1.什么是View
View是Android系统中所有控件的基类,不管是TextView,还是Button,甚至是LinearLayout和RelativeLayout都有共同的基类View。除了View还有ViewGroup,ViewGroup翻译成中就是控件组,顾名思义,他是一组控件。也就是一组View。
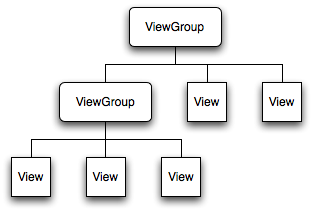
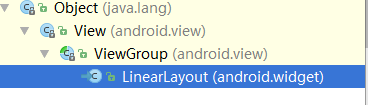

Activity中onCreate()方法中的setContentView()到底干了啥
Android的每个控件都会在界面里面占据一块矩形区域,在Android里面控件大致被分为两类,一类是View,一类是ViewGroup。ViewGroup作为父控件可以包含很多View控件,并且管理View。通常情况下,Activity中使用setContentView()方法来设置一个布局。
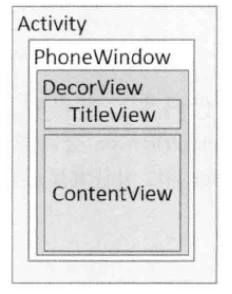
根据上图我们可以看出每个Activity中都包含一个Window对象,通常Window由PhoneWindow来实现了,PhoneWindow将一个DecorView设置成整个窗口的根View,DecorView封装了窗口的一些常用方法,在显示上它将屏幕分为两个部分,一个是TitleView,一个ContentView,所谓的ContentView是一个ID为content的FrameLayout,也就是说Android的根布局是一个FrameLayout,我们可以通过DDMS的Dump来分析Xml
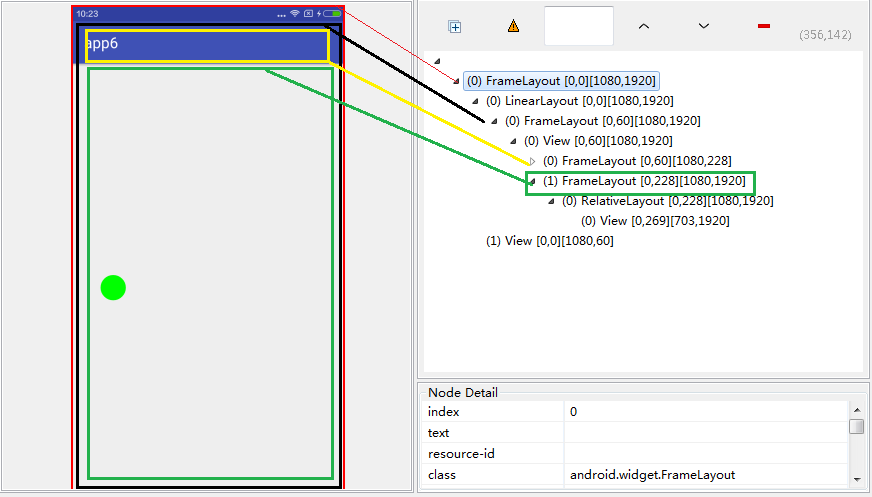
看到上面的分析结果,证明我没骗你吧。
根据上图我们可以看到黄色的FrameLayout和绿色的FrameLayout的父布局就是DecorView,其中黄色的FrameLayout是设置TitleView也就是ActionBar,绿色FrameLayout是设置内容的。这就是我们在去掉标题栏的方法要在setContnetView之前调用的原因。去标题栏的方法如下
requestWindowFeature(Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE)什么是MotionEvent
手指在触摸屏幕产生一系列的事件,都是通过MotionEvent对象来传递的,包括触摸时候和移动时候的坐标
- ACTION_DOWN 手指刚刚接触屏幕
- ACTION_MOVE 手指在屏幕上滑动
- ACYION_UP 手指离开屏幕
通过MotionEvent对象我们可以拿到事件发生时的坐标,系统提供了两组获取方式getX/getY和getRawX/getRawY,他们的区别很简单,getX/getY返回的是当前View左上角的x和y坐标getRawX和getRawY,是返回当前屏幕左上角的x和y轴坐标。
什么是TouchSlop
是系统能够识别最小的滑动距离,最小滑动距离是个常量,和设备有关,获取方式
ViewConfiguration.get(this).getScaledTouchSlop();View的位置参数
View位置主要有四个顶点来决定的,它的的四个属性分别是: left top rght buttom
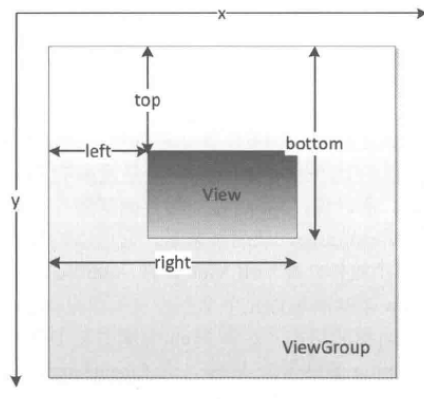
根据上述关系图,就能很快的计算出View的宽高
width=right-left;
height=buttom-top;什么是VelocityTracker
速度追踪,用于追踪手指在滑动过程中的速度,包含水平方向和垂直方向。使用方法如下,需要在onTouchEvent方法中调用
VelocityTracker velocityTracker=VelocityTracker.obtain();
velocityTracker.addMovement(event);当前追踪了当前速度,就可以使用下面方法来获取当前速度
velocityTracker.computeCurrentVelocity(1000);
int x= (int) velocityTracker.getXVelocity();
