树的遍历分为两种,一种是深度优先遍历,另一种是广度优先遍历。
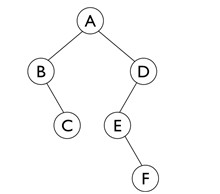
有如下一个 二叉树
广度优先遍历是从根节点开始,沿着树的宽度遍历树的节点。如果所有节点均被访问,则中止。
广度优先遍历 A B D C E F
深度优先遍历是是沿着树的深度遍历树的节点,尽可能深的搜索树的分支
深度优先 A B C D E F
php代码具体实现如下
<?php
// 节点
class Node
{
public $val = null;
public $left = null;
public $right = null;
}
$root = new Node();
$node1 = new Node();
$node2 = new Node();
$node3 = new Node();
$node4 = new Node();
$node5 = new Node();
$node6 = new Node();
$root->val = 1;
$node1->val = 2;
$node2->val = 3;
$node3->val = 4;
$node4->val = 5;
$node5->val = 6;
$node6->val = 7;
$root->left = $node1;
$root->right = $node2;
$node1->left = $node3;
$node1->right = $node4;
$node2->left = $node5;
$node2->right = $node6;
/*
$root 的结构如下
1
2 3
4 5 6 7
*/
// 广度优先遍历 通过队列来实现(非递归)
function breadth_traverse($root)
{
$data = [];
$queue = [];
// 将根节点入队列
array_unshift($queue, $root);
while ($queue) {
$node = array_pop($queue);
array_push($data, $node->val);
if ($node->left) { // 左节点入队列
array_unshift($queue, $node->left);
}
if ($node->right) { // 右节点入队列
array_unshift($queue, $node->right);
}
}
return $data;
}
// 深度优先遍历 递归实现
function depth_traverse($root)
{
if (!$root->left && !$root->right) {
return [$root->val];
}
// merge (当前节点,子节点,右节点)
return array_merge([$root->val], depth_traverse($root->left), depth_traverse($root->right));
}





















 1498
1498











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








