参考了github中给出的解答
Str.h
#pragma once
#include <cstring>
#include <iterator>
#include <memory>
using std::allocator;
using std::istream;
using std::ostream;
using std::ostream_iterator;
using std::strcmp;
using std::strlen;
using std::uninitialized_copy;
class Str {
public:
typedef size_t size_type;
typedef char* iterator;
typedef const char* const_iterator;
Str() { create(0, '\0'); }
Str(size_type n, char c) { create(n, c); }
Str(const Str& s) { create(s.begin(), s.end()); }
Str& operator =(const Str&);
~Str() { uncreate(); }
Str(const char* cp) { create(cp, cp + strlen(cp)); }
template <class In> Str(In i, In j) { create(i, j); }
char& operator [](size_type i) { return chars[i]; }
const char& operator [](size_type i) const { return chars[i]; }
size_type size() const { return length - 1; }
iterator begin() { return chars; }
const_iterator begin() const { return chars; }
iterator end() { return chars + length - 1; }
const_iterator end() const { return chars + length - 1; }
const char* c_str() const { return chars; }
const char* data() const { return chars; }
size_type copy(iterator, size_type, size_type = 0) const;
Str& operator +=(const Str&);
operator bool() const { return (size() > 0); }
Str substr(size_type, size_type) const;
template <class In> void insert(iterator, In, In);
private:
// chars is null-terminated, has length - 1 non-null chars
size_type length;
iterator chars;
allocator<char> alloc;
void create(size_type, char);
template <class In> void create(In, In);
void uncreate();
void grow(size_type);
};
// Public functions
template <class In> void Str::insert(iterator p, In i, In j) {
size_type new_length = length + (j - i);
iterator new_chars = alloc.allocate(new_length);
uninitialized_copy(chars, p, new_chars);
uninitialized_copy(i, j, new_chars + (p - chars));
uninitialized_copy(p, chars + length - 1, new_chars + (p - chars) + (j - i));
alloc.construct(new_chars + new_length - 1, '\0');
uncreate();
length = new_length;
chars = new_chars;
}
// Private functions
template <class In> void Str::create(In i, In j) {
length = j - i + 1;
//根据length分配一定大小的内存空间
chars = alloc.allocate(length);
//调用uninitialized_copy函数初始化allocate函数分配的内存空间,第一、第二个参数所指向的区间内的值复制到第三个参数指向的内存空间
uninitialized_copy(i, j, chars);
alloc.construct(chars + length - 1, '\0');
}
// Other functions
ostream& operator <<(ostream&, const Str&);
ostream_iterator<char>& operator <<(ostream_iterator<char>&, const Str&);
istream& operator >>(istream&, Str&);
istream& getline(istream&, Str&);
Str operator +(const Str&, const Str&);
Str operator +(const char*, const Str&);
Str operator +(const Str&, const char*);
//在c++中,为了解决一些频繁调用的小函数大量消耗栈空间或者是叫栈内存的问题,特别的引入了inline修饰符,表示为内联函数
//栈空间就是指放置程序的局部数据也就是函数内数据的内存空间,在系统下,栈空间是有限的,如果频繁大量的使用就会造成因栈空间不足所造成的程序出错的问题,函数的死循环递归调用的最终结果就是导致栈内存空间枯竭
inline bool operator <(const Str& lhs, const Str& rhs) {
//extern int strcmp(const char *s1, const char * s2)
//当s1<s2时,返回负数
//当s1=s2时,返回值 = 0
//当s1>s2时,返回正数
return (strcmp(lhs.c_str(), rhs.c_str()) < 0);
}
inline bool operator >(const Str& lhs, const Str& rhs) {
return (strcmp(lhs.c_str(), rhs.c_str()) > 0);
}
inline bool operator <=(const Str& lhs, const Str& rhs) {
return (strcmp(lhs.c_str(), rhs.c_str()) <= 0);
}
inline bool operator >=(const Str& lhs, const Str& rhs) {
return (strcmp(lhs.c_str(), rhs.c_str()) >= 0);
}
inline bool operator ==(const Str& lhs, const Str& rhs) {
return (strcmp(lhs.c_str(), rhs.c_str()) == 0);
}
inline bool operator !=(const Str& lhs, const Str& rhs) {
return (strcmp(lhs.c_str(), rhs.c_str()) != 0);
}Str.cpp
#include <algorithm>
#include <cctype>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <vector>
#include "Str.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// Public functions
Str& Str::operator =(const Str& rhs) {
if (&rhs != this) {
uncreate();
create(rhs.begin(), rhs.end());
}
return *this;
}
Str::size_type Str::copy(iterator s, size_type n, size_type pos) const {
if (pos > size()) throw out_of_range("pos > size()");
size_t copy_length = min(n, size() - pos);
::copy(chars + pos, chars + copy_length, s);
return copy_length;
}
Str& Str::operator +=(const Str& s) {