int y= (int) velocityTracker.getYVelocity();获取水平方向和垂直方向的速度前一定要调用computeCurrentVelocity(1000); 指的是一秒内滑动距离(单位时间内滑动的距离就是速度)
当不需要的时候需要回收(一般在ACTION_UP的时候就需要回收了)
velocityTracker.clear();
velocityTracker.recycle();View的测量
在一些娱乐性节目中,常常出现了一个人描述物体,另一个人画出该物体。那么系统是如何画出View的,首先我们得告诉它View的规格吧。在View绘制之前,必须进行测量。Android提供了一个功能强大的辅助类MeasureSpec,通过它能帮助我们完成View的测量
测量有三种模式
EXACTLY
即精准的测量模式,当控件的layout_width和layout_height为具体值时(layout_width=”100dp”),系统使用就是这个精准模式
AT_MOST
即最大值模式,当控件的layout_width=”wrap_content”,控件大小一般随着子控件的大小变化而变化,此时控件大小只要不超过父控件即可。
UNSPECIFIED
这个属性一般在绘制自定义View的时候使用
View默认的onMeasure()方法只支持EXACTLY,如果想让你的控件支持warp_content属性,就必须重写onMeasure()方法,
模版代码,当specMode为EXACTLY模式,直接使用specSize的值,当为其他两种模式时候,需要给他一个默认大小的值。如果为warp_content属性,即AT_MOST模式需要取出我们指定大小和specSize中最小的值作为测量值
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int width = measure(widthMeasureSpec);
int height = measure(heightMeasureSpec);
setMeasuredDimension(width, height);
}
public int measure(int measureSpec) {
int result = 0;
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
if (specMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
result = specSize;
} else {
result = 200; //默认值
if (specMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
result = Math.min(result, specSize);
}
}
return result;
}View的绘制
当测量好了一个View之后,就可以通过重写onDraw()方法,并使用Canvas对象来绘制图形。
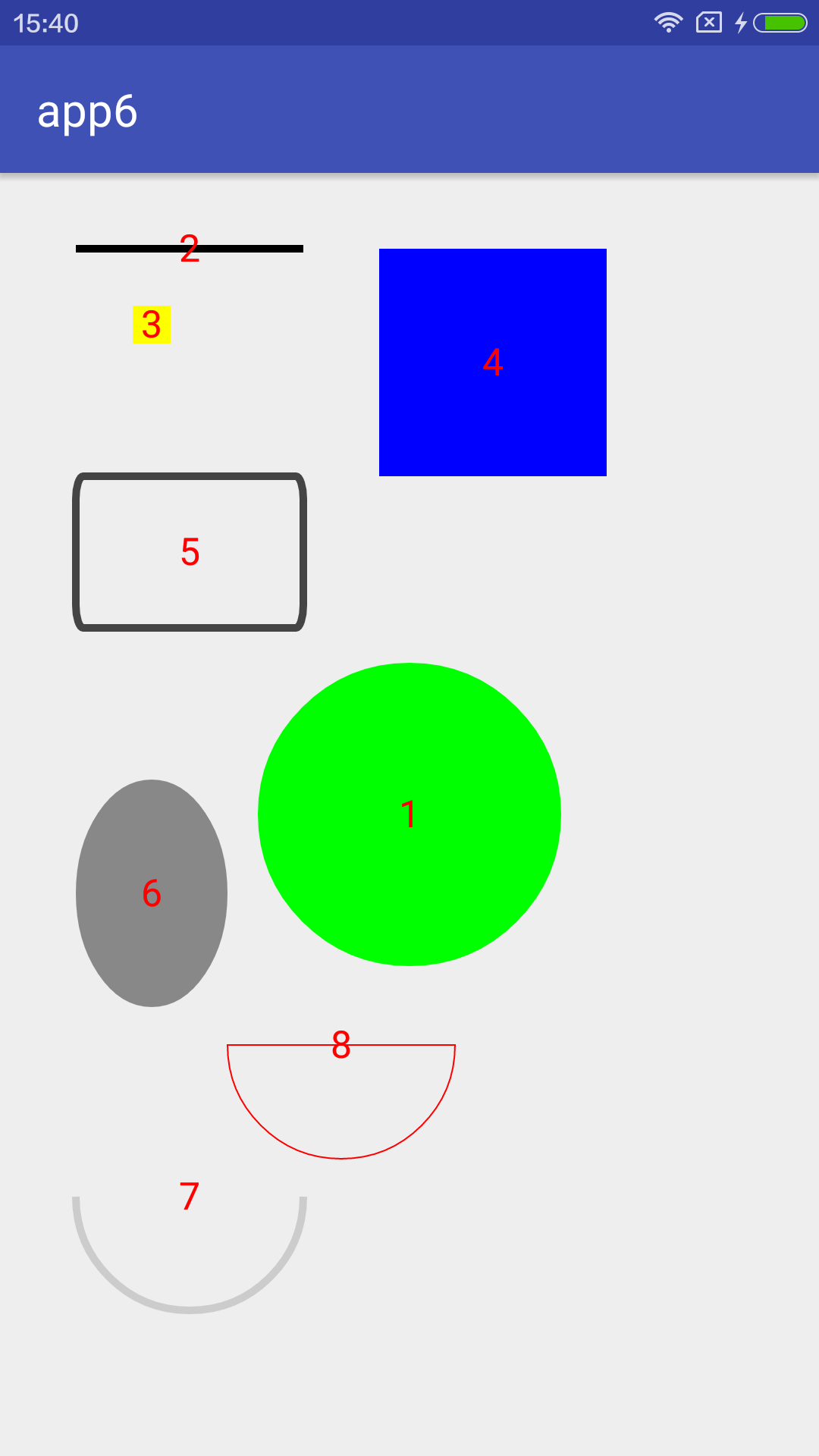
- 画圆
paint.setColor(Color.GREEN);
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
//圆心x和y轴坐标,圆半径
canvas.drawCircle(getWidth() / 2, getHeight() / 2, 200, paint);
paint.setColor(Color.RED);
li(canvas, 1, getWidth() / 2, getHeight() / 2);- 画线
paint.setColor(Color.BLACK);
paint.setStrokeWidth(10);
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
//开始的x和y坐标,结束的x和y坐标
canvas.drawLine(100, 100, 400, 100, paint);
//该线的起点是100,终点为400,中心点的位置是 (stopX-startX)/2+距离左边的距离=中心点位置
li(canvas, 2, (400 - 100) / 2 + 100, 100);- 画点
