) {
Log.v(TAG, "Commit: " + this);
LogWriter logw = new LogWriter(TAG);
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(logw);
dump(" ", pw);
pw.close();
}
mCommitted = true;
if (mAddToBackStack) {
mIndex = mManager.allocBackStackIndex();
} else {
mIndex = -1;
}
mManager.enqueueAction(this, allowStateLoss);
return mIndex;
}FragmentManager中void enqueueAction(@NonNull OpGenerator action, boolean allowStateLoss) {
if (!allowStateLoss) {
if (mHost == null) {
if (mDestroyed) {
throw new IllegalStateException("FragmentManager has been destroyed");
} else {
throw new IllegalStateException("FragmentManager has not been attached to a "
+ "host.");
}
}
checkStateLoss();
}
synchronized (mPendingActions) {
if (mHost == null) {
if (allowStateLoss) {
// This FragmentManager isn't attached, so drop the entire transaction.
return;
}
throw new IllegalStateException("Activity has been destroyed");
}
mPendingActions.add(action);
scheduleCommit();
}
}FragmentManager中
void scheduleCommit() {
synchronized (mPendingActions) {
boolean postponeReady =
mPostponedTransactions != null && !mPostponedTransactions.isEmpty();
boolean pendingReady = mPendingActions.size() == 1;
if (postponeReady || pendingReady) {
mHost.getHandler().removeCallbacks(mExecCommit);
mHost.getHandler().post(mExecCommit);
updateOnBackPressedCallbackEnabled();
}
}
}通过Handler()实现异步
FragmentManager中
private Runnable mExecCommit = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
execPendingActions(true);
}
};execPendingActionsboolean execPendingActions(boolean allowStateLoss) {
ensureExecReady(allowStateLoss);
boolean didSomething = false;
while (generateOpsForPendingActions(mTmpRecords, mTmpIsPop)) {
mExecutingActions = true;
try {
removeRedundantOperationsAndExecute(mTmpRecords, mTmpIsPop);
} finally {
cleanupExec();
}
didSomething = true;
}
updateOnBackPressedCallbackEnabled();
doPendingDeferredStart();
mFragmentStore.burpActive();
return didSomething;
}
进入generateOpsForPendingActions
private boolean generateOpsForPendingActions(@NonNull ArrayList<BackStackRecord> records,
@NonNull ArrayList<Boolean> isPop) {
boolean didSomething = false;
synchronized (mPendingActions) {
if (mPendingActions.isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
final int numActions = mPendingActions.size();
for (int i = 0; i < numActions; i++) {
didSomething |= mPendingActions.get(i).generateOps(records, isPop);//是否加栈
}
mPendingActions.clear();
mHost.getHandler().removeCallbacks(mExecCommit);
}
return didSomething;
}boolean generateOps(@NonNull ArrayList<BackStackRecord> records,
@NonNull ArrayList<Boolean> isRecordPop);BackStackRecord中public boolean generateOps(@NonNull ArrayList<BackStackRecord> records,
@NonNull ArrayList<Boolean> isRecordPop) {
if (FragmentManager.isLoggingEnabled(Log.VERBOSE)) {
Log.v(TAG, "Run: " + this);
}
records.add(this);
isRecordPop.add(false);
if (mAddToBackStack) {
mManager.addBackStackState(this);
}
return true;
}
回到execPendingActions中
进入removeRedundantOperationsAndExecute
private void removeRedundantOperationsAndExecute(@NonNull ArrayList<BackStackRecord> records,
@NonNull ArrayList<Boolean> isRecordPop) {
if (records.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
if (records.size() != isRecordPop.size()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Internal error with the back stack records");
}
// Force start of any postponed transactions that interact with scheduled transactions:
executePostponedTransaction(records, isRecordPop);
final int numRecords = records.size();
int startIndex = 0;
for (int recordNum = 0; recordNum < numRecords; recordNum++) {
final boolean canReorder = records.get(recordNum).mReorderingAllowed;
