数据平滑
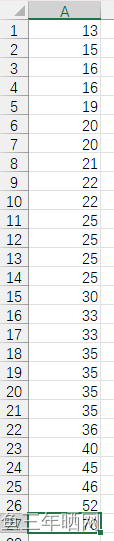
假定用于分析的数据包含属性age。数据元组中age的值如下(按递增序):13, 15, 16, 16, 19, 20, 20, 21, 22, 22, 25, 25, 25, 25, 30, 33, 33, 35, 35, 35, 35, 36, 40, 45, 46, 52, 70。
- 使用按箱平均值平滑法对以上数据进行平滑,箱的深度为3。
- 使用按箱中值平滑法对以上数据进行平滑,箱的深度为3。
- 使用按箱边界值平滑法对以上数据进行平滑,箱的深度为3。
离群点筛选
找出其中的离群点,即1.5倍IQR之外的点
代码
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
def read_data(path):
dataset = pd.read_excel(path, header=None)
data = dataset.iloc[:, 0].values
return np.array(data)
def init_boxes(data, depth=3):
data_sorted = np.sort(data)
boxes = data_sorted.reshape(data.size // depth, depth)
return boxes
def mean_boxes_smooth(boxes):
# 箱平均值平滑法
mean = np.mean(boxes, axis=1).reshape(boxes.shape[0], 1)
mean_boxes = mean.repeat(boxes.shape[1], axis=1)
return mean_boxes
def median_boxes_smooth(boxes):
# 箱中值平滑法
median = np.median(boxes, axis=1).reshape(boxes.shape[0], 1)
median_boxes = median.repeat(boxes.shape[1], axis=1)
return median_boxes
def border_boxes_smooth(boxes):
# 箱边界值平滑法
lborder = boxes[:, 0].reshape(boxes.shape[0], 1)
rborder = boxes[:, -1].reshape(boxes.shape[0], 1)
ldis = boxes - lborder
rdis = rborder - boxes
if_lb = (ldis - rdis) <= 0
border_boxes = lborder*np.int32(if_lb) + rborder*np.int32(~if_lb)
return border_boxes
def detect_outliers(data):
x = np.sort(data)
Q1 = np.percentile(x, 25)
Q3 = np.percentile(x, 75)
IQR = Q3 - Q1
lb = Q1 - 1.5*IQR
rb = Q3 + 1.5*IQR
outliers = x[(x < lb) | (x > rb)]
return outliers
if __name__ == "__main__":
data = read_data(path="age.xlsx")
boxes = init_boxes(data, depth=3)
print("boxes:\n" + str(boxes))
mean_boxes = mean_boxes_smooth(boxes)
print("箱平均值平滑法:\n" + str(mean_boxes))
median_boxes = median_boxes_smooth(boxes)
print("箱中值平滑法:\n" + str(median_boxes))
border_boxes = border_boxes_smooth(boxes)
print("箱边界值平滑法:\n" + str(border_boxes))
outliers = detect_outliers(data)
print("离群点:\n" + str(outliers))
数据样例:























 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