paint.setStrokeWidth(50);
paint.setColor(Color.YELLOW);
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
//点的x和y轴坐标
canvas.drawPoint(200, 200, paint);
li(canvas, 3, 200, 200);- 画矩形
paint.setColor(Color.BLUE);
paint.setStrokeWidth(2);
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
Rect rect = new Rect(500, 100, 800, 400);
canvas.drawRect(rect, paint);
li(canvas, 4, (800 - 500) / 2 + 500, (400 - 100) / 2 + 100); - 画圆角矩形
paint.setColor(Color.DKGRAY);
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
paint.setStrokeWidth(10);
RectF rectF = new RectF(100, 400, 400, 600);
//矩形的位置,矩形的圆角大小
canvas.drawRoundRect(rectF, 10, 30, paint);
li(canvas, 5, (400 - 100) / 2 + 100, (600 - 400) / 2 + 400);- 画椭圆
RectF r1 = new RectF(100, 800, 300, 1100);
paint.setColor(Color.GRAY);
canvas.drawOval(r1, paint);
li(canvas, 6, (300 - 100) / 2 + 100, (1100 - 800) / 2 + 800);- 画圆弧
paint.setColor(Color.LTGRAY);
paint.setStrokeWidth(10);
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
RectF r2 = new RectF(100, 1200, 400, 1500);
//圆弧的位置,弧度的起始角度,结束角度,是否封口,画笔
canvas.drawArc(r2, 0, 180, false, paint);
li(canvas, 7, (400 - 100) / 2 + 100, (1500 - 1200) / 2 + 1200);
paint.setStrokeWidth(2);
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
RectF r3 = new RectF(300, 1000, 600, 1300);
canvas.drawArc(r3, 0, 180, true, paint);
li(canvas, 8, (600 - 300) / 2 + 300, (1300 - 1000) / 2 + 1000);具体效果看这儿
这里贴上关于文字的绘制代码
public void li(Canvas canvas, int i, int x, int y) {
paint.setTextSize(50);
float textWidth = paint.measureText(String.valueOf(i)) / 2;
float textHeight = (paint.descent() + paint.ascent()) / 2;
paint.setStrokeWidth(1);
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
paint.setColor(Color.RED);
canvas.drawText(String.valueOf(i), x - textWidth, y - textHeight, paint);
}关于View绘制的实际案例

代码如下交替圆环
/**
* Created by xiongchengguang on 2016/7/9.