if (!canReorder) {
// execute all previous transactions
if (startIndex != recordNum) {
executeOpsTogether(records, isRecordPop, startIndex, recordNum);
}
// execute all pop operations that don't allow reordering together or
// one add operation
int reorderingEnd = recordNum + 1;
if (isRecordPop.get(recordNum)) {
while (reorderingEnd < numRecords
&& isRecordPop.get(reorderingEnd)
&& !records.get(reorderingEnd).mReorderingAllowed) {
reorderingEnd++;
}
}
executeOpsTogether(records, isRecordPop, recordNum, reorderingEnd);
startIndex = reorderingEnd;
recordNum = reorderingEnd - 1;
}
}
if (startIndex != numRecords) {
executeOpsTogether(records, isRecordPop, startIndex, numRecords);
}
}executeOpsTogether(records, isRecordPop, recordNum, reorderingEnd);进行一些优化的动作
private void executeOpsTogether(@NonNull ArrayList<BackStackRecord> records,
@NonNull ArrayList<Boolean> isRecordPop, int startIndex, int endIndex) {
final boolean allowReordering = records.get(startIndex).mReorderingAllowed;
boolean addToBackStack = false;
if (mTmpAddedFragments == null) {
mTmpAddedFragments = new ArrayList<>();
} else {
mTmpAddedFragments.clear();
}
mTmpAddedFragments.addAll(mFragmentStore.getFragments());
Fragment oldPrimaryNav = getPrimaryNavigationFragment();
for (int recordNum = startIndex; recordNum < endIndex; recordNum++) {
final BackStackRecord record = records.get(recordNum);
final boolean isPop = isRecordPop.get(recordNum);
if (!isPop) {
oldPrimaryNav = record.expandOps(mTmpAddedFragments, oldPrimaryNav);
} else {
oldPrimaryNav = record.trackAddedFragmentsInPop(mTmpAddedFragments, oldPrimaryNav);
}
addToBackStack = addToBackStack || record.mAddToBackStack;
}
mTmpAddedFragments.clear();
if (!allowReordering) {
FragmentTransition.startTransitions(this, records, isRecordPop, startIndex, endIndex,
false, mFragmentTransitionCallback);
}
executeOps(records, isRecordPop, startIndex, endIndex);
int postponeIndex = endIndex;
if (allowReordering) {
ArraySet<Fragment> addedFragments = new ArraySet<>();
addAddedFragments(addedFragments);
postponeIndex = postponePostponableTransactions(records, isRecordPop,
startIndex, endIndex, addedFragments);
makeRemovedFragmentsInvisible(addedFragments);
}
if (postponeIndex != startIndex && allowReordering) {
// need to run something now
FragmentTransition.startTransitions(this, records, isRecordPop, startIndex,
postponeIndex, true, mFragmentTransitionCallback);
moveToState(mCurState, true);
}
for (int recordNum = startIndex; recordNum < endIndex; recordNum++) {
final BackStackRecord record = records.get(recordNum);
final boolean isPop = isRecordPop.get(recordNum);
if (isPop && record.mIndex >= 0) {
record.mIndex = -1;
}
record.runOnCommitRunnables();
}
if (addToBackStack) {
reportBackStackChanged();
}
}不入栈的
Fragment expandOps(ArrayList<Fragment> added, Fragment oldPrimaryNav) {
for (int opNum = 0; opNum < mOps.size(); opNum++) {
final Op op = mOps.get(opNum);
switch (op.mCmd) {
case OP_ADD:
case OP_ATTACH:
added.add(op.mFragment);
break;
case OP_REMOVE:
case OP_DETACH: {
added.remove(op.mFragment);
if (op.mFragment == oldPrimaryNav) {
mOps.add(opNum, new Op(OP_UNSET_PRIMARY_NAV, op.mFragment));
opNum++;
oldPrimaryNav = null;
}
}
break;
case OP_REPLACE: {
final Fragment f = op.mFragment;
final int containerId = f.mContainerId;
boolean alreadyAdded = false;
for (int i = added.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
final Fragment old = added.get(i);
if (old.mContainerId == containerId) {
if (old == f) {
alreadyAdded = true;
} else {
// This is duplicated from above since we only make
// a single pass for expanding ops. Unset any outgoing primary nav.