size_type new_length = length + s.size();
iterator new_chars = alloc.allocate(new_length);
uninitialized_copy(chars, chars + length - 1, new_chars);
uninitialized_copy(s.begin(), s.end(), new_chars + length - 1);
//construct成员函数在尚未被初始化的内存区域中构造单个对象,第一个参数是allocate函数已分配的内存指针,第二个参数是用于复制到该内存块的值
alloc.construct(new_chars + new_length - 1, '\0');
uncreate();
length = new_length;
chars = new_chars;
return *this;
}
Str Str::substr(size_type pos, size_type n) const {
return Str(chars + pos, chars + pos + n);
}
// Private functions
void Str::create(size_type n, char val) {
length = n + 1;
chars = alloc.allocate(length);
//由于allocate函数分配的内存没有被初始化,因此必须调用uninitialized_fill函数以便对它进行初始化
uninitialized_fill(chars, chars + length - 1, val);
alloc.construct(chars + length - 1, '\0');
}
void Str::uncreate() {
if (chars) {
iterator it = chars + length;
while (it != chars) alloc.destroy(--it);
alloc.deallocate(chars, length);
}
chars = 0;
length = 0;
}
// Other functions
ostream& operator <<(ostream& os, const Str& s) {
for (Str::size_type i = 0; i != s.size(); ++i)
os << s[i];
return os;
}
ostream_iterator<char>& operator <<(ostream_iterator<char>& osi, const Str& s) {
copy(s.begin(), s.end(), osi);
return osi;
}
static int is_newline(int c) {
return (c == '\n');
}
static istream& read_until(istream& is, Str& s, int is_stop_char(int)) {
vector<char> data;
char c;
while (is.get(c) && isspace(c));
if (is) {
do data.push_back(c);
while (is.get(c) && !is_stop_char(c));
if (is) is.unget();
}
s = Str(data.begin(), data.end());
return is;
}
istream& operator >>(istream& is, Str& s) {
return read_until(is, s, isspace);
}
istream& getline(istream&is, Str& s) {
return read_until(is, s, is_newline);
}
Str operator +(const Str& s, const Str& t) {
Str r = s;
r += t;
return r;
}
Str operator +(const char* s, const Str& t) {
Str r(s, s + strlen(s));
r += t;
return r;
}
Str operator +(const Str& s, const char* t) {
Str r = s;
r += Str(t, t + strlen(t));
return r;
}Str_test.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <conio.h>
#include "Str.h"
using namespace std;
int main() {
// Default, num of char constructors
//Str()构造函数中调用了void create(size_type, char)成员函数
cout << Str() << endl;
cout << Str(3, 'A') << endl;
// Copy constructor, assignment operator
Str s1 = Str(3, 'X');
//Str(const Str& s)构造函数中调用了template <class In> void create(In, In)成员函数
Str s2 = Str(s1);
cout << s2 << endl;
Str s3;
s3 = s2;//调用复制运算符函数
cout << s3 << endl;
// char*, iterators constructors
//Str(const char* cp)构造函数中调用template <class In> void Str::create(In i, In j)成员函数
Str s4 = "Hello";
cout << s4 << endl;
cout << Str(s4.begin(), s4.end()) << endl;
// Indexed access, size()
Str s5 = "world!";
s5[0] = 'W';//通过索引运算符函数和复制运算符函数将w改为W
cout << s5 << endl;
cout << s5.size() << endl;
// c_str(), data(), copy()
Str s6 = "Hello world!";
char buf[80] = {0};
const char* c_str = s6.c_str();
const char* data = s6.data();
s6[6] = 'W';
cout << c_str << endl;
cout << data << endl;
cout << s6.copy(buf, 79) << endl;//copy函数返回的是一个size_type的值,副作用是将s6的内容复制到buf中
cout << buf << endl;
// Relational operators
Str s7 = "A";
Str s8 = "Z";
cout << (s7 < s8) << endl;
cout << (s7 > s8) << endl;
cout << (s7 <= s8) << endl;
cout << (s7 >= s8) << endl;
cout << (s7 == s8) << endl;
cout << (s7 != s8) << endl;
// Concatenation
Str str9 = "Hello ";
Str str10 = "World!";
cout << (str9 + str10) << endl;
cout << ("Hello " + str10) << endl;
cout << (str9 + "World!") << endl;
// Str as condition
Str str11 = "";
Str str12 = "Not empty";
if (!str11) cout << "Yes" << endl;
if (str12) cout << "Yes" << endl;
// getline(), >>
Str s13;
cout << "Enter space-delimited text: ";
getline(cin, s13);
cout << s13 << endl;
cout << "Enter space-delimited text: ";
cin >> s13;
cout << s13 << endl;
// << via ostream_iterator
Str s14 = "Hello World!";
ostream_iterator<char> out_it(cout, "");
out_it << s14 << "\n";
// insert()
Str s15 = "Hello !";
Str s16 = "World";
s15.insert(s15.begin() + 6, s16.begin(), s16.end());
cout << s15 << endl;
getch();
return 0;
}运行结果:








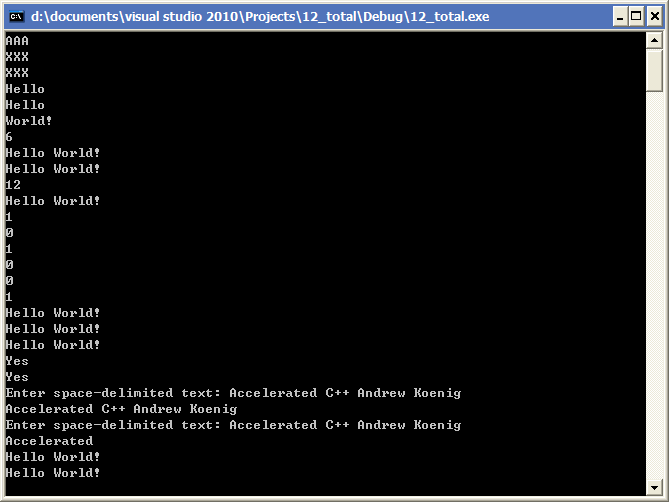














 1410
1410

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