*/
public class CircleView extends View {
private static final int DEFAULT_FIRSTCOLOR = 0xff12ffee;
private static final int DEFAULT_SECONCOLOR = 0xffeeff0e;
private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 50;
private static final int DEFAULT_SPEED = 20;
private int firstColor;
private int seconColor;
private int width;
private int speed;
private Paint paint = new Paint();
private int progress = 10;
public CircleView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init(attrs);
}
public void init(AttributeSet attrs) {
TypedArray typedArray = getContext().obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.CircleView);
firstColor = typedArray.getColor(R.styleable.CircleView_firstColor, DEFAULT_FIRSTCOLOR);
seconColor = typedArray.getColor(R.styleable.CircleView_secondColor, DEFAULT_SECONCOLOR);
width = (int) typedArray.getDimension(R.styleable.CircleView_circleWidth, px2dp(DEFAULT_WIDTH));
speed = typedArray.getInt(R.styleable.CircleView_speed, DEFAULT_SPEED);
typedArray.recycle();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
while (true) {
progress++;
if (progress == 360) {
progress = 0;
}
postInvalidate();
SystemClock.sleep(speed);
}
}
}).start();
}
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
int centent = getWidth() / 2;
int radius = centent - width / 2;
paint.setStrokeWidth(width);
paint.setAntiAlias(true);
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
RectF rectF = new RectF(centent - radius, centent - radius, centent + radius, centent + radius);
paint.setColor(firstColor);
canvas.drawCircle(centent, centent, radius, paint);
paint.setColor(seconColor);
canvas.drawArc(rectF, 0, progress, false, paint);
paint.setStrokeWidth(1);
paint.setColor(Color.LTGRAY);
paint.setTextSize(20);
canvas.drawRect(rectF, paint);
String text = ((int) 100 / 360) + progress + "%";
float textWidth = paint.measureText(text) / 2;
float textHeight = (paint.descent() + paint.ascent()) / 2;
canvas.drawText(text, centent - textWidth, centent - textHeight, paint);
}
public int px2dp(int val) {
return (int) TypedValue.applyDimension(TypedValue.COMPLEX_UNIT_DIP, val, getResources().getDisplayMetrics());
}
public int px2sp(int val) {
return (int) TypedValue.applyDimension(TypedValue.COMPLEX_UNIT_SP, val, getResources().getDisplayMetrics());
}
}
波纹效果
/**
* Created by xiongchengguang on 2016/7/9.
*/
public class MoireView extends View {
private int mMaxRadius;
private int speed = 200;
private long duration = 2000;
private Paint paint;
private List<Circle> arr = new ArrayList<>();
private float x, y;
public MoireView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init();
}
private void init() {
paint = new Paint();
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
paint.setStrokeWidth(2);
paint.setColor(Color.LTGRAY);
paint.setAntiAlias(true);
new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
while (true) {
newCircle();
SystemClock.sleep(speed);
}
}
}).start();
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
x = event.getRawX();
y = event.getRawY();
return super.onTouchEvent(event);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
Iterator<Circle> iterator = arr.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
try {
Circle circle = iterator.next();
if (System.currentTimeMillis() - circle.currentTimeMillis < duration) {
paint.setAlpha(circle.getAlpha());
canvas.drawCircle(x, y, circle.getRadius(), paint);
} else {
iterator.remove();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
break;
}
}
invalidate();
}
@Override
protected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh) {
super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh);
mMaxRadius = Math.min(w, h);
}
public void newCircle() {
Circle circle = new Circle();
arr.add(circle);
}
class Circle {
private long currentTimeMillis;
public Circle() {
currentTimeMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
public int getAlpha() {
float per = (System.currentTimeMillis() - currentTimeMillis) / duration;
return (int) ((1F - per) * 255);
}
public float getRadius() {
float per = (System.currentTimeMillis() - currentTimeMillis) * 1.0f / duration;
return per * mMaxRadius;
}
}
}























 6021
6021

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