if (old == oldPrimaryNav) {
mOps.add(opNum, new Op(OP_UNSET_PRIMARY_NAV, old));
opNum++;
oldPrimaryNav = null;
}
final Op removeOp = new Op(OP_REMOVE, old);
removeOp.mEnterAnim = op.mEnterAnim;
removeOp.mPopEnterAnim = op.mPopEnterAnim;
removeOp.mExitAnim = op.mExitAnim;
removeOp.mPopExitAnim = op.mPopExitAnim;
mOps.add(opNum, removeOp);
added.remove(old);
opNum++;
}
}
}
if (alreadyAdded) {
mOps.remove(opNum);
opNum--;
} else {
op.mCmd = OP_ADD;
added.add(f);
}
}
break;
case OP_SET_PRIMARY_NAV: {
// It's ok if this is null, that means we will restore to no active
// primary navigation fragment on a pop.
mOps.add(opNum, new Op(OP_UNSET_PRIMARY_NAV, oldPrimaryNav));
opNum++;
// Will be set by the OP_SET_PRIMARY_NAV we inserted before when run
oldPrimaryNav = op.mFragment;
}
break;
}
}
return oldPrimaryNav;
}
全部变成 added.add操作
真正执行操作的方法
executeOps(records, isRecordPop, startIndex, endIndex);
private static void executeOps(@NonNull ArrayList<BackStackRecord> records,
@NonNull ArrayList<Boolean> isRecordPop, int startIndex, int endIndex) {
for (int i = startIndex; i < endIndex; i++) {
final BackStackRecord record = records.get(i);
final boolean isPop = isRecordPop.get(i);
if (isPop) {
record.bumpBackStackNesting(-1);
// Only execute the add operations at the end of
// all transactions.
boolean moveToState = i == (endIndex - 1);
record.executePopOps(moveToState);
} else {
record.bumpBackStackNesting(1);
record.executeOps();
}
}
}void executePopOps(boolean moveToState) {
for (int opNum = mOps.size() - 1; opNum >= 0; opNum--) {
final Op op = mOps.get(opNum);
Fragment f = op.mFragment;
if (f != null) {
f.setNextTransition(FragmentManager.reverseTransit(mTransition));
}
switch (op.mCmd) {
case OP_ADD:
f.setNextAnim(op.mPopExitAnim);
mManager.setExitAnimationOrder(f, true);
mManager.removeFragment(f);
break;
case OP_REMOVE:
f.setNextAnim(op.mPopEnterAnim);
mManager.addFragment(f);
break;
case OP_HIDE:
f.setNextAnim(op.mPopEnterAnim);
mManager.showFragment(f);
break;
case OP_SHOW:
f.setNextAnim(op.mPopExitAnim);
mManager.setExitAnimationOrder(f, true);
mManager.hideFragment(f);
break;
case OP_DETACH:
f.setNextAnim(op.mPopEnterAnim);
mManager.attachFragment(f);
break;
case OP_ATTACH:
f.setNextAnim(op.mPopExitAnim);
mManager.setExitAnimationOrder(f, true);
mManager.detachFragment(f);
break;
case OP_SET_PRIMARY_NAV:
mManager.setPrimaryNavigationFragment(null);
break;
case OP_UNSET_PRIMARY_NAV:
mManager.setPrimaryNavigationFragment(f);
break;
case OP_SET_MAX_LIFECYCLE:
mManager.setMaxLifecycle(f, op.mOldMaxState);
break;
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown cmd: " + op.mCmd);
}
if (!mReorderingAllowed && op.mCmd != OP_REMOVE && f != null) {
mManager.moveFragmentToExpectedState(f);
}
}
if (!mReorderingAllowed && moveToState) {
mManager.moveToState(mManager.mCurState, true);
}
}moveToState 又是这个就去调用对应的生命周期了
 、
、
总的就是执行的各种操作add,remove,replace等都放到mOps中,然后做了优化,全部换成了add,如今moveToState走生命周期
还有回退栈的情况流程如下























 2873
2873











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








